Question
In: Chemistry
What is wrong with the name 1‐t‐butyl‐2‐methylpropane?
What is wrong with the name 1‐t‐butyl‐2‐methylpropane?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concept and reason
IUPAC stands for the international union of pure and applied chemistry. IUPAC has given a nomenclature to name the organic compounds. The IUPAC name consists of three parts: root name, prefix, and suffix.
Fundamentals
The IUPAC rules for naming the compound are as follows:
1. Find and name the longest continuous carbon chain.
2. Identify and name groups attached to this chain.
3. Number the chain consecutively, starting at the end nearest a substituent group.
4. Designate the location of each substituent group by an appropriate number and name.
5. Assemble the name, listing groups in alphabetical order using the full name (e.g. cyclopropyl before isobutyl).
6. The prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc., used to designate several groups of the same kind, are not considered when alphabetizing.
The structure of 1-tert-butyl-2-methylpropane is as follows:
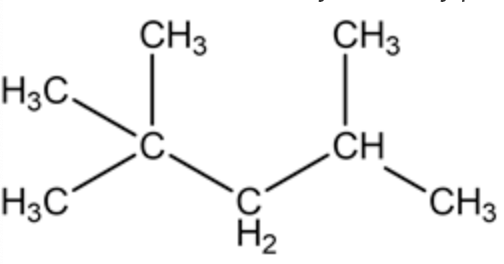
Draw the structure containing three carbon atoms in the long chain and then place the tertiary butyl group at the 1st carbon atom, methyl group at 2 nd carbon atom.
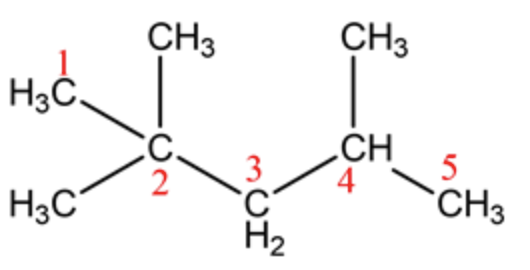
There are five carbon atoms in the long chain and the functional group is an alkane. So, the name of the parent chain is pentane. Number the chain and see that the substituents get the lowest possible number.
This structure contains three methyl groups as substituents.
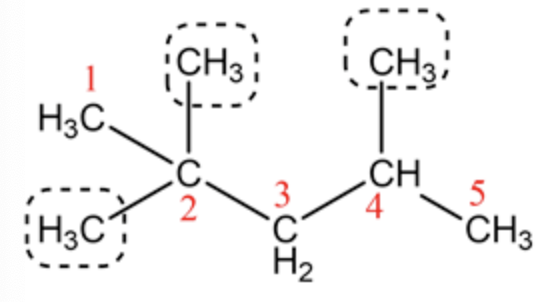
The correct parent chain is pentane.
The two methyl groups are at 2 nd carbon and another methyl group is at 4th carbon atom. So, the correct name of this compound is 2,2,4 -trimethylpentane.
Related Solutions
Six halides: 1-chlorobutane, 2-chlorobutane, Allyl chloride, 2-chloro-2-methylpropane, 1-chloro-2-methylpropane, 2-bromobutane. SN2: w/ sodium iodide in acetone SN1:...
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity toward ethanol solvolysis: t-Butyl bromide, t-Butyl iodide,...
Experiment ( preparation of tert-butyl chloride ) 1- what is the purpose of washing tert-butyl chloride...
Write equations for the reactions investigated. Label Sn1 or Sn2. 1)Butyl bromide in 15%NaI-acetone 2)Butyl bromide...
What is the chemical reaction and mechanism for 2-chloro-2-methylpropane with AgNO3 in ethanol/water? Which reacts fasters:...
What is wrong? 1. PTH is made by the thyroid gland. 2. There is an increased...
1.Find the equation of the tangent to x=t^2-t, y=t^2+t+1, at the point t=1 2.Find the length...
. A reaction in this experiment is started when 3.00 mL of 0.100 M t-butyl chloride...
Provide the major product that will form when t-butyl benzene react with cl2 in the presence...
A 4.43 g sample of 2-methoxy-2-methylpropane (formula C5H12O), is mixed with 119.19 atm of O2 in...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago