Question
In: Computer Science
The hexademical number system uses base 16 with digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,...
The hexademical number system uses base 16 with digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F. Hexadecimal is often used in computer systems programming. Write a Python program, in a file called convertHex.py, to request a decimal number from the user and output the hexadecimal value. To compute the hexadecimal value we have to find the hexadecimal digits hn, hn-1, hn-2, ..., h2, h1, and h0, such that
d = hn x 16n + hn-1 x 16n-1 + hn-2 x 16n-2 + ... + h2 x 162 + h1 x 161 + h0 x 160
These hexadecimal digits can be found by successively dividing d by 16 until the quotient is 0; the remainders are h0, h1, ..., hn-1, hn.
For example, if d=589:
- 589/16 is 36 with a remainder of 13 - 13 in hexadecimal is 'D' - this is h0
- 36/16 is 2 with a remainder of 4 - 4 in hexadecimal is '4' - this is h1
- 2/16 is 0 with a remainder of 2 - 2 in hexadecimal is '2' - this is h2
So 589 in decimal is 24D in hexadecimal.
Your program should include the following functions:
- decToHex(dec_value) - returns the hexadecimal equivalent of dec_value (as a string)
- getHexChar(dec_digit) - returns the hexadecimal digit for dec_digit (note that 10 in decimal is 'A' in hex, 11 in decimal is 'B', etc)
Sample output:
Enter decimal value: 589 589 is equal to 24D in hexadecimal
Solutions
Expert Solution
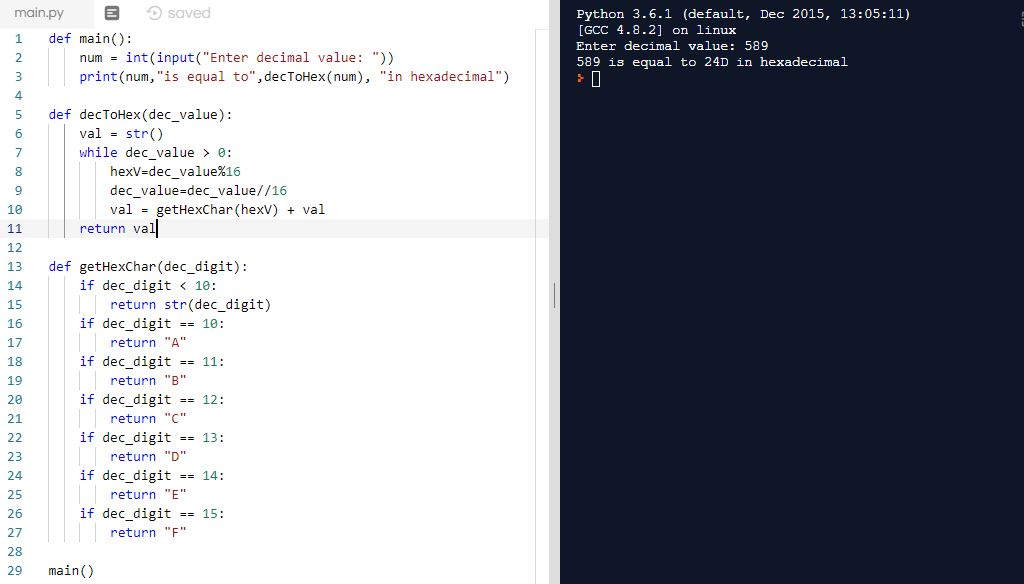
Below is your code: -
def main():
num = int(input("Enter decimal value: "))
print(num,"is equal to",decToHex(num), "in hexadecimal")
def decToHex(dec_value):
val = str()
while dec_value > 0:
hexV=dec_value%16
dec_value=dec_value//16
val = getHexChar(hexV) + val
return val
def getHexChar(dec_digit):
if dec_digit < 10:
return str(dec_digit)
if dec_digit == 10:
return "A"
if dec_digit == 11:
return "B"
if dec_digit == 12:
return "C"
if dec_digit == 13:
return "D"
if dec_digit == 14:
return "E"
if dec_digit == 15:
return "F"
main()
Output
Related Solutions
Recall that hexadecimal numbers are constructed using the 16 digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,...
Hexadecimal digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C,...
exampleInput.txt 1 2 3 0 2 3 4 0 1 3 5 0 1 2 6...
x (Bins) frequency 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 2 4 5 5 8 6...
The binary number system uses just two digits (0 and 1) to represent any counting number....
6 5 4 5 0 0 13 48 6 1 0 7 2 0 1 1...
ID X Y 1 2 3 2 3 6 3 4 6 4 5 7 5...
[4 5 5 2 4 4 6 3 3 7 5 3 6 3 4 4...
[4 5 5 2 4 4 6 3 3 7 5 3 6 3 4 4...
How many 3-digit numbers can we make using the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
 venereology answered 4 months ago
venereology answered 4 months ago