Question
In: Computer Science
Assume that struct Node{ int item; Node* link; }; Write function void list_remove(NodePtr& prev_ptr);...
Assume that
struct Node{
int item;
Node* link;
};
Write function void list_remove(NodePtr& prev_ptr); The function will remove the node after the node pointed by prev_ptr.
c++
Solutions
Expert Solution
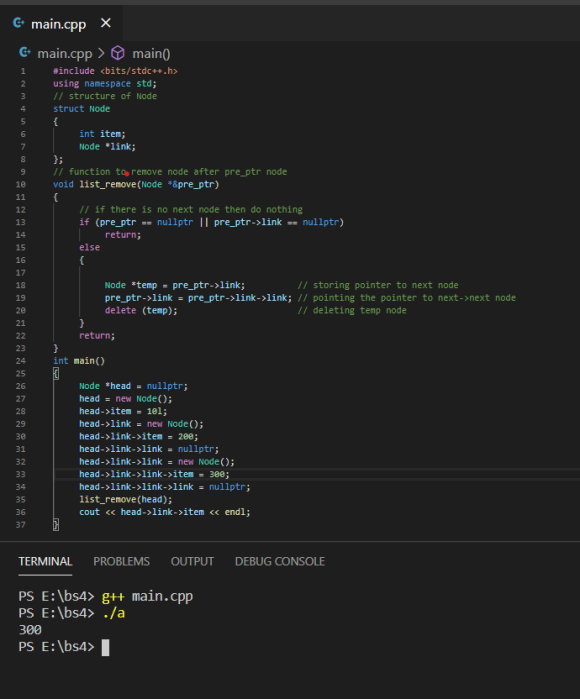
Here is the function and screenshot of how to use it.
// function to remove node after pre_ptr node
void list_remove(Node *&pre_ptr)
{
// if there is no next node then do nothing
if (pre_ptr == nullptr || pre_ptr->link == nullptr)
return;
else
{
Node *temp = pre_ptr->link; // storing pointer to next node
pre_ptr->link = pre_ptr->link->link; // pointing the pointer to next->next node
delete (temp); // deleting temp node
}
return;
}Here is the whole code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of Node
struct Node
{
int item;
Node *link;
};
// function to remove node after pre_ptr node
void list_remove(Node *&pre_ptr)
{
// if there is no next node then do nothing
if (pre_ptr == nullptr || pre_ptr->link == nullptr)
return;
else
{
Node *temp = pre_ptr->link; // storing pointer to next node
pre_ptr->link = pre_ptr->link->link; // pointing the pointer to next->next node
delete (temp); // deleting temp node
}
return;
}
int main()
{
Node *head = nullptr;
head = new Node();
head->item = 10l;
head->link = new Node();
head->link->item = 200;
head->link->link = nullptr;
head->link->link = new Node();
head->link->link->item = 300;
head->link->link->link = nullptr;
list_remove(head);
cout << head->link->item << endl;
}
Related Solutions
Assume that struct Node { int item; Node* link; }; typedef Node* NodePtr; 1. Write function...
Assume that
struct Node
{
int item; Node* link;
};
typedef Node* NodePtr;
1. Write function void list_head_insert(NodePtr& head, int
entry); The function should insert a new Node, in which entry is
the value of attribute item, in front of the linked list that is
pointed by head.
2. Write function void list_head_remove(NodePtr& head); The
function will remove the first node from the linked list that is
pointed by head.
3. Write function NodePtr list_search(NodePtr head, int target);
The function...
C++ language. struct Node { int data; Node *next; } Write a function to...
C++ language.
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}
Write a function to concatenate two linked lists. Given lists A*
= (4, 6) and B* = (3, 7, 12), after return from
Concatenate_Lists(Node A*, Node B*) the list A should be changed to
be A = (4, 6, 3, 7, 12). Your function should not change B and
should not directly link nodes from A to B (i.e. the nodes inserted
into A should be copies of...
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> struct listNode{ int data; struct listNode *nextptr; }; typedef struct listNode node; void insert(node*);...
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct listNode{
int data;
struct listNode *nextptr;
};
typedef struct listNode node;
void insert(node*);
void showList(node*);
void printListBackwards(node *);
int main(void)
{
node *list1;
printf("\n Create a sorted list..");
printf("\n Enter values for the first list (-999 to end):");
list1=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node*)); //Allocate memory for the list
node
insert(list1); //insert values by calling the function insert
showList(list1); //display values entered by user
printf("\n After recursively reversing the list is :\n");
printListBackwards(list1); //print the values in reverse order
using the function...
Consider the following struct that represents a node within a binary tree: struct Node { int...
Consider the following struct that represents a node within a
binary tree:
struct Node {
int data; // Data of interest
Node *left // Link to left subtree (nullptr if
none)
Node *right ; // Link to right subtree (nullptr if
none)
};
Complete the following function that computes the number of
elements in a binary tree:
// Counts the number of elements in the binary tree to
which t points.
// Returns the number of elements.
int size(Node *t)...
#include #include #include int reverse(int); // Stack ADT Type Defintions typedef struct node { void* dataPtr;...
#include #include #include int reverse(int); // Stack ADT Type
Defintions typedef struct node { void* dataPtr; struct node* link;
} STACK_NODE; typedef struct { int count; STACK_NODE* top; } STACK;
/* =============== createStack ============== This algorithm
creates an empty stack. Pre Nothing Post Returns pointer to a null
stack -or- NULL if overflow */ STACK* createStack(void) { // Local
Definitions STACK* stack; // Statements stack =
(STACK*)malloc(sizeof(STACK)); if (stack) { stack->count = 0;
stack->top = NULL; } // if return...
FINISH print and freelist #include<stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct node { int data; struct node *next; }; struct...
FINISH print and freelist
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* insert(struct node* list,int d );
struct node* del(struct node* list,int d );
void print( struct node *list);
void freeList(struct node* list);
void copy ( struct node *q, struct node **s );
int main( ) {
int number = 0, choice = 0;
struct node *pList=NULL;
struct node *nList = NULL;
while(choice!= 4)
{
printf("Do you
want to (1)insert, (2)delete, (3)Copy (4)quit.\n");...
#include<stdlib.h> #include<stdio.h> typedef struct node { void* dataPtr; struct node* next; } QUEUE_NODE; typedef...
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node
{
void* dataPtr;
struct node* next;
} QUEUE_NODE;
typedef struct
{
QUEUE_NODE* front;
QUEUE_NODE* rear;
int count;
} QUEUE;
//Prototype Declarations
QUEUE* createQueue(void);
QUEUE* destroyQueue(QUEUE* queue);
bool dequeue(QUEUE* queue, void** itemPtr);
bool enqueue(QUEUE* queue, void* itemPtr);
bool queueFront(QUEUE* queue, void** itemPtr);
bool queueRear(QUEUE* queue, void** itemPtr);
int queueCount(QUEUE* queue);
bool emptyQueue(QUEUE* queue);
bool fullQueue(QUEUE* queue);
/*================= createQueue ================
Allocates memory for a queue head node from dynamic
memory and returns...
Please do this code with python. Thank you! struct Node { int data; struct...
Please do this code with python. Thank you!
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
// Node creation
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* nn
= new Node;
nn->data = data;
nn->left = NULL;
nn->right = NULL;
return nn;
}
// Function to insert data in BST
struct Node* insert(struct Node* root, int data)
{
if (root == NULL)
return
newNode(data);
else {...
IN C++ Given a struct Node { int value; Node *left, *right;}; , implement the functions...
IN C++
Given a struct Node { int value; Node *left, *right;}; ,
implement the functions below.
a) int getSmallest(Node * r); // return smallest value in the
BST with root r. Assume r not null.
b) int getSecondSmallest(Node * r); // return 2nd smallest value
in BST with root r. Assume r not null and r has a nonnull left or
right child.
c) void removeSecondSmallest(Node * r); // remove 2nd smallest
value in BST with root r. Assume...
IN C Write a function in the form: void play( int key, int duration) // duration...
IN C
Write a function in the form:
void play( int key, int duration) // duration units are tenths of a second
which generates and prints samples of sin(w*t) for
t=0,1,2,...,n-1 which represent a tone corresponding to piano key
number key, where:
n = (duration/10.0)*8000
w = (2π440rkey-49)/8000
r = 21/12
In the main program call your function to play the first three
notes of three blind mice.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
ADVERTISEMENT
 venereology answered 3 years ago
venereology answered 3 years ago