Question
In: Chemistry
Draw a glycerophospholipd containing the following: a) A C12 saturated fatty acid b) A C12 omega...
Draw a glycerophospholipd containing the following:
a) A C12 saturated fatty acid
b) A C12 omega 4-cis unsaturated fatty acid
c) serine
Solutions
Expert Solution
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes.
The term glycerophospholipid signifies any derivative of glycerophosphoric acid that contains at least one O-acyl, or O-alkyl, or O-alk-1'- enyl residue attached to the glycerol moiety.
The alcohol here is glycerol, to which two fatty acids and a phosphoric acid are attached as esters. This basic structure is a phosphatidate. Phosphatidate is an important intermediate in the synthesis of many phosphoglycerides. The presence of an additional group attached to the phosphate allows for many different phosphoglycerides.
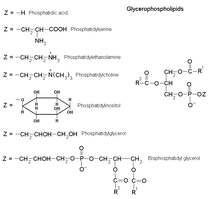
a)  C12 saturated fatty acid.
C12 saturated fatty acid.
b) An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least onedouble bond within the fatty acid chain.
A fatty acid chain is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double bond.
Omega-4 fatty acids — also called ω-4 fatty acids or n-4 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) with a double bond(C=C) at the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain. The fatty acids have two ends, the carboxylic acid (-COOH) end, which is considered the beginning of the chain, thus "alpha", and the methyl (CH3) end, which is considered the "tail" of the chain, thus "omega." The way in which a fatty acid is named is determined by the location of the first double bond, counted from the methyl end, that is, the omega (ω-) or the n- end.

c) Serine
Serine
Related Solutions
172. Which of the following is an example of a polyunsaturated fatty acid? Omega-6 Oleic acid...
63. Which of the following is an omega 3 fatty acid? A. 18:0 B. 18:3 Δ9,12,15 ...
Arrange these biological molecules (nucleic acid, cellulose, unsaturated fatty acid, saturated fatty acid) in order from...
What is the delta notation of a fatty acid with the omega notation 20:5 (w-3)?
1) Consider the oxidation of Stearic acid (18 carbon fatty acid, fully saturated) to CO2, NADH...
For each molecule of fully saturated fatty acid sterarate that is degraded throguh bet- oxidation: a....
very emergence For each 2-carbon increase in the length of a saturated fatty acid chain, how...
1. Myristoyl-CoA is a saturated fatty acid with 14 carbons attached to coenzyme A. How many...
sort the descriptions into properties that describe saturated phospholipids or unsaturated phospholipids. -fatty acid tails pack...
Distinguish between the roles Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids play in the body. Discuss...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago