Question
In: Physics
The wavelength of the four Balmer series lines for hydrogen are found to be 410.1, 434.3,...
The wavelength of the four Balmer series lines for hydrogen are found to be 410.1, 434.3, 486.6, and 655.9 nm. What average percentage difference is found between these wavelength numbers and those predicted?
Solutions
Related Solutions
The wavelength of the four Balmer series lines for hydrogen are found to be 410.1, 434.3,...
The wavelength of the four Balmer series lines for hydrogen are
found to be 410.1, 434.3, 486.6, and 655.9 nm. What average
percentage difference is found between these wavelength numbers and
those predicted by 1 λ = R 1 nf2 − 1 ni2 ? It is amazing how well a
simple formula (disconnected originally from theory) could
duplicate this phenomenon.
The only visible spectral lines of hydrogen are the four Balmer series lines (transitions to n=2)....
The only visible spectral lines of hydrogen are the four Balmer
series lines (transitions to n=2). We wish to cause hydrogen gas to
glow with all its characteristic visible colors.
a) To how high an energy level must the electrons be
excited?
b) Energy is absorbed in collisions with other particles. Assume
that after absorbing energy in one collision, an electron jumps
down through lower levels so rapidly so that it is in the ground
state before the collision occurs....
D. The Balmer Series 1. When Balmer found his famous series for hydrogen in 1886, he...
D. The Balmer Series 1. When Balmer found his famous series for
hydrogen in 1886, he was limited experimentally to wavelengths in
the visible and near ultraviolet regions from 250 nm to 700 nm, so
all the lines in his series lie in that region. a) Based on the
entries in Table 2 and the transitions on your energy level
diagram, what common characteristic do the lines in the Balmer
series have? B) What would be the longest possible wavelength...
Explore the Balmer series of atomic transitions for a hydrogen atom. Assume the shortest wavelength possible...
Explore the Balmer series of atomic transitions for a
hydrogen atom. Assume the shortest wavelength possible occurs when
the atom is ionized or when n = ∞ . What is the longest and
shortest wavelengths possible?
What is the frequency, wavelength and energy of the longest
wavelength?
longest λ = ___________ nm
frequency = _________ Hz
energy = _________ eV
Shortest λ = ___________ nm
(a) Find the photon energy and wavelength for the series limit (shortest wavelength) in the Balmer...
(a) Find the photon energy and wavelength for the series limit
(shortest wavelength) in the Balmer series (nf
= 2) for the hydrogen atom.
___________eV
_________ nm
(b) Calculate the wavelength for the three longest wavelengths in
this series.
longest
____________nm
second longest
____________nm
third longest
____________nm
1. The lines observed in H-lamp are parts of Balmer Series. All these lines are due...
1. The lines observed in H-lamp are parts of Balmer Series. All
these lines are due to a transition from various higher n value to
a common n. What is this common lower n value for all these
lines?
0
1
2
3
2. The lines on Absorption Atomic Spectra correspond to energies
needed for electrons to be excited from a lower energy level to a
higher energy level. Assume that the energy needed for an electron
in 2p orbital...
Question 1 The lines observed in H-lamp are parts of Balmer Series. All these lines are...
Question 1
The lines observed in H-lamp are parts of Balmer Series. All
these lines are due to a transition from various higher n value to
a common n. What is this common lower n value for all these
lines?
0
1
2
3
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 2
The bright violet line of Hg lamp has a wavelength of 435.8 nm.
What is the energy of the photon associated with this emission
line?
4.56*10^-19 J
4.56*10^-28 J
6.88*10^14 J
2.89*10^-31 J...
1-The lines observed in H-lamp are parts of Balmer Series. All these lines are due to...
1-The lines observed in H-lamp are parts of Balmer Series. All
these lines are due to a transition from various higher n value to
a common n. What is this common lower n value for all these
lines?
a-0
b-1
c-2
d-3
Flag this Question
Question 2
The bright violet line of Hg lamp has a wavelength of 435.8 nm.
What is the energy of the photon associated with this emission
line?
a-4.56*10^-19 J
b-4.56*10^-28 J
c-6.88*10^14 J
d-2.89*10^-31 J...
The Balmer series for the hydrogen atom corresponds to electronic transitions that terminate in the state...
The Balmer series for the hydrogen atom corresponds to electronic transitions that terminate in the state with quantum number n = 2 as shown in the figure below. Consider the photon of longest wavelength corresponding to a transition shown in the figure. (a) Determine its energy (b) Determine its wavelength Consider the spectral line of shortest wavelength corresponding to a transition shown in the figure (c) Find its photon energy (d) Find its wavelength (e) What is the shortest possible wavelength in the Balmer series?
4. The Balmer Series The Balmer series is limited to wavelengths in the visible regions from...
4. The Balmer Series
The Balmer series is limited to
wavelengths in the visible regions from 250 nm to 700 nm. On the
basis of your entries in the above table and the transitions on
your energy level diagram what common characteristic do the lines
in the Balmer series have?
What would be the shortest and
longest possible wavelengths for a line in the Balmer
series?
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- C PROGRAMMIMG I want to check if my 2 input is a number or not all...
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
ADVERTISEMENT

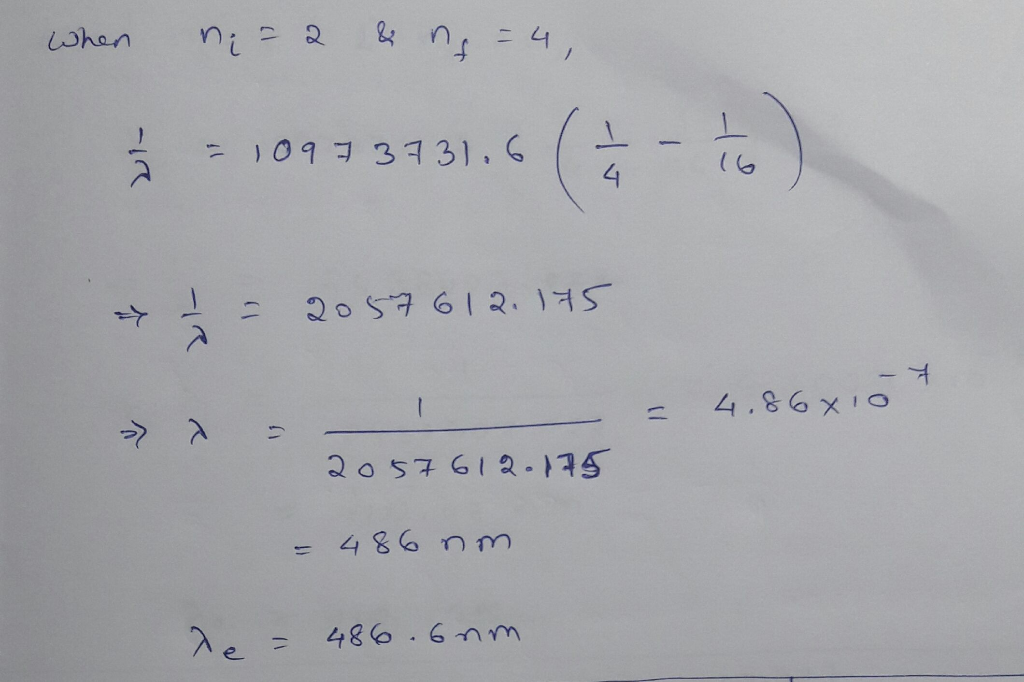
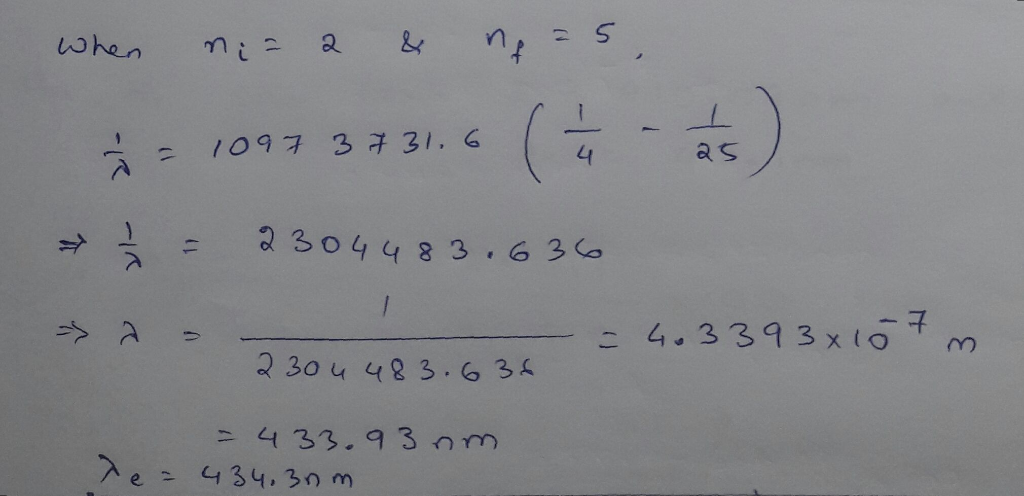
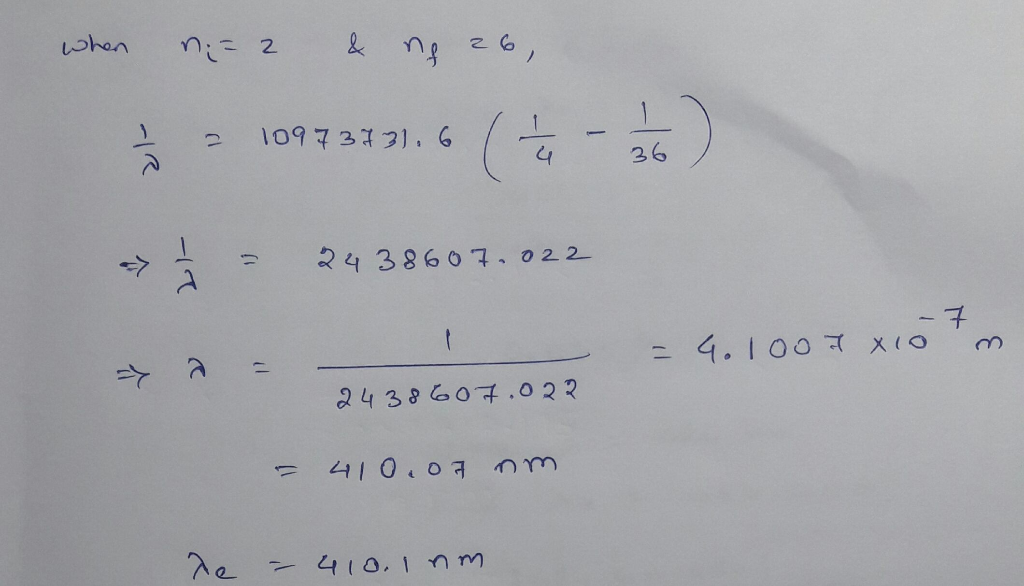
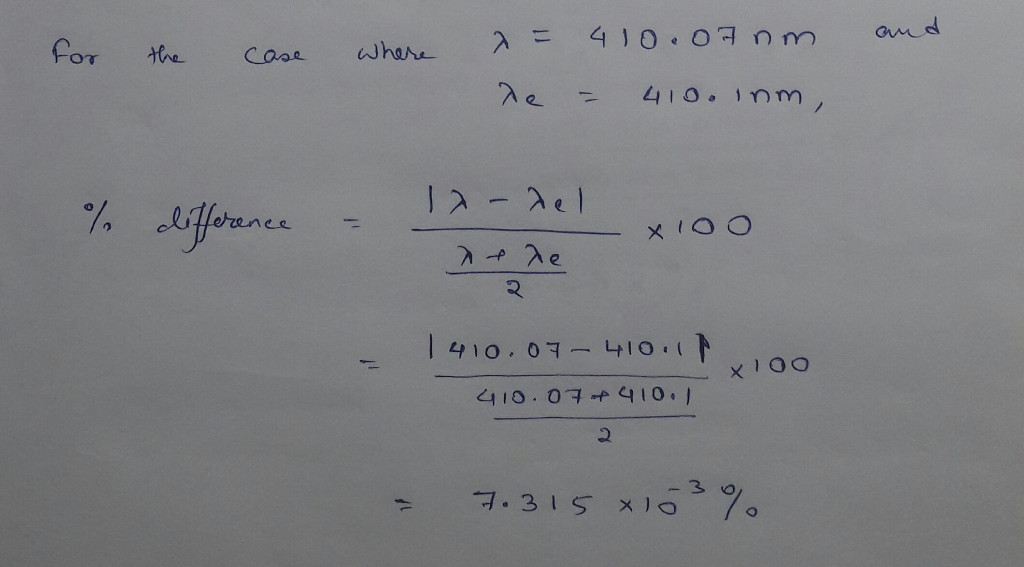

 genius_generous answered 4 months ago
genius_generous answered 4 months ago