Question
In: Chemistry
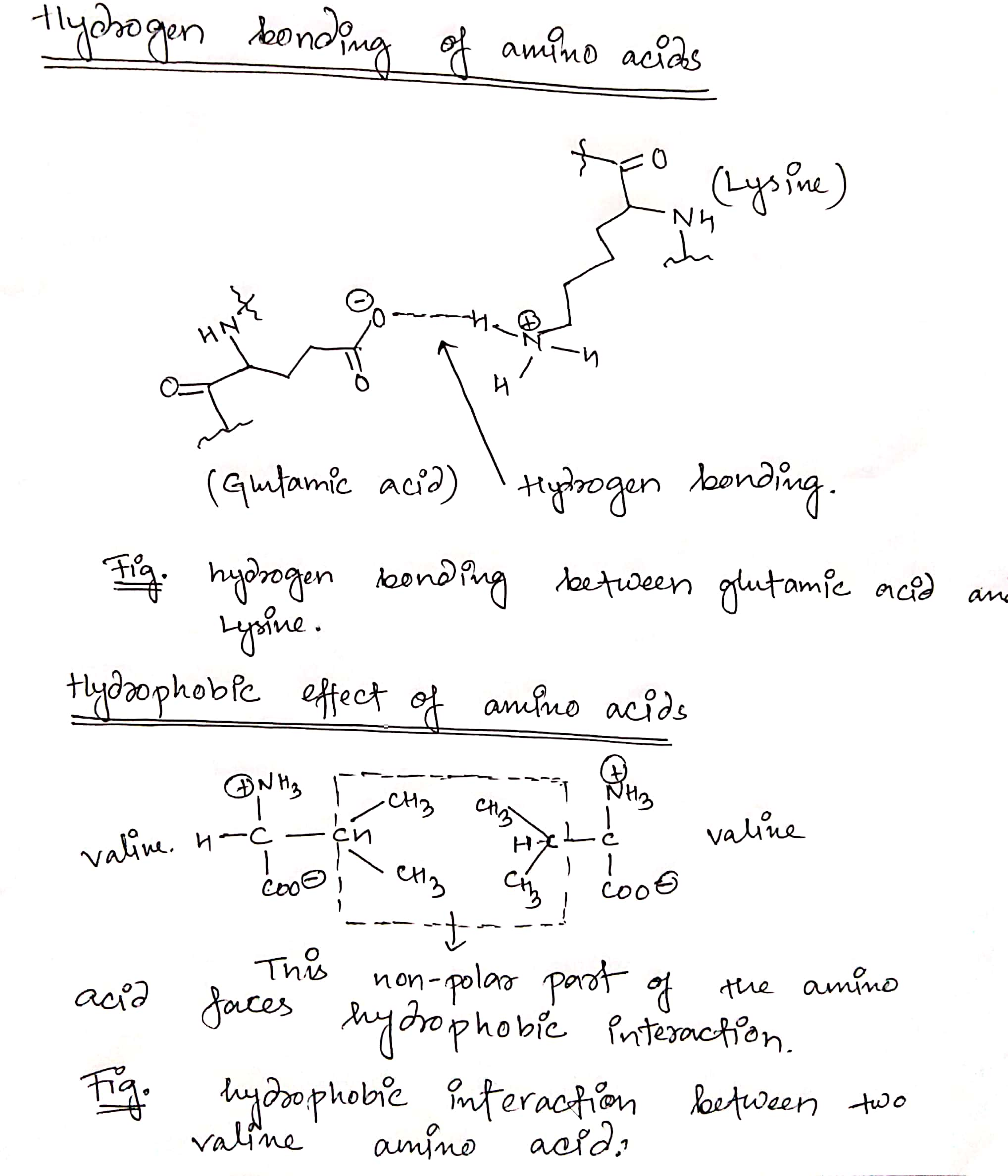
Describe the chemical basis for the following interactions: hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic effect and sketch the...
Describe the chemical basis for the following interactions:
hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic effect and sketch the interaction
using appropriate amino acids side chains in an aqueous environment
for each of the following intermolecular interactions.
Solutions
Related Solutions
Discuss how the protein structures are affected by di-sulfide bridge, hydrogen bonding, dispersion forces (hydrophobic interactions),...
Discuss how the protein structures are affected by di-sulfide
bridge, hydrogen bonding, dispersion forces (hydrophobic
interactions), and salt bridge.
Differentiate between the four types of protein structure and
say what each is responsible for.
Comment on three peacetime uses of nuclear energy.
Rank the penetrating power of nuclear radiation from the least
to most penetrating and describe the nature of the material needed
to block each radiation
describe the chemical nature of the non-covalent bonding interactions between peptides and lipids.
describe the chemical nature of the non-covalent bonding
interactions between peptides and lipids.
whic of these interactions can be explained by hydrogen bonding. Select all that apply. HF is...
whic of these interactions can be explained by hydrogen
bonding.
Select all that apply.
HF is a weak acid neutralized by NaOH.
HF has a higher boiling point than HCl.
CH4 molecules interact more closely in the liquid than in the
gas phase.
Ice, H2O, has a solid structure with alternating H?O
interactions.
H2Te has a higher boiling point than H2S.
Watch the animation and select the interactions that can be explained by hydrogen bonding. Check all...
Watch the animation and select the interactions that can be
explained by hydrogen bonding. Check all that apply. Check all that
apply. HF has a higher boiling point than HCl. HF is a weak acid
neutralized by NaOH. CH4 molecules interact more closely in the
liquid than in the gas phase. Ice, H2O, has a solid structure with
alternating H−O interactions. H2Te has a higher boiling point than
H2S.
Describe all types of associations (hydrophobic interactions, ionic interactions, etc.) that lead to stabilization of tertiary...
Describe all types of associations (hydrophobic interactions,
ionic interactions, etc.)
that lead to stabilization of tertiary structure. Be detailedin
your descriptions. Indicate how
eachof these associations can be lost due to denaturation. Give an
example of a denaturation
cause (high temperature, change in pH, salt, or chemical) that
results in the loss of eachtype of
association.
Indicate whether hydrogen bonding is present in the following compounds or mixtures. If hydrogen bonding is...
Indicate whether hydrogen bonding is present in the following
compounds or mixtures. If hydrogen bonding is present, indicate how
two molecules can hydrogen bond. For example, in a mixture of water
and methanol the Hof the H2O can
hydrogen bond to the O in the CH3OH.
Also possible is that the OH of the
CH3OH can hydrogen bond to the O of the
H2O. (Of course, the H on one H2O can
hydrogen bond to the O on another H2O,...
* Predict solubility based on hydrogen bonding interactions Predict electron distribution in a bond from electronegativity...
* Predict solubility based on hydrogen bonding
interactions
Predict electron distribution in a bond from
electronegativity
Define the chemical basis of hydrogen bonding.
Identify and construct hydrogen bond donor and acceptor
groups
Predict hydrogen bonding potential among various functional
groups
Relate hydrogen bonding with solvent water to solubility
Distinguish among covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. What is electronegativity? How does...
Distinguish among covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds
and hydrophobic interactions. What is electronegativity? How does
electronegativity influence ionization? the polarity of covalent
bonds? Which types of bonds are the weakest? strongest? What are
isotopes? Know the basic principles of carbon dating and of use of
radioactive tracers. On your own Molecular Shape and Function
Describe the importance of amino acid R group properties for bonding and non-bonding interactions within proteins.
Describe the importance of
amino acid R group properties for bonding and
non-bonding interactions within proteins.
Describe how hydrogen bonding determines many properties of water.
Properties of Water
Describe how hydrogen bonding determines many properties of water.
List the properties of water that make it a valuable solvent, and distinguish between hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances.
Explain how the molarity of a solution—the number of moles of a solute per liter of solution—is used to measure the concentration of solutes in solution.
Discuss the properties of water that are critical for the survival of living organisms.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
ADVERTISEMENT

 queen_honey_blossom answered 1 month ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 1 month ago