Question
In: Biology
What does it mean when two loci are(a) unlinked(b) partially linked(c) completely linked?...
What does it mean when two loci are
(a) unlinked
(b) partially linked
(c) completely linked?
Explain with respect to the expected phenotypic ratios in the F2 in a typical Mendelian dihybrid testcross (e.g. Assume two loci, A and B, with two alleles each, such that the A and B alleles are completely dominant over a and b).
Solutions
Expert Solution
When the genes are unlinked, they show independent assortment. They segregate independently of each other during gamete formation. All the gametes formed in this case are in equal ratio. In this case both parental and Recombinant gametes are formed.
When the genes are partially linked, then they do not show independent assortment. They do not segregate independently of each other during gamete formation. In this case both Recombinant and parental gametes are formed. All the gametes formed in this case are according to the distance present between the participating genes.
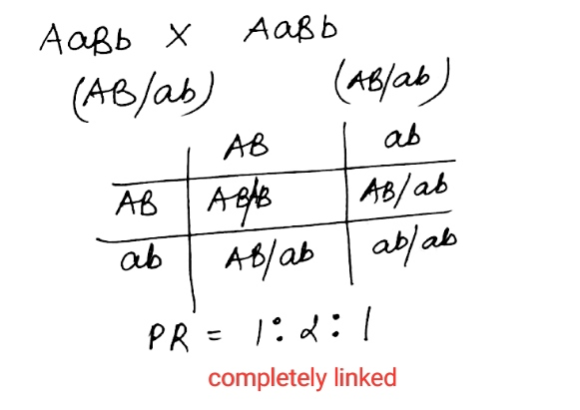
When the genes are completely linked with each other, then also they do not show independent assortment. In this case only parental gametes are formed in equal proportion.


Related Solutions
Consider two unlinked loci, A, a and B, b. The frequencies of the nine genotypes in...
What is a mistyped loci ? What does that mean?
Consider three unlinked loci, each with a dominant and a recessive allele. Start by crossing two...
The "E" ears represent a dihybrid cross in which two unlinked loci govern seed color. (Note...
What does X-linked mean?
what does this "->" mean in c? when can you use it?
What does the term performance mean? Expected performance? b. What does the term risk mean? c....
a) What does it mean if there is a correlation between two variables? b) What does...
In the band diagram of potassium, the valence band would be: a) completely filled b) partially...
In C++ what does it mean when it says: "error: stray '\226' inprogram"
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago