Question
In: Other
Given an array of numbers, find the index of the smallest array element (the pivot), for...
Given an array of numbers, find the index of the smallest array element (the pivot), for which the sums of all elements to the left and to the right are equal. The array may not be reordered.
Example arr=[1,2,3,4,6]
the sum of the first three elements, 1+2+3=6. The value of the last element is 6.
Using zero based indexing, arr[3]=4 is the pivot between the two subarrays.
The index of the pivot is 3.
Function Description
Complete the function balancedSum in the editor below.
balanced Sum has the following
parameter(s):
int arr(n): an array of integers
Returns:
int: an integer representing the index of the pivot
Constraints
3≤n≤105
1≤ arr[i]≤ 2 * 104, where 0≤i
It is guaranteed that a solution always exists.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Approach used:
>>Maintain two pointers, leftptr, rightptr
>>Traverse array from both sides at once and calculate left_sum and right_sum to store array sum from right and left.
>>If left_sum < right_sum increment leftptr
>>If left_sum > right_sum decrement rightptr
>>When left_sum = right_sum and leftptr and rightptr have only one element in between which is pivot,
>>Return the pivot
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I have included my code and screenshots in this answer. In case, there is any indentation issue due to editor, then please refer to code screenshots to avoid confusion.
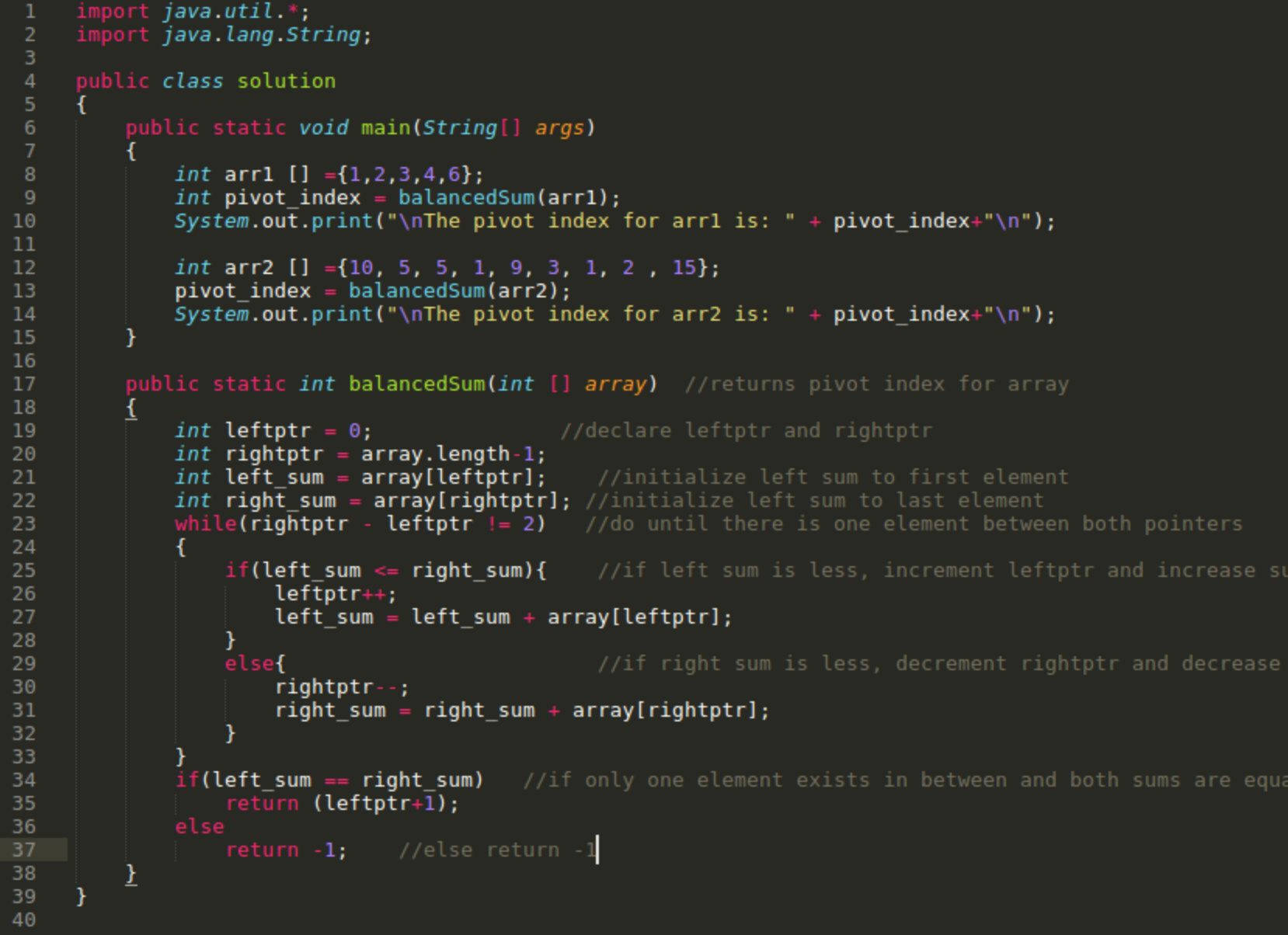
----------------solution.java---------
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.String;
public class solution
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1 [] ={1,2,3,4,6};
int pivot_index = balancedSum(arr1);
System.out.print("\nThe pivot index for arr1 is: " + pivot_index+"\n");
int arr2 [] ={10, 5, 5, 1, 9, 3, 1, 2 , 15};
pivot_index = balancedSum(arr2);
System.out.print("\nThe pivot index for arr2 is: " + pivot_index+"\n");
}
public static int balancedSum(int [] array) //returns pivot index for array
{
int leftptr = 0; //declare leftptr and rightptr
int rightptr = array.length-1;
int left_sum = array[leftptr]; //initialize left sum to first element
int right_sum = array[rightptr]; //initialize left sum to last element
while(rightptr - leftptr != 2) //do until there is one element between both pointers
{
if(left_sum <= right_sum){ //if left sum is less, increment leftptr and increase sum
leftptr++;
left_sum = left_sum + array[leftptr];
}
else{ //if right sum is less, decrement rightptr and decrease sum
rightptr--;
right_sum = right_sum + array[rightptr];
}
}
if(left_sum == right_sum) //if only one element exists in between and both sums are equal, then return pivot
return (leftptr+1);
else
return -1; //else return -1
}
}
----------------Screenshot solution.java---------
Related Solutions
Write a program on C defining an array. Find the element at given index k. Replace the element at given index k.
Using Java Write a method that returns the index of the smallest element in an array...
In Java Find the second largest and second smallest element in a given array. You can...
Find the K'th smallest element in an unsorted array of integers. Find the K'th largest element...
How would you take a given array of non-repeating random integers and sort every 5th element. Meaning index 0 is the smallest element in the array.
Consider sorting n numbers stored in array A by first finding the smallest element of A...
Develop a recursive algorithm to find the smallest and largest element in an array and trace...
Write a recursive method to find the smallest int in an unsorted array of numbers. int[]...
write a method that returns the index of the second smallest element in an array of integers. If the number of such elements is greater than 1.
You will build some methods that search for the smallest element and the index of the...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 Amanda K answered 3 years ago
Amanda K answered 3 years ago