Question
In: Chemistry
What does the angle of twist mean in chemical compunds? Specifically BINOL. Where can I find...
What does the angle of twist mean in chemical compunds? Specifically BINOL.
Where can I find references?
Solutions
Expert Solution
it means chirality
1,1'-Bi-2-naphthol (BINOL) is an organic compound that is often used as a ligand for transition-metal catalysed asymmetric synthesis. BINOL has axial chirality and the two enantiomers can be readily separated and are stable toward racemisation. Thespecific rotation of the two enantiomers is +/- 35.5° (c=1 in THF). BINOL is a precursor for another chiral ligand called BINAP.
]
The organic synthesis of BINOL is not a challenge as such but the preparation of the individual enantiomers is.
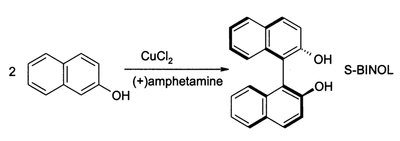
(S)-BINOL can be prepared directly from an asymmetric oxidative coupling of 2-naphthol with copper(II) chloride. The chiral ligand in this reaction is (S)-(+)-amphetamine.[2]
Racemic BINOL can also be produced using iron(III) chloride as an oxidant. The mechanism involves complexation of iron(III) into the hydroxyl, followed by a radical coupling reaction of the naphthol rings initiated by iron(III) reducing into iron(II).
Optically active BINOL can also be obtained from racemic BINOL by optical resolution. In one method, the alkaloid N-benzylcinchonidinium chloride form a crystalline inclusion compound. The inclusion compound of the S-enantiomer is soluble inacetonitrile but that of the R-enantiomer is not.[3]
In another method BINOL is reacted with the acid chloride pentanoyl chloride to obtain the di-ester compound. The enzymecholesterol esterase is then added in the form of bovine pancreas acetone powder which is able to hydrolyse the (S)-di-ester but not the (R)-di-ester.[3] The (R)-dipentanoate is hydrolysed in a second step with sodium methoxide.[4]
Third method employs HPLC with chiral stationary phases.[5]
Related Solutions
What does it mean to "Provide Liquidity"? More specifically what does it mean to provide liquidity...
What does it mean to run a program "in the background"? Specifically, what is the key...
What does it mean for the pendulum to have a small angle? How far does the...
the concept of the Right to Privacy. What does that mean and where does it come...
When we say that momentum is conserved for an isolated system, what specifically does that mean?
where can i find the answers to the actual TEAS V test?
How do you find the total internal reflection angle? I know that if the incident angle...
You've devised a new twist on the traditional 'What number am I thinking of?' game to...
I am looking for a formula where I can find the relative humidity (RH) of air...
1) what class of organic compunds does the carbon-containing reactant in the reaction above belong to...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago