Question
In: Economics
Q TC 0 $ 100 1 110 2 130 3 160 4 200 5 250 6...
|
Q |
TC |
|
0 |
$ 100 |
|
1 |
110 |
|
2 |
130 |
|
3 |
160 |
|
4 |
200 |
|
5 |
250 |
|
6 |
310 |
|
7 |
380 |
|
8 |
460 |
|
9 |
550 |
|
10 |
650 |
|
11 |
760 |
- Say the firm is in a perfectly competitive market. If the current market (equilibrium) price is $ 60, at what output level will the firm as a profit maximizer produce at?
- Say the market price rises to $ 80. At what output level (as a perfect competitor) will this produce at?
- How much profit is the firm making at a price of $80? Based on this calculation, do you expect firms to enter or leave this market?
- Say instead this firm is a monopoly. If the firm maximizes profit at an output level where marginal revenue equals $ 50, what output level will this be?
Solutions
Expert Solution
The perfectly competitive firm produces where the marginal cost
equals the marginal revenue and the market price is also equal to
the average and marginal revenue. 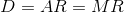 .
.
In this graph we have to find out the marginal cost at every output produced, the marginal cost is the addition made to the total cost when an additional unit is produced.
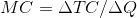 .
.
| Q | TC | MC |
| 0 | 100 | - |
| 1 | 110 | 10 |
| 2 | 130 | 20 |
| 3 | 160 | 30 |
| 4 | 200 | 40 |
| 5 | 250 | 50 |
| 6 | 310 | 60 |
| 7 | 380 | 70 |
| 8 | 460 | 80 |
| 9 | 550 | 90 |
| 10 | 650 | 100 |
| 11 | 760 | 110 |
a). If the market price is $60 and that is also equal to the marginal revenue , the firm produces marginal cost equals the marginal revenue. The firm would produce 6 units.
b). If the price rises to $80 the firm would produce 8 units.
c). The profit is calculated by 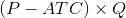 .
.
Here we divide the total cost by the quantity to get the average cost.
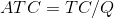 .
.
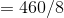 .
.
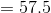 .
.
Profit .
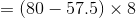 .
.
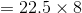 .
.
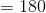 .
.
Profit equals $180.
The firm is earning a positive profit and the price is well above the average cost , so the firm should produce in this context. Due to positive profits in the market new firms will enter the market.
d).The monopolist also maximizes the profit where the marginal revenue equals the marginal cost ,so if this is a monopoly the firm would produce 5 units.
Related Solutions
Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 TC 10 18 24 30 38...
Period Demand 1 110 2 115 3 125 4 127 5 130 6 134 a) Prepare...
exampleInput.txt 1 2 3 0 2 3 4 0 1 3 5 0 1 2 6...
Output TC MC ATC AFC TVC AVC TFC 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7...
x (Bins) frequency 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 2 4 5 5 8 6...
6 5 4 5 0 0 13 48 6 1 0 7 2 0 1 1...
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Project A -$300 -$387 -$193 -$100 $600 $600...
Q-1 # of workers Output (flags( 0 0 1 50 2 110...
Period Forecast 1 200 2 500 3 300 4 400 5 200 6 200 Regular time:...
Year Cash Flow 0 $0 1 $250 2 $400 3 $500 4 $600 5 $600 What...
- Aniline hydrochloride, [C6H5NH3]Cl, is a weak acid. Its conjugate base is the weak base aniline, C6H5NH2....
- Explain the RAAS by listing (and briefly describing) several steps that occur in this process. What...
- 1.What will the result of this form be? (cadr ‘(1 2 3 4 5 6)) a....
- Question 5. Why do macroeconomist require tools to bring forth policies? What are these tools? (10...
- In C++ Write an IterativeMergeSort function given these parameters and following the prompt IterativeMergeSort(vector<int> v, int...
- Current Year Preceding Year Balance Sheet: Cash $24,000 $25,000 Short-term Investments 17,000 28,000 Net Accounts Receivables...
- If the interest rate is 11%, what is the Equivalent Annual Cost (EAC) of the following...
 Rahul Sunny answered 21 hours ago
Rahul Sunny answered 21 hours ago