Question
In: Physics
(a) Which might describe a heat engine? (b) Which might describe a heat pump? (c) Which might describe a refrigerator? Explain.
(a) Which might describe a heat engine?
(b) Which might describe a heat pump?
(c) Which might describe a refrigerator? Explain.
The figure shows PV diagrams for five cyclical processes. (Cycle D is a simplified model of a steam engine cycle.)
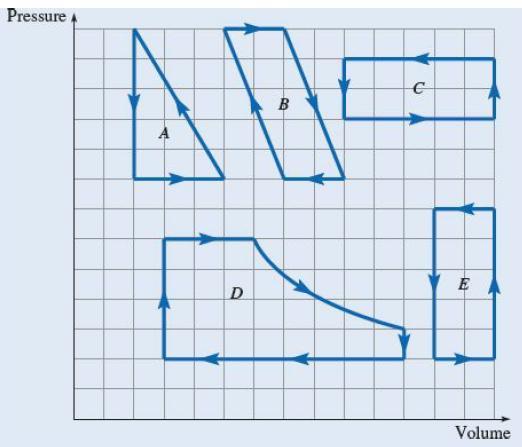
Solutions
Expert Solution
(a)
Heat engine converts heat into work and the cycle operates in the clockwise direction consisting of thermodynamic processes that are repeated in the same way. The processes B and D describe heat engine as the cycle in these processes move in clockwise direction.
(b)
Heat pumps pump heat from the colder outdoors into the warmer house. The energy transfer will be in a direction opposite to the heat engine. Therefore the processes A, C, and E describe heat pump as the cycle in these processes move in the counterclockwise direction.
(c)
Refrigerators pump the heat out of the food compartment into the warmer room. The work of refrigerator will be similar to the heat pump. Therefore the processes A, C, and E describe refrigerator as the cycle in these processes move in the counterclockwise direction.
Related Solutions
Professor Modyn wants to power his refrigerator with a heat engine. A Carnot heat engine receives...
A heat engine running backward is called a refrigerator if its purpose is to extract heat...
What is the difference between a refrigerator and a heat pump? What is the difference between...
A "Carnot" refrigerator (reverse of a Carnot engine) absorbs heat from the freezer compartment at a...
An insulated pump receives liquid engine oil (density ρ = 55 lbm/ft3 , specific heat c...
A heat pump is used to heat a house with an indoor temperature of 21 ◦C....
Explain the direct use of geothermal energy and a geothermal heat pump. Describe the types of...
A Carnot heat pump moves heat to a warm house at 24°C at a rate of...
Explain the thermodynamic principle of a geothermal heat pump.
3A. Draw a diagram of a heat engine and label (a) heat input, (b) heat output,...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
 Junaid answered 3 years ago
Junaid answered 3 years ago