Question
In: Anatomy and Physiology
Name:____________________________________________ Sleep and Sleep Disorders Practice Questions Questions 1 – 12: Choose the best answer. 1. Which...
Name:____________________________________________
Sleep and Sleep Disorders
Practice Questions
Questions 1 – 12: Choose the best answer.
1. Which is NOT one of the sleep theories discussed in class?
A. Humans need sleep in order to consolidate memories.
B. Humans need sleep in order to repair and restore systems that are worn out during waking hours.
C. One can predict the sleep pattern of a species from their diet.
D. One can predict the sleep pattern of a species from the bumps on their heads.
2. According to your lecture, what is the average number of hours of sleep that is needed to function optimally the next day?
A. 1-3
B. 4-6
C. 8-10
D. 12-14
3. Which theory of dreaming states that the cortex incorporates sensory information that the sleeper is exposed to during sleep into the dream?
A. activation synthesis hypothesis
B. clinico-anatomical hypothesis
C. evolutionary theory
D. melatonin hypothesis
4. Moderate sleep deprivation is associated with all of the following behavioral symptoms EXCEPT
A. irritability.
B. problems concentrating.
C. impaired judgement.
D. decreased immune system functioning.
5. Biological patterns of an organism that occur on a daily basis are called
A. circadian rhythms
B. circannual rhythms
C. zeitgebers
D. free-running rhythms
6. Which of the following structures exerts the main control over sleep and temperature rhythms?
A. melatonin
B. suprachiasmatic nucleus
C. pineal gland
D. retinohypothalamic path
7. During a normal night's sleep, the average person experiences ___ periods of REM sleep:
A. 1-2
B. 20-25
C. 5-6
D. 10-15
8. During this stage, the sleeper is starting to doze.
A. EEG sleep
B. Stage 1 sleep
C. REM sleep
D. Stage 4 sleep
9. During Stage 4 sleep, what is the sleeper experiencing?
A. REM sleep
B. very deep sleep
C. very light sleep
D. paradoxical sleep
10. What brain wave phenomena indicate that a person is in Stage 2 of their sleep cycle?
A. alpha waves and sleep spindles
B. sleep spindles and K-complexes
C. K-complexes and alpha waves
D. none of the above
11. Enzo is sleeping heavily and does not hear the alarm clock, causing him to miss an important job interview. It is likely that Enzo is in which stage of sleep?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 6
C. Stage 2
D. Stage 4
12. When are dreams most likely to occur?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. REM sleep
D. all the above
Questions 13 – 20: Match each sleep disorder with the correct definition/symptom.
Sleep DisorderDefinition/Symptom
____13. Sleep apneaA. Sudden shift from being awake to falling into REM sleep
____14. NarcolepsyB. Repeated involuntary movement of the legs and arms while sleeping
____15. Night terrorsC. Ambulating while dreaming
____16. InsomniaD. Cessation of breathing during sleep
____17. REM behavior disorderE. Speaking that typically occurs during deep sleep
____18. Sleep walkingF. Panic behavior during deep sleep
____19. Periodic limb movement disorderG. Ambulating during deep sleep
____20. Sleep talkingH. Inability to sleep
Solutions
Expert Solution
1. D. One can predict the sleep pattern of a species from the bumps on their heads.
2. C. 8-10
While sleep requirements vary slightly from person to person, most healthy adults need between 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night to function at their best. Children and teens need even more. And despite the notion that our sleep needs decrease with age, most older people still need at least 7 hours of sleep.
3. A. activation-synthesis hypothesis
According to activation-synthesis hypothesis dreams begin with spontaneous activity in pons and pons activates many parts of the cortex that synthesize story from the pattern of activation.
4. B. problems concentrating
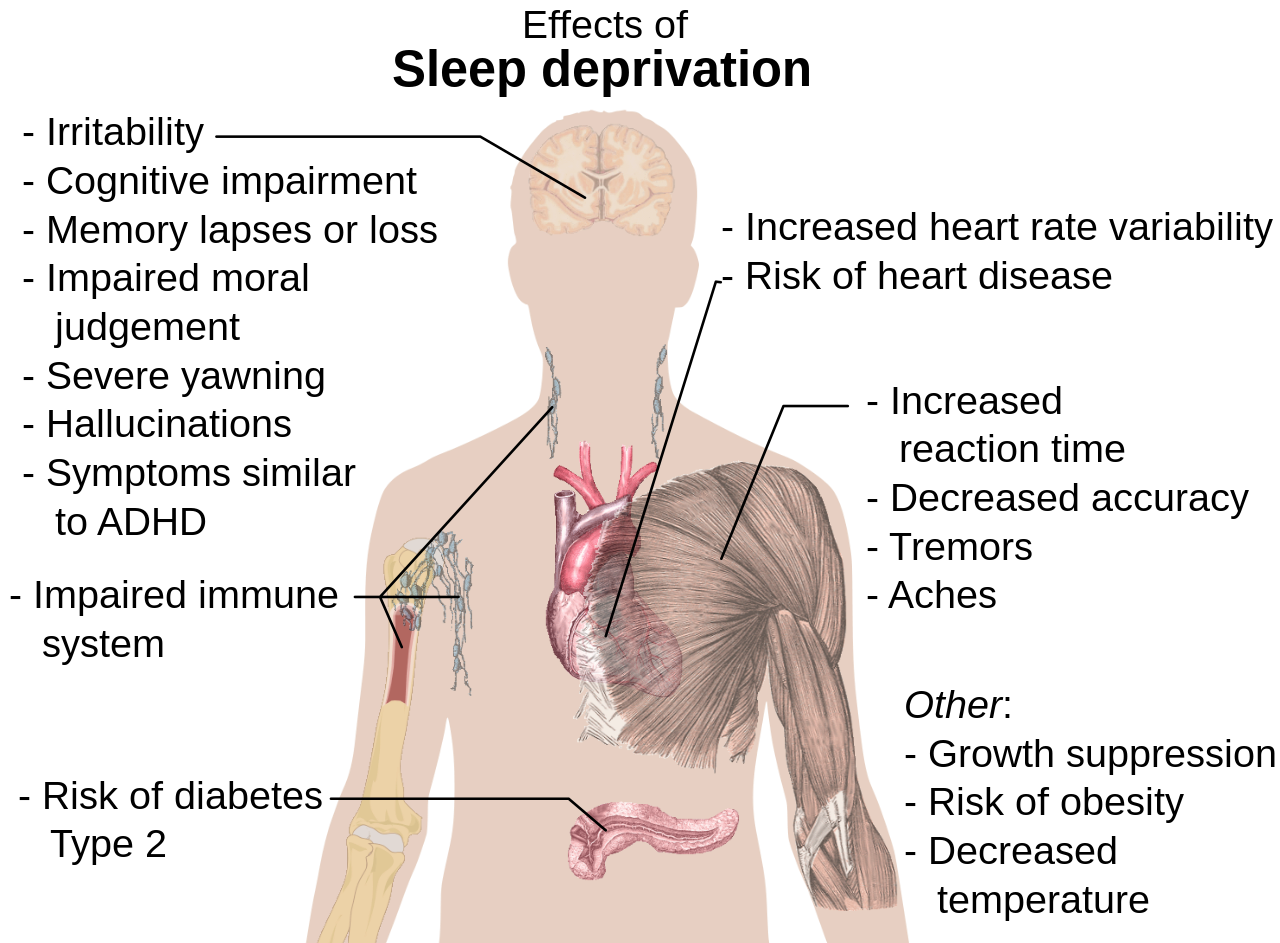
reference: picture from Wikipedia
All the four mentioned options are results of sleep deprivation,with irritability, impaired judgment, and decreased immune system to be the most important.
5. A. circadian rhythms
A circadian rhythm is any biological process in the body that repeats itself over a period of approximately 24 hours and maintains this rhythm in the absence of external stimuli.
6. B. suprachiasmatic nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus, is the principal circadian pacemaker in the mammalian brain. It generates circadian rhythms in rest and activity, core body temperature, neuroendocrine function, autonomic function, memory, and psychomotor performance, and is also a host of other behavioral and physiological processes.
7. A. 1-2
The sleep cycle of alternate NREM and REM sleep takes an average of 90 minutes, occurring 4–6 times in a good night's sleep (Sleeper goes to sleep stages 1, 2, 3, and 4, then returns through the stages 3 and 2 to a stage called REM. REM sleep occurs as a person returns to stage 2 or 1 from a deep sleep.).
8. B. Stage 1 sleep
Stage 1 sleep is when sleep has just begun. The is jagged with irregular, jagged, low voltage waves and brain activity begins to decline at this stage.
9. B. very deep sleep
Stage 4 is the deepest sleep stage. During deep sleep, your breathing, heartbeat, body temperature, and brain waves reach their lowest levels.
10. B. sleep spindles and K-complexes
Sleep spindles: 12 to 14 Hz waves during a burst that lasts for at least half a second.
k complex: a sharp high amplitude negative wave followed by a smaller slower positive wave.
11. D. Stage 4
Stages 3 and 4 are characterized as the NREM deep stages of sleep and are often the hardest to wake up from. Stages 3 and 4 are often grouped together because they are the periods of slow-wave sleep (SWS).
12. C. REM sleep
Dreams can be experienced in all stages of sleep but usually are most vivid in REM sleep. Most dreaming occurs during Stage Five, known as REM. REM sleep is characterized by eye movement, increased respiration rate, and increased brain activity.
|
13. Sleep apnea |
D. Cessation of breathing during sleep |
| 14. Narcolepsy | A. Sudden shift from being awake to falling into REM sleep |
| 15. Night terrors | F. Panic behavior during deep sleep |
| 16. Insomnia | H. Inability to sleep |
| 17. REM behavior disorder | C. Ambulating while dreaming |
| 18. Sleep walking | G. Ambulating during deep sleep |
| 19. Periodic limb movement disorder | B. Repeated involuntary movement of the legs and arms while sleeping |
| 20. Sleep talking | E. Speaking that typically occurs during deep sleep |
Related Solutions
Answer all the following questions: - I- Choose the best correct answer: 1- The ……………...
Question 1: Which is best practice? A. Contrasts of interest are determined by research questions and...
Choose the best answer Which of the following best explains what is the margin of error...
Choose the BEST answer for the following question. Which one is NOT an example of IT...
Name and explain two sleep disorders. List the five major categories of psychoactive drugs and give...
short answer on each questions. 1). which biome is found on the eastern USA? name and...
Name _____________________________________________________ Part 1: Practice- Choose the most likely category for each of the following situations....
Answer the following questions 1-10: 1# Which of the following transactions would best use the present...
choose the best answer and explain why. Which of the following statements below is consistent with...
Part II: Choose the best answer Which of the following is a fundamental product adjacent to...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
 Sydney Mullin answered 2 years ago
Sydney Mullin answered 2 years ago