Question
In: Economics
For each of the following changes, what happens to the real interest rate and output in...
For each of the following changes, what happens to the real interest rate and output in the long run, after the price level has adjusted to restore general equilibrium? How would the results differ, if at all, between the classical and Keynesian model? Draw a diagram for each part to illustrate your result.
(a)Wealth rises.
(b)Money supply rises.
(c)The future marginal productivity of capital increases.
(d)Expected inflation declines.
(e)Future income declines
Solutions
Expert Solution
In the long run, a higher rate of money growth leads to higher ongoing inflation with no effect on output or employment. The effects on interest rates are similar. If the central bank permanently increases the money growth rate, nominal and real interest rates may fall initially.
a. If wealth rises - According to classical model, if wealth
rises in the economy, the level of employment will increase which
will result in increase in output . Also increase in employment
will increase the aggregate demand in the economy. Thus investors
will invest more and interest rate will also increase at its
real.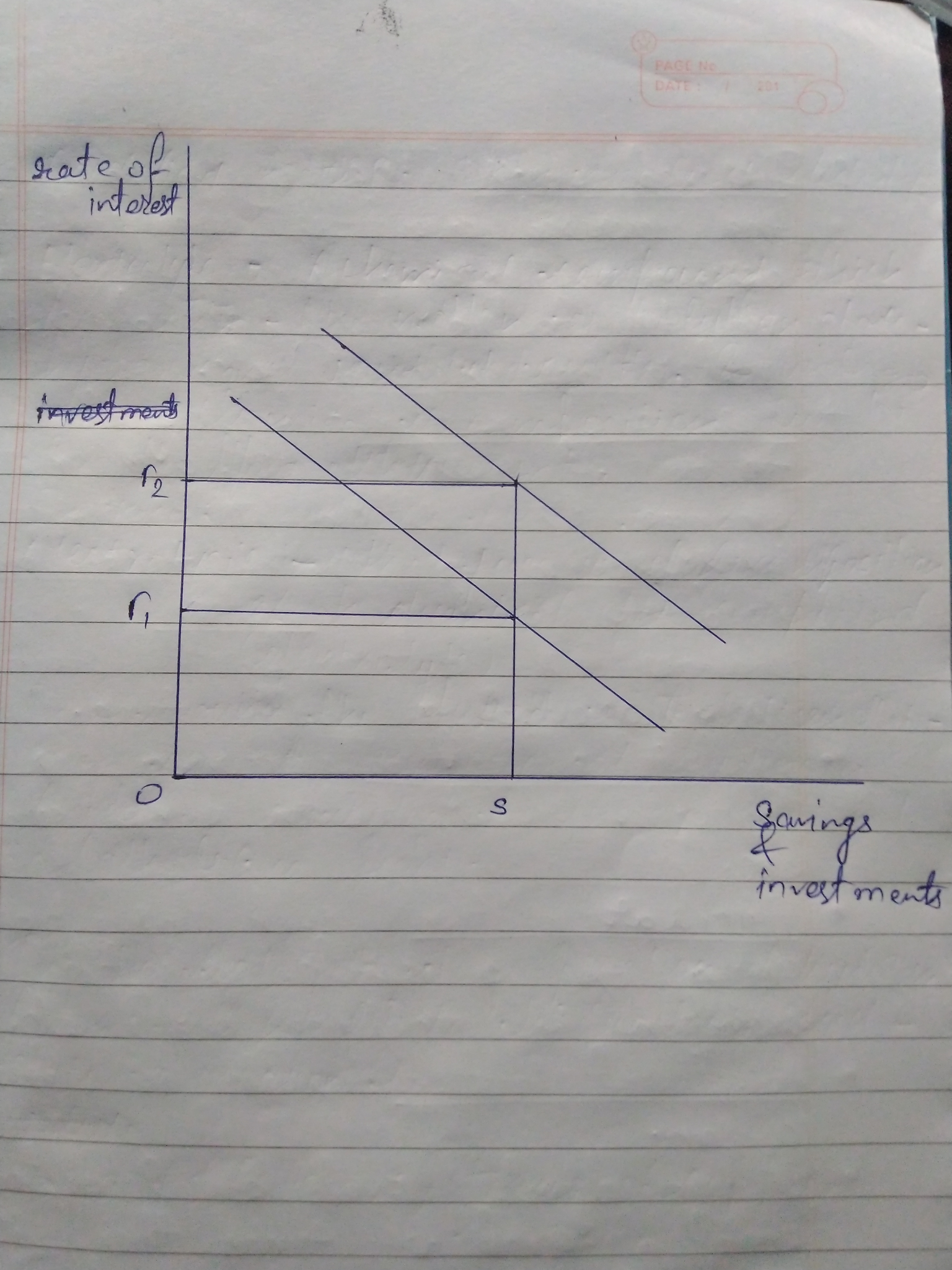
Again according to keynsian model there will be same effect on interest rate and output but the situation will not always same. Before the point of full employment , the economy will acquire it's equilibrium point.
b. As mentioned above, when money supply rises savings as well as investment will increase in the economy which will increase the rate of interest in long run.
But according to Keynsian model, this activity of central bank will increase the inflation rate in the economy. The rate of interest will increase. But Keynes has not talked about long run effect. In words of Keynes, in long run, we will die.
c. If the future marginal productivity of capital increases, there will be more production in less capital. Thus rate of investment as well as interest rate will decrease. Also output will be same in short run and will decrease gradually in the long run as in the situation of decrease in employment the employment rate will also decrease.
According to Keynes, there will be no any effect on output and rate of interest as these are affected by present things not of future.
d. If expected inflation declines the investors start to save more thus money flow in economy will decrease. This will directly affect the rate of interest and output as both will start decline.
According to Keynes the result will be same as above. To overcome on this situation Keynes suggests that there should be always some increase in inflation rate of the economy. Also rate of expected inflation should be always greater than the real rate of inflation.
e. When future income declines of the economy, the aggregate demand will decrease. Thus rate of interest as well as output will start declining.
Related Solutions
For each of the following changes, what happens to the real interest rate and output in...
using the IS-LM and the AD-LRAS-SRAS figures what happens to real interest rate, output and prices...
Explain what happens to saving, investment, and the real interest rate in each of the following scenarios in a closed economy.
Using the Keynesian-cross model, explain what happens to output following a decrease in the interest rate?
1A.Using the Keynesian-cross model, explain what happens to output following a decrease in the interest rate?...
What happens to expected inflation, nominal interest rate and real money demand when there is a...
What happens to interest rate, output, prices and wages; as government expenditures decrease within a general...
The IS curve shows the combinations of the real interest rate and the aggregate output that...
The IS curve shows the combinations of the real interest rate and the aggregate output that...
Explain what happens to real money supply and real money demand in each of the following...
- To increase revenue, you should increase price of your product. Is that always true? explain.
- On 26 February, Hong Kong’s Financial Secretary Paul Chan announced that all permanent residents in Hong...
- This is an old classic which I don't think ever got a clear answer. The Gribov-Froissart...
- Explain the links between quality and productivity and quality and cost
- In perfectly competitive market, we sum horizontally individual firms’ marginal cost curves and use it as...
- Why does the aggregate supply have 3 regions? What type of economy would you see if...
- Chapter 6 Government Actions in Markets 5) What happens to the quantity of labor supplied, the...
 Rahul Sunny answered 3 weeks ago
Rahul Sunny answered 3 weeks ago