Question
In: Chemistry
This flowsheet is from the MIT OpenCourseware website, “Separation Processes for Biochemical Products”, taught in 2005.
This flowsheet is from the MIT OpenCourseware website, “Separation Processes for Biochemical Products”, taught in 2005. It shows the downstream steps for recovery of alkaline protease, a biological enzyme. You can view these interesting lecture notes at http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/chemical-engineering/10-445-separationprocesses- for-biochemical-products-summer-2005/lecture-notes/lecture_10.pdf after the midterm (they tie in nicely with 4N4 also).
1. What is the general purpose of flocculation?
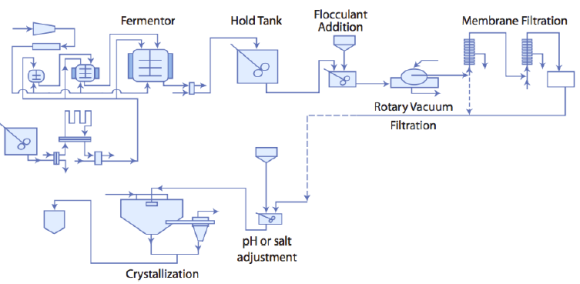
2. What is the purpose of flocculation in this flowsheet?
3. What is the purpose of the membrane step here?
4. Why are these membrane units in series?
5. Is it the retentate or permeate that is of interest?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Solution
1. Flocculation is a chemical treatment of the feed to cause particle agglomeration; these larger size particles settle faster, allowing the feed to be easily dewatered and concentrated
2. Flocculation here likely has the same purpose: to bring the biological suspension together, form flocs, and aid the subsequent filtration step. Larger particles have more open spaces, so there is a potential reduction of energy requirements in the filtration step. Large particles will also be more likely to be retained from passing through the subsequent membrane step’s pores. It also leads to a reduced volume of material to treat in the membrane.
3. To increase the enzyme concentration and reduce the volume of solvent (broth) in the downstream crystallization step. It will also remove particles not trapped by flocculation.
4. The individual membrane module is not able to achieve the desired concentration; the second module accepts the retentate from the first module and increases its concentration further.
5. The enzymes will be in the retentate. The permeate may have some value, but this is not subsequently processed in the given flowsheet.
Related Solutions
separation processes for bioproducts from E. coli . Recombinant protein production from E. coli resulted in...
Why is mass transfer a major factor in separation processes?
Describe three different separation processes and identify the physical/chemical/biological principle on which the separation is based.
In the study of biochemical processes, a common buffering agent is the weak base trishydroxymethylaminomethane, (HOCH2)3CNH2,...
In the study of biochemical processes, a common buffering agent is the weak base trishydroxymethylaminomethane, (HOCH2)3CNH2,...
In the study of biochemical processes, a common buffering agent is the weak base trishydroxymethylaminomethane, (HOCH2)3CNH2,...
The main energy-coupling compound in biochemical reactions that allows thermodynamically unfavorable processes to become favorable is...
Briefly describe two biochemical transformations that occur in biological unit processes to remove colloidal or dissolved...
Tris, (HOCH2)3CNH2 (pKb = 5.91), a very common buffer for studying biochemical processes, is prepared by...
Visit a retailer’s website and choose two related and comparable products from two different competitors.
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
 SUN BUNRA answered 3 years ago
SUN BUNRA answered 3 years ago