Question
In: Physics
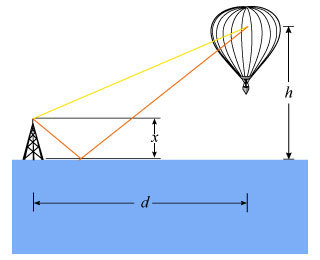
A radar tower sends out a signal of wavelength λ. It is x meters tall, and...
A radar tower sends out a signal of wavelength λ. It
is x meters tall,
and it stands on the edge of the ocean. A weather balloon is
released from a boat that is a distance d out to sea.
The balloon floats up to an altitude h.In this
problem, assume that the boat and balloon are so far away from the
radar tower that the small angle approximation holds.


a) Due to interference with reflections off the water,
certain wavelengths will be weak when they reach the balloon. What
is the maximum wavelength λ that
will interfere destructively?
b) What is the maximum wavelength λ that
will interfere constructively?
A radar tower sends out a signal of wavelength lambda. It is x meters tall, and it stands on the edge of the ocean. A weather balloon is released from a boat that is a distance d out to sea. The balloon floats up to an altitude h.In this problem, assume that the boat and balloon are so far away from the radar tower that the small angle approximation holds.
a) Due to interference with reflections off the water, certain wavelengths will be weak when they reach the balloon. What is the maximum wavelength lambda that will interfere destructively?
b) What is the maximum wavelength lambda that will interfere constructively?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The concepts used to solve this problem are constructive interference and destructive interference.
According to the principle of super position when several light waves coincide the result is equal to the sum of individual waves.
Use the condition for the destructive interference to find the value of maximum wavelength that will interfere destructively.
Then use the condition for the constructive interference to find the value of maximum wavelength that will interfere constructively.
Fundamentals
If two waves of same wavelength and phase travel different distances to reach the same point their interference will be two types.
Constructive, if difference in path length is integer number of wavelengths.
Destructive, if difference in path length is half integer number of wavelength.
Condition for constructive interference is,

Here,  is the separation distance between two slits,
is the separation distance between two slits,  is the angle from the midline to the spot on the balloon,
is the angle from the midline to the spot on the balloon,  is the integer, and
is the integer, and  is the wavelength.
is the wavelength.
Condition for destructive interference is,

(a)
Condition for destructive interference is,
 …… (1)
…… (1)
From the figure the value of  is,
is,

Here,  is the altitude of the balloon and
is the altitude of the balloon and  is the horizontal distance between tower and balloon.
is the horizontal distance between tower and balloon.
The value of  is much greater than
is much greater than  then the equation becomes,
then the equation becomes,

Substitute  for
for  ,
,  for
for  , and
, and  for
for  in equation (1).
in equation (1).

Here,  is the distance between the two rays.
is the distance between the two rays.
Therefore, the maximum wavelength that will interfere destructively is  .
.
(b)
Condition for constructive interference is,

Substitute  for
for  ,
,  for
for  , and
, and  for
for  in equation (1).
in equation (1).

Therefore, the maximum wavelength that will interfere constructively is  .
.
The maximum wavelength that will interfere destructively is  .
.
The maximum wavelength that will interfere constructively is  .
.
Related Solutions
X-rays of wavelength λ = 0.140 nm are scattered from carbon. A. What is the Compton...
X-rays of wavelength λ = 0.140 nm are scattered from carbon.
A. What is the Compton wavelength shift for photons detected at
angle (relative to the incident beam) of exactly 45.0 degrees?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the
appropriate units.
λ'- λ = ?
B. What is the Compton wavelength shift for photons detected at
angle (relative to the incident beam) of exactly 120 degrees?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the
appropriate...
1. An x-ray photon of initial wavelength (λ 0) = 0.097 nm is scattered off an...
1. An x-ray photon of initial wavelength (λ 0) = 0.097 nm is
scattered off an electron (initially at rest). If the photon is
backscattered (scattering angle = 180°), what is the resulting
wavelength of the scattered photon? Give your answer in nm, but
enter only the numerical part in the box.
2. An x-ray photon of initial wavelength (λ 0) = 0.093 nm is
scattered off an electron (initially at rest). If the photon is
backscattered (scattering angle =...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
ADVERTISEMENT
 genius_generous answered 3 years ago
genius_generous answered 3 years ago