Question
In: Economics
1. Suppose the government cuts transfer payments in an economy with an inflationary gap. How would...
Solutions
Expert Solution
1) An inflationary gap suggests that actual output is more than the full employment level of output. A cut in govt. transfer payments mean that govt expenditure is reduced, so IS curve shifts to the left, which means that AD curve will shift to the left(AD-AD'). A fall in government expenditure reduces the interest rate(IS-IS'). A fall in aggregate demand also lowers the price level. Since there is an inverse relationship between interest rate and bond price, a fall in interest rate increases the bond price.
Fall in interest rate increases the investment. But an overall reduction in aggregate output and price level can also affect decision of the firm to invest.
A fall in interest rate leads to capital outflows from a country, which depreciates the currency. So, exchange rate rises. A depreciated exchange rate, along with lower price levels make our exports cheaper, so net exports rises.
Since there is an inflationary gap, the real GDP will fall until it reaches the full employment level, as shown in the graph below:
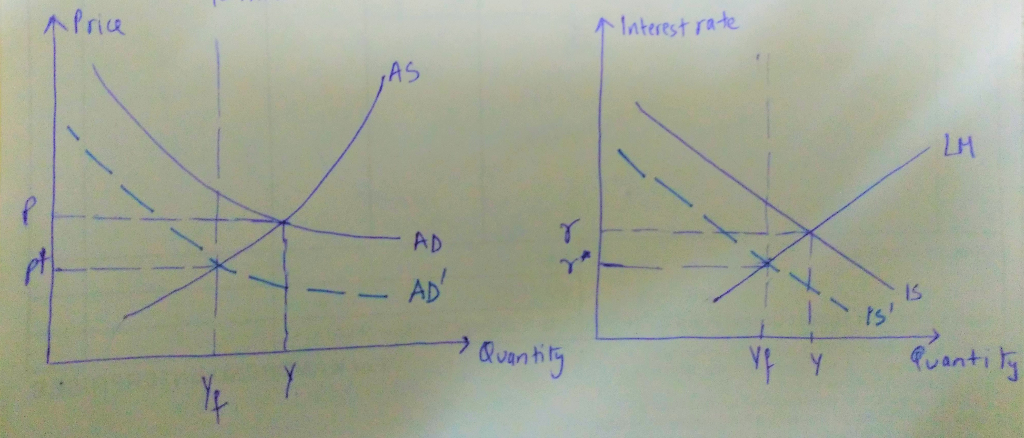
The left graph is Price-output graph and on the right is the IS-LM graph. Yf represent full employment level of output. P* and r* are full employment levels of price level and interest rate respectively. After reduction in govt transfer payments, output eventually returns to full employment level.
2) To reduce implementation lag, access to real-time high quality data should be available to the policymakers. After it is done with policy-making, the executives of the government, i.e. those who will implement it, should be brought on the same page as soon as possible to reduce implementation lag. All the officials need to move in tandem. Also, any uncertainty regarding a policy should be addressed, so that economic players do not delay their actions.
3) Such programs represent government transfer payments. Yes, they do work as automatic stabilizers because for every $1 addition, govt is reducing $1, so that the economy is in balance and there is no further overheating of the economy.
4) Lets assume that oil prices increase. In that case, overall price level will shoot up. On the other hand, since cost of production has increased, many firms might cut down on production, which will lead to unemployment. This is the situation of stagflation, where economy is stagnant and there is persistent inflation. Conversely, a fall in oil prices will lead to overall price decrease as well as an expansion in output, thus reducing unemployment
Related Solutions
1. Suppose the government cuts transfer payments in an economy with an inflationary gap. How would...
Question 3: Monetary Policy Suppose the economy is in an inflationary gap, and the Fed responds...
how fiscal policy such as changing government expenditure may close recessionary gap/ inflationary gap.
Is a recessionary or inflationary gap bad for an economy? Have you ever wondered how the...
Is a recessionary or inflationary gap bad for an economy? Have you ever wondered how the...
6. The economy is in an inflationary gap. a) Describe the appropriate monetary policy and the...
Question 1: Fiscal Policy Suppose the economy is in a recessionary gap, and the government reponds...
1.On a fully labelled AD/AS diagram, which shows that the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap,...
Explain the following two cases of self- regulating economy: Inflationary gap and recessionary gap . Discuss...
How did market self correct inflationary gap and recessionary gap?
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
 Rahul Sunny answered 3 months ago
Rahul Sunny answered 3 months ago