Question
In: Chemistry
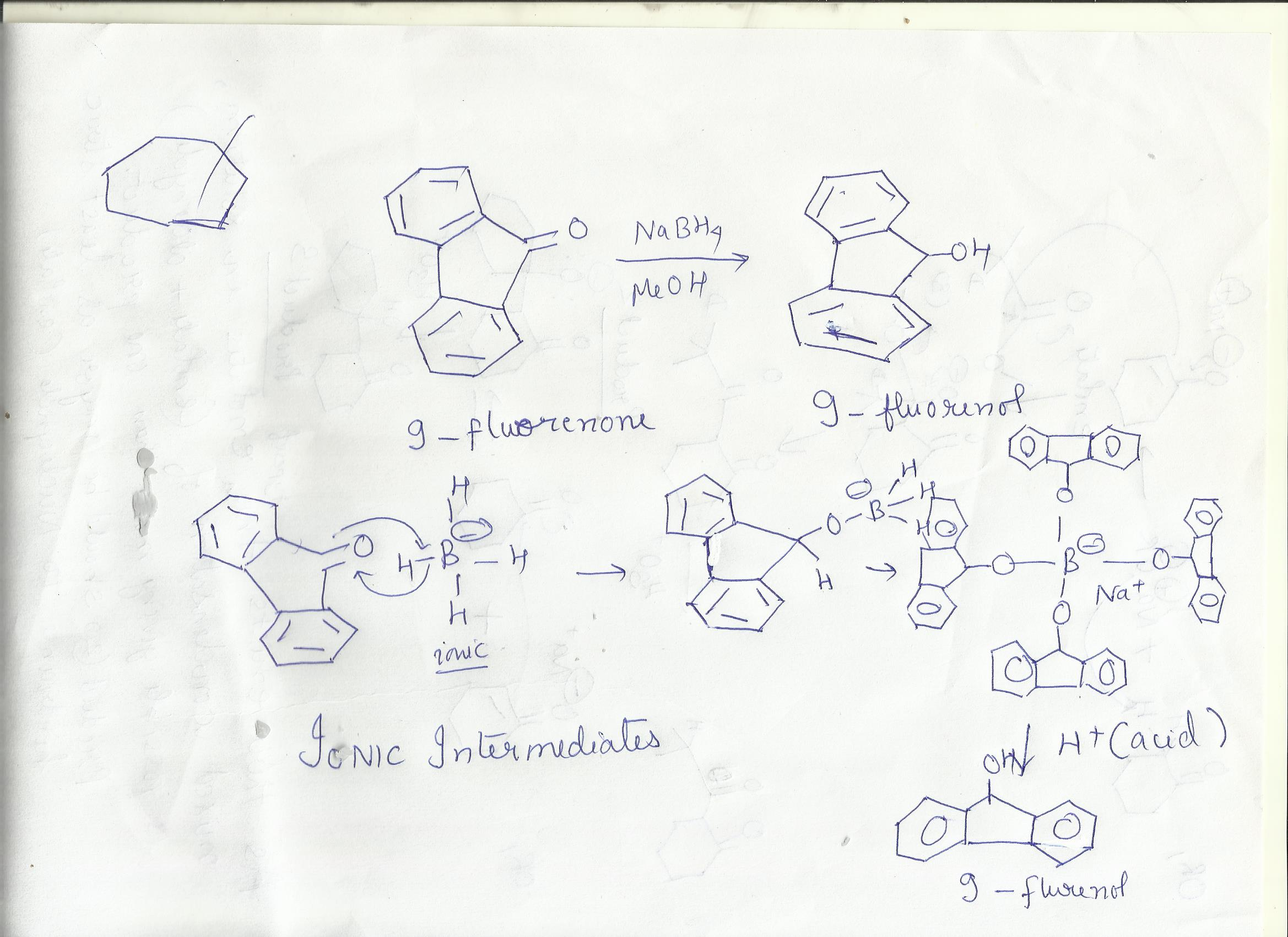
In a Sodium Borohydride reduction of 9-fluorenone to 9-fluorenol, methanol is used as the solvent because...
In a Sodium Borohydride reduction of 9-fluorenone to 9-fluorenol, methanol is used as the solvent because it will not react with the products and reactants and because the products and reactants are very sluble in methanol. Would 2-propanone also be a suitable solvent for this reaction? Why/Why not?
Solutions
Expert Solution
methanol=polar protic solvent( can form hydrogen bonds,have acidic hydrogen,can dissolve ionic compounds)
acetone(2-propanone)=polar aprotic solvent(cannot form hydrogen bonds,do not have acidic hydrogen,cannot dissolve ionic compounds
1)No, 2-propanone would not be a suitable solvent for this reaction,as the reaction involves the use of sodium borohydride(NaBH4) as the reducing agent to reduce the ketone functional group in 9-fluorenone to -OH group in the product 9-fluorenol.As 2-propanone itself is a ketone so it will react with the reducing agent and thus interfere with the reaction.
2) NaBH4 reducing agent is ionic in nature so needs a prolar protic solvent to stabilize it in solution ,by electrostatic interactions.Also acid is added for the work up of the final product, soluble in protic solvents and not aprotic solvents like H2SO4
Moreover , the solubility of 9-fluorenone and 9-fluorenol is very high in methanol , a polar protic solvent.It can form hydrogen bonding with the -OH and polar -C=O groups in reactant and product.
2-propanone (or acetone) is a polar aprotic solvent ,which can have dipole-dipole interactions with the reactant and product ,but the interactions are weaker compared to hydrogen bonding.So not good solvent.
check the reaction
Related Solutions
In regards to the synthesis of 9-fluorenone via sodium hypochlorite oxidation of 9-fluorenol (9-Fluorenol -> 9-fluorenone)...
What are some possible sources of error in the oxidation of 9-fluorenol to 9-fluorenone with sodium...
Will the product of this reaction (9-fluorenone to 9-fluorenol) differ if LAH is used instead of...
In the reduction of benzophenone with NaBH4... After dissolving benzophenone in methanol and adding sodium borohydride,...
Can you please explain the oxidation reaction of 9-fluorenol to 9-fluorenone using sodium hypochlorite, preferably a...
You will apply the oxidation reaction to 9-fluorenol to obtain 9-fluorenone: 1. Describe the role of...
Expt 55 Micro: Borohydride Reduction of a Ketone: Hydrobenzoin from Benzil 3. Sodium borohydride can be...
Discuss the reduction of acetophenone with sodium borohydride and a workup of ethanol. My % yield...
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of a Ketone 1. How will the dibenzalacetone product be isolated from the...
why can sodium borohydride be preferred in reduction to alcohols over H2/Pt?
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 queen_honey_blossom answered 1 month ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 1 month ago