Question
In: Economics
Pricing Concepts -Transportation Engineering A transportation firm is producing a transport service (with quantity Q trips)...
Pricing Concepts -Transportation Engineering
A transportation firm is producing a transport service (with quantity Q trips) with the following cost and revenue functions:
Total Cost: TC=$36,000 + $200Q + $0.4Q^2
Total Revenue: TR=$900Q-$0.1Q^2
Set up a table or spreadsheet for trip output/supply (Q), price (P), total revenue (TR), marginal revenue (MR), total cost (TC), marginal cost (MC), average cost (AC), total profit (π), and marginal profit (Mπ). Establish a range for Q from 0 to 1,000 in increments of 100 (i.e., 0, 100, 200, ..., 1,000). Using this spreadsheet, create a graph with AC and MC as dependent variables and trip output/supply (Q) as the independent variable.
a) At what combination of price P and supply Q is profit maximized? Why?
b) At what price P and supply Q is average cost (AC) minimized? Why?
Solutions
Expert Solution
TR = 900Q - 0.1Q2
TC = 36,000 + 200Q + 0.4Q2
- P = TR/Q = 900 - 0.1Q
- MR =
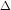 TR/
TR/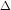 Q
and MC =
Q
and MC = 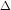 TC/
TC/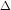 Q
Q - AC = TC/Q = (36,000/Q) + 200 + 0.4Q
- Profit (
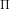 ) =
TR - TC
) =
TR - TC - Marginal profit =
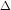
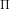 /
/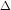 Q
Q
(1)
Data table:
| Q | TR | TC | P | MR | MC | AC | Profit | Marginal profit |
| 0 | 0 | 36,000 | -36,000 | |||||
| 100 | 89,000 | 60,000 | 890 | 890 | 240 | 600 | 29,000 | 650 |
| 200 | 1,76,000 | 92,000 | 880 | 870 | 320 | 460 | 84,000 | 550 |
| 300 | 2,61,000 | 1,32,000 | 870 | 850 | 400 | 440 | 1,29,000 | 450 |
| 400 | 3,44,000 | 1,80,000 | 860 | 830 | 480 | 450 | 1,64,000 | 350 |
| 500 | 4,25,000 | 2,36,000 | 850 | 810 | 560 | 472 | 1,89,000 | 250 |
| 600 | 5,04,000 | 3,00,000 | 840 | 790 | 640 | 500 | 2,04,000 | 150 |
| 700 | 5,81,000 | 3,72,000 | 830 | 770 | 720 | 531.43 | 2,09,000 | 50 |
| 800 | 6,56,000 | 4,52,000 | 820 | 750 | 800 | 565 | 2,04,000 | -50 |
| 900 | 7,29,000 | 5,40,000 | 810 | 730 | 880 | 600 | 1,89,000 | -150 |
| 1,000 | 8,00,000 | 6,36,000 | 800 | 710 | 960 | 636 | 1,64,000 | -250 |
(2)
Graph:

(a) Profit is maximized (= 209,000) when Q = 700 and P = 830.
(b) AC is minimized (= 440) when Q = 300 and P = 870.
Related Solutions
Assume a certain firm is producing Q = 1,000 units of output. At Q = 1,000,...
27) A firm has a production function Q = KL, where Q is the quantity of...
A firm has a production function Q = KL, where Q is the quantity of output,...
For a firm to maximize profit, it must minimize the cost of producing whatever quantity it...
A firm with a production function given by ?=170?q=170N, where ?q is the quantity produced and...
Scenario 14-2 Assume a certain firm is producing Q = 1,000 units of output. At Q...
Suppose the firm is producing a quantity on the downward sloping portion of its average cost...
The firm is producing softball bats and baseball bats. let q1 denote the quantity of softball...
1)If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a quantity where P < MC, then profit: Group...
1.If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue,...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
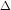 TR/
TR/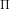 ) =
TR - TC
) =
TR - TC Rahul Sunny answered 3 years ago
Rahul Sunny answered 3 years ago