Question
In: Statistics and Probability
Describe the relationship between the width of a confidence interval and the size of the sample....
Describe the relationship between the width of a confidence interval and the size of the sample. Also describe the relationship between the width of the confidence interval and the degree of confidence. If a study yields an unsatisfactorily large confidence interval, what should be done? What prevents a researcher from continually increasing the sample size until a very small confidence interval is achieved?
Solutions
Expert Solution
The relationship between the width of a confidence interval and the sample size:
- As we increase the sample size, the width of the interval gradually decreases.
- Mathematically.

=====================================================================
The relationship between the width of the confidence interval and the degree of confidence:
- As the width of interval becomes larger, the degree of confdence also increases.
- Mathematically,

NOTE: Degree of confidence is the probability that the interval will capture the true parameter.
=====================================================================
If a study yields an unsatisfactorily large confidence interval,
- We should increase the sample size. that help in gaining more information so that confidence interval become smaller.
- We can decrease the level of significance
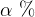 which is the probability of rejection of hypothesis when it is
true.
which is the probability of rejection of hypothesis when it is
true.
=====================================================================
The restrictions a researcher from continually increasing the sample size until a very small confidence interval is achieved are:
- Increasing the sample size increases the cost in collection, man power and at the same time increases the time taken.
- The resources from which the samples are being collected are one of the major restrictions.
- Increasing the sample size also leads to the chances of error that is a Type 2 error which is the probability of acceptance of hypothesis when it is actually false.
======================================================================
Related Solutions
As the sample size INCREASES for computing a confidence interval, the width of the confidence interval...
The width of a confidence interval will be: A) Wider when the sample standard deviation is...
Determine confidence intervals for each of the following: Sample Statistic Sample Size Confidence Level Confidence Interval...
Find the critical value corresponding to a sample size of 9 and a confidence interval of...
2. What is the sample size, n, for a 95% confidence interval on the mean, if...
For a random sample sample of size 22, one has calculated the 98% confidence interval for...
Difference between Means, Sample size selection. Explain Confidence Interval for a Mean, Total, Proportion, Standard Deviation....
Use the applet "Sample Size and Interval Width when Estimating Proportions" to answer the following questions....
The 95% confidence interval for the mean, calculated from a sample of size n = 25...
13) What is the minimal sample size needed for a 95% confidence interval to have a...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
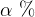 which is the probability of rejection of hypothesis when it is
true.
which is the probability of rejection of hypothesis when it is
true. orchestra answered 3 years ago
orchestra answered 3 years ago