Question
In: Biology
a) Discuss the operation of the heart lung machine, detailing the individual functionality with necessary diagram/s....
a) Discuss the operation of the heart lung machine, detailing the individual functionality with necessary diagram/s. [10 marks]
Solutions
Expert Solution
The " heart-lung machine " also known as cardiopulmonary bypass machine. It replaces the heart’s pumping action and add oxygen to the blood. The heart will be ready for the operation, which is necessary when the heart has to be opened. Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, and maintains the blood circulation and the oxygen content of the patient's body. CPB mechanically circulates and oxygenates blood for the body while bypassing the heart and lungs. It uses a heart–lung machine to maintain perfusion to other body organs and tissues while the surgeon works in a bloodless surgical field. The surgeon places a cannula in the right atrium, venacava, or vein to withdraw blood from the body. Venous blood is removed from the body by the cannula and then filtered, cooled or warmed, and oxygenated before it is returned to the body by a mechanical pump. The cannula used to return oxygenated blood is usually inserted in the ascending aorta, but it may be inserted in the femoral artery, axillary artery, or brachiocephalic artery.
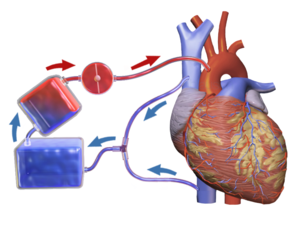
fig 1 shows the heart-lung machine which is connected to the veins and arteries near the heart. The three implements on the left represent (from top to bottom) the pump, the oxygenator, and the reservoir.
To function, the heart-lung machine must be connected to the patient in a way that allows blood to be removed, processed, and returned to the body. Therefore, it requires two hook-ups. One is to a large artery where fresh blood can be pumped back into the body. The other is to a major vein where "used" blood can be removed from the body and passed through the machine.
It consists of two main functional units, the pump and the oxygenator which removes relatively oxygen-depleted blood from a patient's body and replaces it with oxygen-rich blood through a series of tubes . A heat exchanger is used to control body temperature by heating or cooling the blood in the circuit. It is important that all components of the circuit are coated internally by heparin or another anticoagulant to prevent clotting within the circuit.
- Centrifugal pump : Many CPB circuits now employ a centrifugal pump for the maintenance and control of blood flow during CPB. By altering the speed of revolution (RPM) of the pump head, blood flow is produced by centrifugal force. This type of pumping action is considered to be superior to the action of the roller pump by many because it is thought to prevent overpressurization, clamping or kinking of lines, and produce less damage to blood products.
- Roller pump : The pump consists of several rotating motor-driven pumps that peristaltically "massage" tubing. This action gently propels the blood through the tubing. This is commonly referred to as a roller pump, or peristaltic pump. The pumps are more affordable than their centrifugal counterparts, but are susceptible to overpressurization if the lines become clamped or kinked. They are also more likely to cause a massive air embolism and require constant, close supervision by the perfusionist.
- Oxygenator : The oxygenator is used to add oxygen to infused blood and remove carbon dioxide from the venous blood. The main reasons for this are that membrane oxygenators tend to generate many fewer micro-bubbles, referred to as gaseous microemboli, which is generally considered harmful to the patient and reduce damage to blood cells, compared to bubble oxygenators. More recently, the use of hollow-fiber oxygenators has become more widespread. These derivatives of membrane oxygenators further reduce the occurrence of microemboli by reducing the direct air-blood interface while simultaneously providing adequate gas exchange.
Related Solutions
Discuss the physical, psychological and social impacts on daily livingactivities for the individual with Coronary Heart...
2. Discuss/explain congestive heart failure, asthma, emphysema, cystic fibrosis, lung cancer, and sudden infant death syndrome.
Provide two community and two in-hospital resources for the individual with Coronary Heart Disease (CHD). Discuss...
9. Discuss the mechanism(s) by which heart rate and strength of contraction are impacted by sympathetic...
One of the assumptions made by economists is that firms maximise profits. Using appropriate diagram/s, discuss...
Discuss how members of a military unit could openly bring themselves to kill some individual(s) and...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago