Question
In: Computer Science
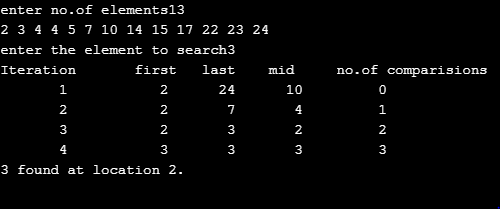
Given the following list of values, perform a binary search for the indicated search item. Use...
Given the following list of values, perform a binary search for the indicated search item. Use the binary search algorithm on pg. 1026 of our textbook. Show the values of first, last and middle, and the number of comparisons made after each iteration of the loop. Your should create a table like the following to show your work, where first and last are the values of the variables at the beginning of the loop, and mid is the midpoint used during that iteration, list[mid] is the value in the list at the midpoint, and No. of key comparisons should be the number of comparisons made during this iteration by the algorithm:
Iteration first last mid list[mid] No. of key comparisons 1 0 12 ? ? ?
List:
[ 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 7, 10, 14, 15, 17, 22, 23, 24 ]
Searching for value: 3
Solutions
Expert Solution
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int f,l,mid,i,comp=0,key,n;
int list[20];
printf("enter no.of elements");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&list[i]);
printf("enter the element to search");
scanf("%d",&key);
f= 0;
l=n-1;
i=0;
mid=(f+l)/2;//caluculate mid
printf("Iteration\tfirst\tlast\tmid\tno.of comparisions\n");
while (f<= l) {//while the first value becomes greater than last
then element not found
printf("%8d%12d%8d%8d%10d\n",i+1,list[f],list[l],list[mid],comp);//print
values
i++;
if (list[mid] < key){//if mid is less than key it is in second
half
f = mid+1;
comp++;//increase comparisions
}
else if (list[mid] == key) {
comp++;//check if equals and increment comparisions
printf("%d found at location %d.\n", key, mid+1);
break;
}
else//if mid greater than key it is in first half
{
l= mid-1;
comp++;//increment comparisions
}
mid = (f+ l)/2;//change the mid value
}
if(f>l)
{
printf("The element not found");
}
return 0;
}
Related Solutions
Design a program which uses functions to sort a list and perform a binary search. Your...
Perform the following arithmetic in Binary assuming 16 bit registers (67)10 + (-89)10 List the values...
A binary search tree can be built with a traditional insertion method given a list of...
A binary search tree can be built with a traditional insertion method given a list of...
Binary Search. Write a MIPS assembly program to perform a binary search on A[10], which is an array of 10 positive integers.
Consider the recursive formulation of the Binary Search algorithm. Given a sorted and non-decreasing list of...
Create a List object that uses the binary search algorithm to search for the string "A"....
A search for “car” on a shopping website gave a list of the following items: Item...
Suppose I have a list of 128 unsorted numbers. If I use the binary search to...
Given the array a and the binary search function below, list all ACTIVATIONS IN FINDING t=19....
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 venereology answered 1 month ago
venereology answered 1 month ago