Question
In: Other
111 m3/min of hydrogen measured at normal conditions and nitrogen at a 300% excess enter an...
111 m3/min of hydrogen measured at normal conditions and nitrogen at a 300% excess enter an isobaric reactor. The inlet gases at 490°C are reacted in the presence of a catalyst to synthesize ammonia. The process has an efficiency of 33%. The exhaust gases are cooled to -40°C to condense the ammonia. Assume that the Cp of the gas phase species can be used in the temperature range, and that Cp NH3 (l) = 0.071938 kJ/mol K. Calculate the overall heat flow of the system in kW.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Hydrogen fed = 111 m3/min
NTP conditions
T = 293 K
P = 1 atm = 1.013×105 Pa
n = PV/(RT)
n = (1.013×105×111) /(8.314×293)
n = 4615.882 mol/min
H2 fed = 4615.882 mol/min
The reaction occuring is
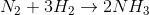
N2 required according to stiochometry =
4615.882/3 = 1538.276 mol/min
N2 fed is 300% in excess
N2 supplied = 1538.276+ (1538.276) (3) = 6153.104 mol/min
Process efficiency = 33%
Here efficiency of process is asummed as conversion
Conversion = 33%
H2 reacted = (4615.882) (0.33)
= 1523.241 mol/min
N2 reacted according to stiochometry = 1523.241/3 = 507.747 mol/min
The reaction occurs at 490°C
From handbook
At T = 25°C
∆Hf(NH3) (g) = -45. 94 KJ/mol
∆Hf(N2) and ∆Hf(H2) = 0
∆Hr = ∆Hproducts - ∆Hreactants
∆Hr = (-45.94×2) -0= -91. 88 KJ/mol
According to kirchoffs law
∆H(490°C) = ∆H(25°C) + ∆Cp(490-25)
∆Cp= (nCp) products -(nCp) reactants
Cp is taken from handbook at average temperature of
(25+490) /2 = 257.5°C
Cp(NH3)(g) = 0.043015 KJ/mol°C
Cp(N2) = 0.029738 KJ/mol°C
Cp(H2) = 0.02927 KJ/mol°C
∆Cp = (2×0.043015) -(0.029738) -(3×0.02927) = -0. 031518 KJ/mol°C
∆H(490°C) = ∆H(25°C) + ∆Cp(490-25)
∆H(490°C) = -91. 88+(-0.031518) (490-25)
∆H(490°C) = -106. 535 KJ/mol
Moles of amminia formed = (2×507.747) = 1015.494 moles
∆Hr= -106. 535(1015.494) =
-108185. 6533 KJ/min
Enthalpy reference temperature = 25°C
Reactants average temperature = (25+490) /2 = 257.5°C
Products average temperature = (490-40) /2 = 225°C
B. P of ammonia = -33°C
Cp(liquid) = 0.071938 KJ/mol°C
∆H = nCp(Hf- Hi)
| Component | inlet moles/min | Cp(KJ/mol°C) | Hi(KJ/min) | outlet moles (mol/min) | Cp(KJ/mol°C) | Ho(KJ/min) |
| N2 | 6153.104 | 0.029738 | 85086.168 | 6153.104- (4615.882×0.33) /3)= 5645.356 | 0.02957 | -88474.583 |
| H2 | 4615.882 | 0.02927 | 62824.692 | 4615.882(1-0.33) =3092.640 | 0.029258 | -48484.554 |
| NH3 | - | 0.043015 | - | 1015.494 | 0.04196 | 1015.494((0.04196(-33-490) +(0.071938(-33+40)) = -21773. 728 |
| Total | 147910.8608 | -158732. 865 |
NH3 condenses at T = -33°C
Latent heat of ammonia = 23.5 KJ/mol
Latent heat removed =- 23.5(1015.494) = -23864.109 KJ/min
Q = latent heat + ∆H(r) + Hreactants + Hproducts
Q = -23864. 109 - 108185.6533 +147910.8608 -158732.865 = -142871. 766 KJ/min
Q= -2381. 196 KW
Please upvote if helpful
Related Solutions
111 m3/min of hydrogen measured at normal conditions and nitrogen at a 300% excess enter an...
141m3 / min of hydrogen measured at normal conditions and nitrogen in 300% excess enter an...
3) A vortex tube receives 0.3 m3/min of air at 600 kPa and 300 K. The...
Nitrogen gas is contained in a rigid 1-m3 tank, initially at 5 bar, 300 K. Heat...
Design a fluidized bed gasifier with a required syngas output of 2.5 m3/min (standard conditions) using...
A single stage double acting air compressor delivers 15 m3/min. measured at 1.013 bar and temperature...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Amanda K answered 2 months ago
Amanda K answered 2 months ago