Question
In: Physics
A planet has the same density as Earth but has a surface gravitational acceleration of nine...
Solutions
Expert Solution
Escape velocity is the minimum speed an object must possess to
escape the planet's gravitational field. We can easily calculate
the expression for escape velocity( you must have done it in
class). Let us say that the object is initially at a distance r
from the center of the planet. If the object is on the surface,
r=R, the planet's radius. So, it has potential energy  where M and m are masses of planet and object respectively. Let us
say it has velocity v initially. SO, the kinetic energy
is
where M and m are masses of planet and object respectively. Let us
say it has velocity v initially. SO, the kinetic energy
is  . Let us say it escapes the gravitational field eventually. SO
potential energy finally is 0.
. Let us say it escapes the gravitational field eventually. SO
potential energy finally is 0.  . Since we want to find the minimum initial velocity such that
this happens, let us set final velocity to 0. SO,
. Since we want to find the minimum initial velocity such that
this happens, let us set final velocity to 0. SO,  . By conservation of energy,
. By conservation of energy, 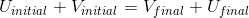 .
.
So,  and rearranging we get the escape velocity
and rearranging we get the escape velocity 
This makes use of the mass and radius of the planet which we don't know.
So, we can write  where rho is the density and
where rho is the density and  is the volume of the planet (considering it as a perfect
sphere)
is the volume of the planet (considering it as a perfect
sphere)
Also, gravitational accleration of a planet is given by
 which gives
which gives 
We have  . Replacing M,
. Replacing M,
 Substitute the expression for R
Substitute the expression for R

So, given that the densities of the two planets is same, the escape velocity depends directly depends on the gravitational acceleration. Since g of the planet is nine times that of earth, the escape velocity is 9 times earth's escape velocity, Since earth's escape velocity is 11,186m/s, the planet's escape velocity is 100,674m/s
The maximum distance that a moon could orbit a planet is called
the radius of its sphere of influence. Within this sphere, the
influence of the planet exceeds the influence of the star on the
moon. This radius is given by  where a is the orbital radius of the planet and M_s is the mass of
the star.
where a is the orbital radius of the planet and M_s is the mass of
the star.
We know that the mass of the planet is 
 Everything here is a constant except density and gravitational
acceleration and since density is the same as earth and density is
9 times, the mass of the planet is
Everything here is a constant except density and gravitational
acceleration and since density is the same as earth and density is
9 times, the mass of the planet is  times the mass of earth.
times the mass of earth.
We know that the mass of earth is  in terms of solar masses. SO, the mass of the given planet is
in terms of solar masses. SO, the mass of the given planet is

Therefore, the radius of influence is 

The moon could orbit at a maximum distance of 0.0863AU
Related Solutions
On planet Tehar, the free-fall acceleration is the same as that on Earth, but there is...
A planet has 8 times the mass of earth but has the same density. what is...
Another planet has the same spherical radius as Earth, but has 3 times Earth's density. (a)...
The average density of planet earth is 5.52 g/cm3. Knowing that Earth has a mass of...
You are touring a distant planet on which the magnitude of the gravitational acceleration is 65%...
what is the gravitational acceleration ON the surface of Mars, if its mass is 6.39∙1023 kg,...
3. Planet Z has diameter 1.8 × 107 m. On the planet's surface, the acceleration due...
1. On a planet where the gravitational acceleration is g=10 m/s², a solid cube of wood...
At what altitude above Earth’s surface would the gravitational acceleration be 4.9m/s2? Show all the steps...
Suppose our experimenter repeats his experiment on a planet more massive than Earth, where the acceleration...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 genius_generous answered 3 years ago
genius_generous answered 3 years ago