Question
In: Physics
Streamlines represent the path of the flow of a fluid
Learning Goal: To understand the continuity equation.
Streamlines represent the path of the flow of a fluid. You can imagine that they represent a time-exposure photograph that shows the paths of small particles carried by the flowing fluid. The figure shows streamlines for the flow of an incompressible fluid in a tapered pipe of circular cross section. The speed of the fluid as it enters the pipe on the left is v1. Assume that the cross-sectional areas of the pipe are A1 at its entrance on the left and A2 at its exit on the right.
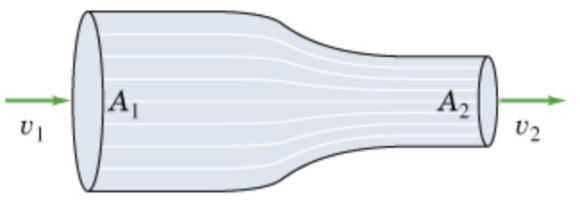
Part A
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The concept required to solve this problem is the continuity equation. Initially, find the volume of fluid which is entering in the pipe and then find the length of the region from where the fluid has entered the pipe in time interval \(\Delta t\). Then, find the volumetric flow rate. Later, find the volumetric flow rate flowing out of the pipe. Then, use the continuity equation to find the velocity of the fluid flowing out of the pipe. Finally, find which quantity increases with the increase in the density of the streamlines.
Fundamentals
The expression of the volume is, \(V=A L\)
Here, \(\mathrm{V}\) is the volume, \(\mathrm{A}\) is the area, and \(\mathrm{L}\) is the length. The expression of the speed is, \(v=\frac{L}{t}\)
Here, v is the speed, Lis the distance, and \(t\) is the time. The expression of the continuity equation is, \(A_{1} v_{1}=A_{2} v_{2}\)
Here, \(A_{1}\) is the area of the pipe through which the fluid is entering, \(v_{1}\) is the speed of the fluid entering the pipe, \(A_{2}\) is the area of the pipe from where the fluid is flowing out, and \(v_{2}\) is the speed of the fluid through which it is going outside the pipe.
(A) The expression of the volume of fluid which is entering in the pipe using the area and the length of the region covered by the fluid in time \(\Delta t\) is, \(\Delta V=A_{1} L_{1}\)
The length of the region from where the fluid has entered the pipe in time interval \(\Delta t\) is, \(L_{1}=v_{1} \Delta t\)
Substitute \(v_{1} \Delta t\) for \(L_{1}\) in the expression of the volume \(\Delta V\) \(\Delta V=A_{1} v_{1} \Delta t\)
Rearrange the equation for volumetric flow rate. \(\frac{\Delta V}{\Delta t}=A_{1} v_{1}\)
Substitute \(F_{1}\) for \(\frac{\Delta V}{\Delta t}\) \(F_{1}=A_{1} v_{1}\)
Part A
The volumetric flow rate is \(F_{1}=A_{1} v_{1}\)
The volumetric flow rate can be defined as the volume of a fluid flowing per unit time. The length of the region from where the fluid has entered the pipe in time interval \(\Delta t\) is equal to the speed of the fluid entering in the pipe multiplied by time.
(B) The mass is conserved. The expression of mass in terms of density is, \(m=\rho V\)
Here, \(\mathrm{m}\) is the mass, \(\rho\) is the density, and \(\mathrm{V}\) is the volume. Divide the expression by the time interval t. \(\frac{m}{t}=\rho \frac{V}{t}\)
The flow rate is, \(F_{1}=F_{2}\)
The volumetric flow \(F_{2}\) out of the pipe per unit time is, \(F_{2}=A_{2} v_{2}\)
Here, \(A_{2}\) is the area of the pipe when the fluid id flowing out with the speed \(v_{2}\). Use continuity equation. \(A_{1} v_{1}=A_{2} v_{2}\)
Rearrange for \(v_{2}\). \(v_{2}=\frac{A_{1} v_{1}}{A_{2}}\)
Part B The velocity \(v_{2}\) of the fluid flowing out of the right end of the pipe is \(v_{2}=\frac{A_{1} v_{1}}{A_{2}}\).
The continuity equation states that the volumetric flow into the pipe and out of the pipe should be same. The velocity \(v_{2}\) of the fluid flowing out of the right end of the pipe can be written in terms of the area of the pipe through which the fluid is entering the pipe with the velocity \(v_{1}\) and the area \(A_{2}\) of the pipe through which the fluid is flowing out.
(C) The streamline flow implies that the flow of fluid in which the speed at any point is constant. The closer the streamline implies the increasing density of streamlines which leads to the increase in the velocity of the fluid. The velocity of the flow will increase with the increase of the density of streamlines.
Part \(C\) Velocity.
If the picture of a streamline is shown, it can be concluded that the velocity of the fluid is greater where the streamlines are closer together. The velocity of the flow will increase with the increase of the density of streamlines.
Part A The volumetric flow rate is \(F_{1}=A_{1} v_{1}\)
Part B The velocity \(v_{2}\) of the fluid flowing out of the right end of the pipe is \(v_{2}=\frac{A_{1} v_{1}}{A_{2}} .\)
Part \(C\) Velocity.
Related Solutions
Learning Goal:To understand the continuity equation.Streamlinesrepresent the path of the flow of a fluid....
Plot several streamlines (including the stagnation and a few internal and external streamlines) of a 2-D...
Trace the path of cerebrospinal fluid from where it is formed to where it is reabsorbed...
Discuss the significance of Reynold number for the classification of the type of fluid flow.
A common parameter that can be used to predict turbulence in fluid flow is called the...
Fluid Mechanics Topic Why is it important to know if the flow is laminar or turbulent...
The mechanics of blood flow in the body follows the laws of fluid dynamics for tubes...
1. Which of the following must be satisfied by the flow of any fluid, real or...
1. Discuss the significance of Reynold number for the classification of the type of fluid flow....
List the flow (path) of an erythrocyte from the renal artery ending in the renal vein...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago