Question
In: Chemistry
2) Indicate the structural change and reaction that occurred to produce each positive test a. Bromine...
2) Indicate the structural change and reaction that occurred to produce each positive test a. Bromine Unsatuation b. Baeyer Unsaturation c. Chromic Acid d. Tollen’s e. Iodoform
Solutions
Expert Solution
Bromine Unsatuation
This test is used for finding unsaturation (not aromatic unsaturation). Here bromine adds to alkene to give 1,2-dibromocompound.

Baeyer Unsaturation
This also a qualitative test for the presence of unsaturation, Baeyer's reagent is an alkaline solution of cold potassium permanganate, which is a powerful oxidant making this a redox reaction. Reaction with double or triple bonds (-C=C- or -C?C-) in an organic material causes the color to fade from purplish-pink to brown. It is a syn addition reaction. But Aldehydes and formic acid also give a positive test.
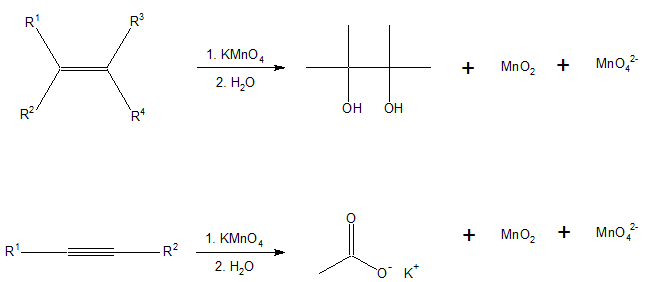
Chromic Acid Test
This test is for 1o and 2o alcohols and aldehydes. This test distinguishes primary and secondary alcohols from tertiary. Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol first to an aldehyde and then to a carboxylic acid and it will oxidize a secondary alcohol to a ketone. Tertiary alcohols do not react. The OH-bearing carbon must have a hydrogen atom attached.
Since the carbon atom is being oxidized in primary and secondary, the orange chromium Cr6+ ion is being reduced to the blue-green Cr3+ ion.

Tollen’s Test
The Tollen’s test is used to test for the presence of aldehydes. In this reaction, an aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid while the Ag1+ is reduced to silver metal, which deposits as a thin film on the inner surface of the glass. The generic reaction is as follows and is specific for aldehydes:

lodoform test
It will show the positive test for acetaldehyde and methyl ketones. The methyl group of the ketone is removed from the molecule and produces iodoform (CHI3). The formation of a yellow precipitate or suspension of iodoform is a positive test.

Related Solutions
What does a positive Biuret reaction indicate? How is the Barfoed test different from the Benedict...
2. (a) For each of the following statements, indicate whether it is a positive statement or...
1. Name three observations/signs that might indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred. 2. Write a...
For the exothermic reaction below, currently at equilibrium, indicate for every change whether the reaction will...
Which of the following compounds would produce a negative test for chromicacidand a positive test for...
For each of the following transactions that occurred during the year, indicate the dollar amount to...
A compound gives no reaction on the silver nitrate test( it was hexane), a positive on...
Indicate the effect on this period's FCFF and FCFE of a change in each of the...
For the test of significance questions, clearly indicate each of the formal steps in the test...
For the test of significance questions, clearly indicate each of the formal steps in the test...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago