Question
In: Advanced Math
Q1. The normal distribution is a bell-shaped curve defined by: y=e^(〖-x〗^2 ) Use the golden-section search...
Q1. The normal distribution is a bell-shaped curve defined by: y=e^(〖-x〗^2 ) Use the golden-section search to determine the location of the inflection point of this curve for positive x.
PLEASE do the iterations on excel and show the written text in the cells. Thank you!
Solutions
Expert Solution
An inflection point can be found by finding a minimum of the first derivative of a function. This point is where the first derivative, that is the slope, equals zero. So it is the point where the function changes from being positive to negative or vice versa. The golden section search method uses the fact that if we evaluate the function at two points relatively far apart, and then at two points in between these two, we can narrow our search range by determining which of the inner points is closest to the actual value where the derivative will be equal to 0. The search uses the principle that the golden ratio can help to determine the solution more quickly by determining good guesses for the two interior points.
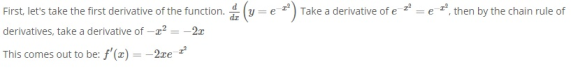
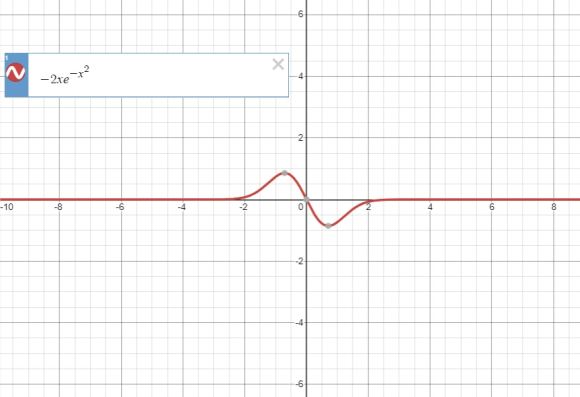
Now, we take a look at the derivative graphically so as to try to determine a beginning interval. The graph of the function obtained using Desmos.com is:


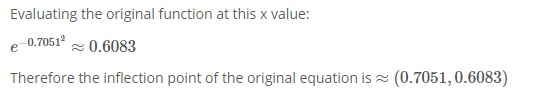
Related Solutions
1. Explain the Bell-shaped curve? 2. What is the difference between the Normal Distribution and the...
The normal distribution or bell-shaped curve from statistics provides an example of a continuous probability distribution...
Use the Internet to research the following distributions. Uniform Distribution Normal Distribution (Bell-Shaped Distribution) Skewed Distribution...
Use the golden Section search method to find the minimum of f(x)= x/5−sin(x) . Start with...
Assume that the height of male adults in some country have a normal (bell shaped) distribution...
A particular population, for which the frequency curve is bell-shaped (normal), has a mean of μ=100...
1. Use the guidelines of this section to sketch the curve. y = x(x − 4)^3...
The binormal distribution for (X, Y) is defined as the marginal distribution X ∼ N (1,4)...
Let X and Y be jointly normal random variables with parameters E(X) = E(Y ) =...
A curve c is defined by the parametric equations x= t^2 y= t^3-4t a) The curve...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Colby Messinger answered 1 year ago
Colby Messinger answered 1 year ago