Question
In: Economics
two duopoly markets with a homogeneous good have a demand function of P= 100 - Q....
two duopoly markets with a homogeneous good have a demand function of P= 100 - Q. Their costs are TC1=50q1 and TC2= 40q2. The two firms collude. What are the producer surplus, consumer surplus and profit?
Solutions
Expert Solution
P = 100 - q1 - q2
MC1 = dTC1/dq1 = 50
MC2 = dTC2/dq2 = 40
For firm 1,
TR1 = P x q1 = 100q1 - q12 - q1q2
MR1 = 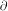 TR1/
TR1/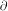 q1
= 100 - 2q1 - q2
q1
= 100 - 2q1 - q2
Setting MR1 = MC1,
100 - 2q1 - q2 = 50
2q1 + q2 = 50..........(1) [best response, firm 1]
For firm 2,
TR2 = P x q2 = 100q2 - q1q2 - q22
MR2 = 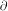 TR2/
TR2/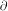 q2
= 100 - q1 - 2q2
q2
= 100 - q1 - 2q2
Setting MR2 = MC2,
100 - q1 - 2q2 = 40
q1 + 2q2 = 60..........(2) [best response, firm 2]
Multiplying (2) by 2,
2q1 + 4q2 = 120........(3)
2q1 + q2 = 50..........(1)
(3) - (1) yields:
3q2 = 70
q2 = 23.33
q1 = 60 - 2q2 [from (2)] = 60 - (2 x 23.33) = 60 - 46.66 = 13.34
Q = 13.34 + 23.33 = 36.67
P = 100 - 36.67 = 63.33
When Q = 0, P = 100
Total consumer surplus = (1/2) x (100 - 63.33) x 36.67 = (1/2) x 36.67 x 36.67 = 672.34
For firm 1,
Producer surplus (PS1) = (63.33 - 50) x 13.34 = 13.33 x 13.34 = 177.82
For firm 2,
Producer surplus (PS2) = (63.33 - 40) x 23.33 = 23.33 x 23.33 = 544.29
Total PS = PS1 + PS2 = 177.82 + 544.29 = 722.11
For firm 1,
Profit (Z1) = q1 x (P - MC1) = 13.34 x (63.33 - 50) = 13.34 x 13.33 = 177.82
For firm 2,
Profit (Z2) = q2 x (P - MC2) = 23.33 x (63.33 - 40) = 23.33 x 23.33 = 544.29
Total profit = Z1 + Z2 = 177.82 + 544.29 = 722.11
Related Solutions
Consider a homogeneous good Cournot duopoly with inverse demand function given by p = 1 –...
Consider a market for a homogeneous good with a demand curve P = 100 − Q....
Q: A homogenous-good duopoly faces an inverse market demand function of P = 57 – Q....
The demand function in a duopoly is: P = 100 – 2(Q1 + Q2). If the...
The inverse market demand for a homogeneous good is given by p = 1 – Q,...
4. Consider a Cournot duopoly with inverse demand function P = 100 – Q. Firm 1’s...
The demand function for iPhone is Q(p) = 100 – P and the cost function is...
The inverse demand for a homogeneous good is given by P(Q) = 5 – 2Q, where...
Assume there is a duopoly. Assume that the market demand is : P=100-2Q Assume the good...
a.) Two identical firms compete as a Cournot duopoly. The market demand is P=100-2Q, where Q...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
 Rahul Sunny answered 3 weeks ago
Rahul Sunny answered 3 weeks ago