Question
In: Biology
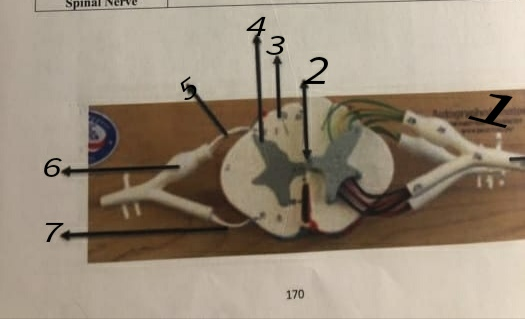
Activity 3: Identify the parts of the spinal cord in spinal cord cross section model:
Activity 3: Identify the parts of the spinal cord in spinal cord cross section model:
Spinal Cord Cross Section Parts Description / Function.
Grey Matter
White Matter
Central Canal
Dorsal Root
Dorsal Root Ganglia
Ventral Root
Spinal Nerve

Solutions
Expert Solution
|
Spinal Cord Cross Section Part |
Description | Function |
| Grey Matter |
Contains nerve cell bodies, dendrites and axonal terminals of neurons. Mostly unmyelinated. Butterfly shaped, central region of grey matter sorrounds central canal. |
The anterior grey column are responsible for movement of muscles. The posterior Grey column contain the points where sensory neurons synapse. |
| White Matter | Consists mostly of glial cells and myelinated axons. White because of the myelin that surrounds the nerve fibers. | It is the tissue through which messages pass between different areas of grey matter within the nervous system. |
| Central Canal | Central canal is a fluid-filled space in the spinal cord . | Has a protective function and allows for nutrient transport. |
| Dorsal Root | Emerges from the posterior part of the spinal cord. Lateral division of the dorsal root contains lightly myelinated and unmyelinated fibres of small diameter. |
Carry pain and temperature sensation, transmit information of discriminative touch, pressure, vibration. |
| Dorsal Root Ganglia | Lie in the intervertebral foramina. Have a cell body with two branches that act as a single axon. | Nerve endings of dorsal root ganglion neurons have a variety of sensory receptors for mechanical, thermal, chemical, and noxious stimuli. |
| Ventral Root | Is attached to the spinal cord by a series of rootlets that emerge from the ventrolateral sulcus of the spinal cord. | Contains outgoing, efferent fibers that carry information destined to control motor or glandular function. |
| Spinal Nerve | Formed from the combination of nerve fibers from its dorsal and ventral roots. |
The dorsal root is the afferent sensory root . Ventral root is the efferent motor root and carries motor. |
The parts of the spinal cord are as:
- Spinal nerve
- Central Canal
- White Matter
- Grey Matter
- Dorsal Nerve
- Dorsal Nerve Ganglia
- Ventral nerve
Related Solutions
parts of the spinal cord significance( function and importance) in the body
Q1-Briefly describe (in sentence form) the various parts of the spinal cord and summarize the functions...
makes myelin for neurons in the spinal cord
Motor signals leave the spinal cord through the __________ roots, while sensory signals enter the spinal cord through the __________ roots.
How does inflammation and the resulting edema from a spinal cord injury temporaily impair neuronal activity...
Differentiate the motor and sensory pathways of the spinal cord
The spinal cord achieves the function of locomotion through _______
Functions of the spinal cord include which of the following?
describe in detail the physiological functions of spinal cord
A typical spinal cord has how many pairs of spinal nerves, and it ends at the...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...

 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago