Question
In: Statistics and Probability
A door-to-door salesman sells pots and pans. He only gets in 50 percent of the houses...
A door-to-door salesman sells pots and pans. He only gets in 50 percent of the houses that he visits. Of the houses that he enters, 1/6 of the householders are still not interested in purchasing anything, 1/2 of them end up placing a $60 order, and 1/3 of them end up placing a $100 order. Estimate the average sales receipts per house visit by simulating 25 house visits using a die. Calculate the theoretical value and compare it with the estimate obtained from your simulation.
Solutions
Expert Solution
We have 5 scenarios of the problem.
- He could not enter the house.
- He only gets in 50 percent of the houses that he visits.
- Of the houses that he enters, 1/6 of the householders are still not interested in purchasing anything.
- Of the houses that he enters, 1/2 of them end up placing a $60 order.
- Of the houses that he enters, 1/3 of them end up placing a $100 order.
For simulation with a die we can restate the above scenarios as follows-
- We cast one die. If the outcome of the die is odd, he can not enter the house.
- We cast first die. If the outcome of the die is even, he gets in the house. This has a probability of 0.5 or 50%.
- Now we cast a second die. If the outcome of the first die is
even and the second die is 1, he gets in the house but householders
are still not interested in purchasing anything. This has a
probability of
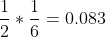 .
. - We are still checking the outcome of the second die. If the
outcome of the first die is even and the second die is also even,
he gets in the house and householders end up placing a $60 order.
This has a probability of
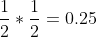 .
. - We are still checking the outcome of the second die. If the
outcome of the first die is even and the second die is also 3 or 5,
he gets in the house and householders end up placing a $100 order.
This has a probability of
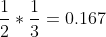 .
.
We create a simulation of 25 sample points for two dice.
| Simulation No. | First Die | Second Die | scenario | Order value |
| 1 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 60 |
| 2 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 60 |
| 5 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 100 |
| 6 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 100 |
| 8 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 60 |
| 9 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 100 |
| 10 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 60 |
| 12 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 13 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| 14 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| 15 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| 16 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 60 |
| 17 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 60 |
| 18 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 19 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 60 |
| 20 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 60 |
| 21 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 60 |
| 22 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 23 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 60 |
| 24 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 100 |
| 25 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 60 |
| Total | - | - | - | 1060 |
Note: Scenario 3,4,5 can only happen if scenario 2 occurs.
[
The simulation is done in R using the code as,
set.seed(123)
#set.seed keeps the takes the same sample from user to user
first_die <- sample(6,25,replace=T)
set.seed(321)
second_die <- sample(6,25,replace=T)
data.frame(first_die,second_die)
]
Now the Simulated estimate of average sales receipt per house
will be 
Simulated estimate of average sales receipt per house is $42.4.
Theoretical average Sales receipt per house will be

Theoretical average Sales receipt per house is $31.7.
So Simulated estimate of average sales receipt per house is higher than theoretical average sales receipt.
Please Upvote if the answer solves your problem.
Related Solutions
Teton Inc sells its only product for 50 per unit Teton, Inc. sells its only product for $50 pe
Someone gets more than 8 hours of sleep 50 percent of the time, less than 3...
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
 .
.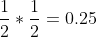 .
.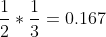 .
. orchestra answered 3 years ago
orchestra answered 3 years ago