Question
In: Math
Q3. Hypothesis: Informing people about recycling causes them to recycle more. Study design: 50 households were...
Q3. Hypothesis: Informing people about recycling causes them to recycle more.
Study design: 50 households were randomly assigned to a treatment group where they were
informed by letter about proper recycling habits and its benefit on environment, while 50
different households were randomly assigned to a control group that did not receive such a letter.
After 3 months, the weekly average recycling amount in the treatment group was 12.4 lbs (
sd
=
2.5), while the weekly average recycling amount in the control group was 3.7 lbs (
sd
= 1.1)
d. Determine the appropriate test: z-test or t-test. Explain why you chose that test.
e. Calculate the appropriate test statistic
f. Decide whether you should reject the null hypothesis.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Q3. Hypothesis: Informing people about recycling causes them to recycle more.
Study design: 50 households were randomly assigned to a treatment group where they were
informed by letter about proper recycling habits and its benefit on environment, while 50
different households were randomly assigned to a control group that did not receive such a letter.
After 3 months, the weekly average recycling amount in the treatment group was 12.4 lbs (sd=2.5), while the weekly average recycling amount in the control group was 3.7 lbs (sd= 1.1)
d. Determine the appropriate test: z-test or t-test. Explain why you chose that test.
T test is used because population standard deviation is not known.
Two sample t test
Ho: µ1 = µ2 H1: µ1 > µ2
Upper tail t test
e. Calculate the appropriate test statistic
t=22.5234
f. Decide whether you should reject the null hypothesis.
DF = n1+n2-2 =98
Table value of t with 98 DF at 0.05 level = 1.6606
Rejection Region: Reject Ho if or t > 1.6606
Calculated t = 22.5234 falls in the rejection region
The null hypothesis is rejected.
We conclude that informing people about recycling causes them to recycle more.
|
Pooled-Variance t Test for the Difference Between Two Means |
|
|
(assumes equal population variances) |
|
|
Data |
|
|
Hypothesized Difference |
0 |
|
Level of Significance |
0.05 |
|
Population 1 Sample |
|
|
Sample Size |
50 |
|
Sample Mean |
12.4 |
|
Sample Standard Deviation |
2.5 |
|
Population 2 Sample |
|
|
Sample Size |
50 |
|
Sample Mean |
3.7 |
|
Sample Standard Deviation |
1.1 |
|
Intermediate Calculations |
|
|
Population 1 Sample Degrees of Freedom |
49 |
|
Population 2 Sample Degrees of Freedom |
49 |
|
Total Degrees of Freedom |
98 |
|
Pooled Variance |
3.7300 |
|
Standard Error |
0.3863 |
|
Difference in Sample Means |
8.7000 |
|
t Test Statistic |
22.5234 |
|
Upper-Tail Test |
|
|
Upper Critical Value |
1.6606 |
|
p-Value |
0.0000 |
|
Reject the null hypothesis |
|
Related Solutions
A study of 50 people who were not on a diet showed that they consumed an...
In a study, people were observed for about 10 seconds in public places, such as...
Hypothesis: Anti-smoking television PSAs reduces cigarette smoking. Study design: 500 Individuals were randomly assigned to watch...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
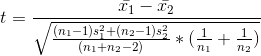
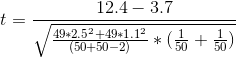
 milcah answered 4 months ago
milcah answered 4 months ago