Question
In: Computer Science
Create a program in C that performs the following tasks: Define a macro arraySize of size...
Create a program in C that performs the following tasks:
- Define a macro arraySize of size n
- Create two arrays of size n.
- Pass these arrays to a function fillArrays that randomizes enough integers between 1-100 (inclusive) to fill both arrays.
- Print both of these arrays.
- Pass the filled arrays to a second function mergeArrays that creates a third array of size 2n.
- Still in mergeArrays, store the values from the original two arrays into your new array in reverse.
- Print out your sorted array.
Solutions
Expert Solution
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE 10
void mergeArrays( int *var1, int *var2)
{
int n1= 2*ARRAY_SIZE; //To double the size of new array
int arrnew[n1];
int x1 = ARRAY_SIZE; //To process 2nd array from newarray's index n, bcz there are already n elements.
int index = 0;
for(int i = ARRAY_SIZE-1 ; i>=0 ;--i){
arrnew[index++] = var2[i];
}
for(int i = ARRAY_SIZE-1 ; i>=0 ;--i){
arrnew[index++] = var1[i];
}
//To sort an array
for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n1; ++j)
{
if (arrnew[i] > arrnew[j])
{
int tempval = arrnew[i];
arrnew[i] = arrnew[j];
arrnew[j] = tempval;
}
}
}
//To print new sorted array
printf("\nValues in new sorted array are:");
for(int x=0; x<n1; x++)
{
printf("%d ", arrnew[x]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
}
void fillArray(int arr[]){
for (int i=0;i<ARRAY_SIZE;i++){
//To generate random number within 100
int randno =rand() % 100 + 1; //Includes 1 and 100
arr[i]=randno;
}
}
int main()
{
//Variable declarations
int arr1[ARRAY_SIZE]; //array1
int arr2[ARRAY_SIZE]; //array2
int min,max,randno; //To generate random number
//The srand() function sets its argument as the seed for a new sequence of pseudo-random integers to be returned by rand()
srand (time(NULL) );
fillArray(arr1);
//Fill array with random number
printf("Values in array1 are:");
for(int x=0; x<ARRAY_SIZE; x++)
{
printf("%d ",arr1[x]) ;
}
printf("\n");
fillArray(arr2);
//Fill array with random number
printf("Values in array2 are:");
for(int x=0; x<ARRAY_SIZE; x++)
{
printf("%d ",arr2[x]) ;
}
printf("\n");
//Call merge array fuction to merge and sort array
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2);
return 0;
}
======================================
SEE OUTPUT
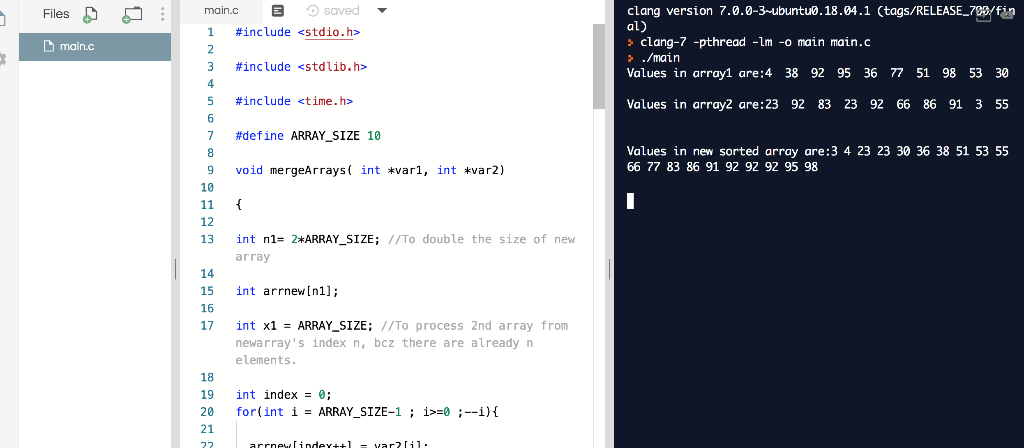
Thanks, PLEASE COMMENT if there is any concern. Please UPVOTE
Related Solutions
You should write a small C++ program that performs the following tasks: First, your program should...
Create a C program that performs the following (please comment the codes): a) Create a Stack...
Create a C++ integer linked list program that performs the following methods below: Please create these...
Write a program that performs the following two tasks in java Reads an arithmetic expression in...
Modify the GreenvilleRevenue program so that it uses the Contestant class and performs the following tasks:...
Write a program that performs the following two tasks: Reads an arithmetic expression in an infix...
Consider the following program: 1 #define Size 64 int A[Size; Size], B[Size; Size], C[Size; Size]; int...
In Java: Problem 1. Write a program that performs the following two tasks: 1. Reads an...
Create a C++ program based on the following criteria: Define an integer for the user selection...
Write a C++ code for these 2 questions 1. Create an integer variable named ‘arraySize’ and...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 venereology answered 3 months ago
venereology answered 3 months ago