Question
In: Biology
If you cross two heterozygous fuzzy, white-spotted monsters where the gene for fuzziness (F) is dominant...
If you cross two heterozygous fuzzy, white-spotted monsters where the gene for fuzziness (F) is dominant to hairlessness (f) and white spots (R) are dominant to rainbow spots (r), what proportion of the offspring will be hairless and rainbow-spotted? What are the genotypes of the parents? What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring?
Solutions
Expert Solution
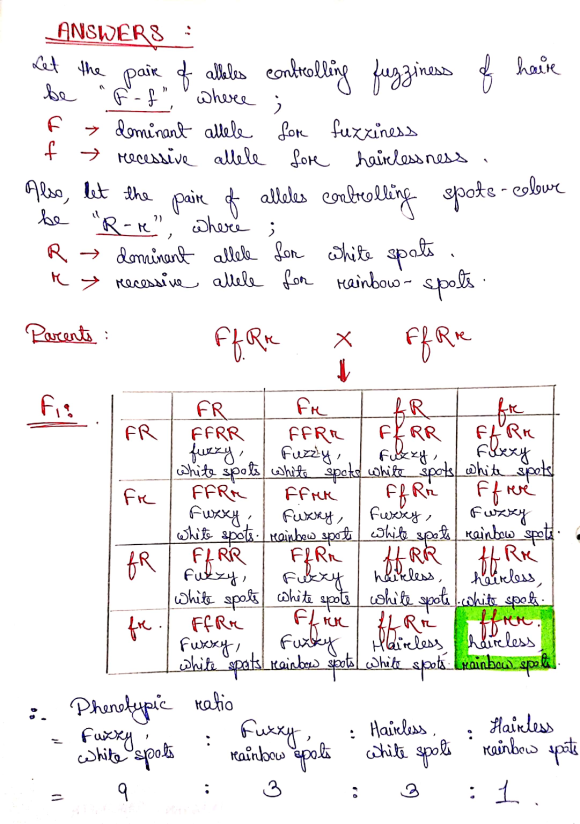
The genotypes of the parents and offsprings have been given in the cross mentioned above.
Hence, 1/16 proportion of the offsprings will be hairless and rainbow-spotted.
Related Solutions
In cocker spaniels, solid coat color is dominant over spotted coat color. If two heterozygous dogs...
In cocker spaniels, solid coat color is dominant over spotted
coat color. If two heterozygous dogs were crossed to each other,
what would be the probability of the following combinations of
offspring?
a. A litter of eight pups, two with solid fur
and six with spotted fur.
b. A first litter of six pups, four with solid
fur and two with spotted fur, and then a second litter of five
pups, all with solid fur.
c. A first litter of...
In dogs, solid coat color (S ) is dominant over white spotted coat (s ). In...
In dogs, solid coat color (S ) is dominant over white spotted
coat (s ). In a cross between two heterozygous dogs, what would be
the probability of having a first litter of six pups, the firstborn
with spotted fur, and then among the next five, three with solid
fur and two with spotted fur; and then a second litter of seven
pups in which the firstborn is spotted, the second born is solid,
and then the remaining five pups...
Huntington is a dominant disorder. A man is heterozygous for the Huntington gene (Hh). He marries...
Huntington is a dominant disorder. A man is heterozygous for the
Huntington gene (Hh). He marries a woman who is (Hh). Will the man
or woman develop the disease? What is the probability that their
first child will develop the disease? Draw a Punnet Square.
If green is dominant to white, what is the predicted phenotypic ratio of a cross between...
If green is dominant to white, what is the predicted phenotypic
ratio of a cross between 2 green heterozygotes?
Group of answer choices
all green
3 green:1 white
3 white: 1 green
2 green:2 white
A female mouse that is heterozygous for fur color where dark fur is dominant to light...
A female mouse that is heterozygous for fur color where dark fur
is dominant to light fur and homozygous dominant for long-tail
length is mated with a male that is heterozygous for both traits.
How many genotypes will be represented in the F1 generation?
A.
1/32
B.
1/16
C.
1/8
D.
1/4
E.
1/2
A homozygous polled Hereford bull (with dominant hornless gene (PP) , dominant white-face spotting pattern (WW)...
A homozygous polled
Hereford bull (with dominant hornless gene (PP) , dominant
white-face spotting pattern (WW) and recessive brown coat color
(bb) is crossed to an Angus female with horns (recessive, pp), no
spots (recessive, ww) and a dominant solid black coat color
(dominant, BB). All the F1 animals are polled (hornless), have a
solid black coat and a white-face spotting pattern. These three
loci are autosomal and independent from each other. The F1 animals
are crossed to F1 animals...
1.Define these Basic concepts: Cross-fertilization, self-cross test-cross Genotype/phenotype, dominant/recessive, homozygous/heterozygous/hemizygous Mendel’s laws of inheritance: equal segregation...
1.Define these Basic concepts:
Cross-fertilization,
self-cross
test-cross
Genotype/phenotype,
dominant/recessive,
homozygous/heterozygous/hemizygous
Mendel’s laws of inheritance: equal segregation and independent
assortment.
How Mendel’s experiments were different from others?
Chromosomal theory of inheritance (evidence to support it?) and
its relation to life cycle.
Autosome,
sex chromosome,
homologous
differential regions
hemizygote Penetrance,
expressivity,
lethality,
incomplete dominance
Genetic map,
crossing-over,
linkage analysis,
map unit,
recombinant frequency
What is the expected phenotypic ratio for a cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for...
What is the expected phenotypic ratio for a cross between two
individuals that are heterozygous for a given trait? Use one of
Mendel's pea plant traits as an example.
A child having two heterozygous parents with a dominant genetic disorder has with chance of inheriting...
A
child having two heterozygous parents with a dominant genetic
disorder has with chance of inheriting that disorder? Explain your
answer.
Response should be minimum 300 words
Consider the gene for the character “freckles”. We’ll use “F” to designate the dominant allele (which...
Consider the gene for the character “freckles”. We’ll use “F” to
designate the dominant allele (which produces freckles), and “f” to
designate the recessive allele (no freckles).
a.
Suppose one parent has freckles. What are the possible genotypes
for that parent? ____________________
b.
Suppose one parent has no freckles. What do we know about that
parent’s genotype? ___________________
c.
If the parent with freckles is homozygous (FF), what proportion of
offspring will have freckles?
A)
None of them
B)
25%...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
ADVERTISEMENT
 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago