Question
In: Economics
The market demand curve for a pair of duopolists is given as P=50- 2Q where Q=...
The market demand curve for a pair of duopolists is given as P=50- 2Q where Q= Q1+ Q2. The constant per unit marginal cost is 7 for firm 1 and 5 for firm 2. Both firms also have no fixed costs. Find the equilibrium price, quantity and profit for each firm if firm 1 is the Stackelberg leader and firm 2 a follower. Now re-do the computations assuming that firm 2 is the leader and firm 1 the follower.
(a) Firm 1 is leader
Equilibrium Price:
Equilibrium Quantity for Firm 1:
Equilibrium Quantity for Firm 2:
Profit for firm 1:
Profit for firm 2:
(b) Firm 2 is
leader
Equilibrium Price:
Equilibrium Quantity for Firm 1:
Equilibrium Quantity for Firm 2:
Profit for firm 1:
Profit for firm 2:
Solutions
Related Solutions
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 -Q where Q is...
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 -Q
where Q is total market demand. Each firm can produce output at a
constant marginal cost of 30 per unit. There are no fixed costs.
Determine the (1) equilibrium price, (2) quantity, and (3) economic
profits for the total market,(4) the consumer surplus, and (5) dead
weight loss.Show Work
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 - Q where Q...
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 -
Q where Q is total market demand. Each firm can produce output at a
constant marginal cost of 30 per unit. There are no fixed costs.
Determine the (1) equilibrium price, (2) quantity, and (3) economic
profits for the total market, (4) the consumer surplus, and (5)
dead weight loss.
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 - Q where Q...
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 -
Q where Q is total market demand. Each firm can produce output at a
constant marginal cost of 30 per unit. There are no fixed cost.
(Just need B through C answer please)
a. Find the equilibrium price, quantity and economic profit for
the total market, consumer surplus and Dead weight loss
b. If the duopolists in question above behave, instead,
according to the Bertrand model, what...
25.) Duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 - Q where Q...
25.) Duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 - Q
where Q is total market demand. Each firm can produce output at a
constant marginal cost of 30 per unit. There are no fixed costs. If
the duopolists behave, according to the Bertrand model, determine
the (1) equilibrium price, (2) quantity, and (3) economic profits
for the total market and (4) the consumer surplus, and (5) dead
weight loss.
The market demand curve for a pair of Cournot duopolists is given as: P = 36...
The market demand curve for a pair of Cournot duopolists is
given as: P = 36 - 3Q, (Q = Ql + Q2). The constant per unit
marginal cost is 12 for each duopolist.
12) What is the Cournot equilibrium price?
a) 0
b) 10
c) 18
d) 20
e) None of the above
13) What is the Cournot equilibrium quantities for each
firm?
a) 1.33
b) 2.66
c) 18.14
d) 20
e) None of the above
14) What is...
The market demand curve for a pair of Cournot duopolists is given as: P = 60...
The market demand curve for a pair of Cournot duopolists is
given as: P = 60 – 3Q. The constant per unit marginal cost is
$6/unit for each duopolist. (Round your answers to two decimal
points)
a) Find the Cournot equilibrium price, quantity, and profits
b) Solve the same problem as a Bertrand equilibrium. Find the
longrun equilibrium price, quantities, and profits.
c) Solve the same problem as a Stakelberg Leader-Follower
equilibrium. Assume Firm 1 is the leader.
24. Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 - Q where...
24. Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P =
90 - Q where Q is total market demand. Each firm can produce output
at a constant marginal cost of 30 per unit. There are no fixed
costs. Determine the (1) equilibrium price, (2) quantity, and (3)
economic profits for the total market, (4) the consumer surplus,
and (5) dead weight loss.
25. If the duopolists in question 24 behave according to the
Stackelberg Leader-Follower model, determine the...
The inverse market demand curve for protocol droids is P = 4,000 – 2Q, where Q...
The inverse market demand curve for protocol droids is
P = 4,000 – 2Q, where Q is the quantity
of protocol droids and P is the market price. Protocol
droids can be produced at a constant marginal cost of $1,000, and
all protocol droids are identical.
a. Suppose the market for protocol droids is served by two firms
that form a cartel and evenly split the market output. What are the
market output and price level?
b. Suppose the market...
Consider a market with a demand curve given (in inverse form) by P(Q)=50−0.25QP(Q)=50−0.25Q, where QQ is...
Consider a market with a demand curve given (in inverse form) by
P(Q)=50−0.25QP(Q)=50−0.25Q, where
QQ is total market output and PP is the price of
the good. Two firms compete in this market by sequentially choosing
quantities q1q1 and q2q2 (where
q1+q2=Qq1+q2=Q).
This is an example of:
Choose one:
A. Cournot competition.
B. Bertrand competition.
C. perfect competition.
D. Stackelberg competition.
Part 2(4 pts)
Now suppose the cost of production is constant at $20.00 per
unit (and is the same...
Stackelberg Leader-Follower duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 120 - 3Q where...
Stackelberg Leader-Follower duopolists face a market demand
curve given by P = 120 - 3Q where Q is total market demand. Each
firm can produce output at a constant marginal cost of 20 per unit.
The equilibrium price for the total market will be...?
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- When preparing government-wide statements, which of the following is not true? Multiple Choice Entries are necessary...
- Hawaiian Location (e.g., what can be grown there because of the climate, soils, etc.) Culture (e.g.,...
- A merry-go-round is spinning around a frictionless axle at its center with a person standing at...
- Im writing a matlab script called vecadd that deals with vectors and is converting them between...
- Write a program, using C#, windows forms, that will find the mean and standard deviation of...
- 50 pts) True – False questions (Please write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false) Engineering...
- The capital accounts of Trent Henry and Tim Chou have balances of $147,400 and $92,600, respectively....
ADVERTISEMENT



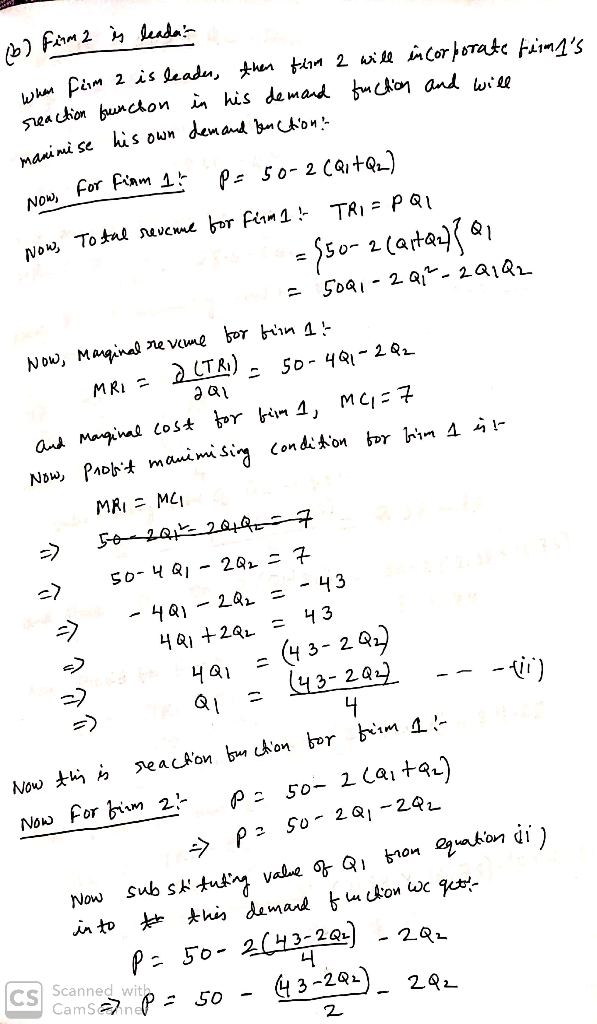
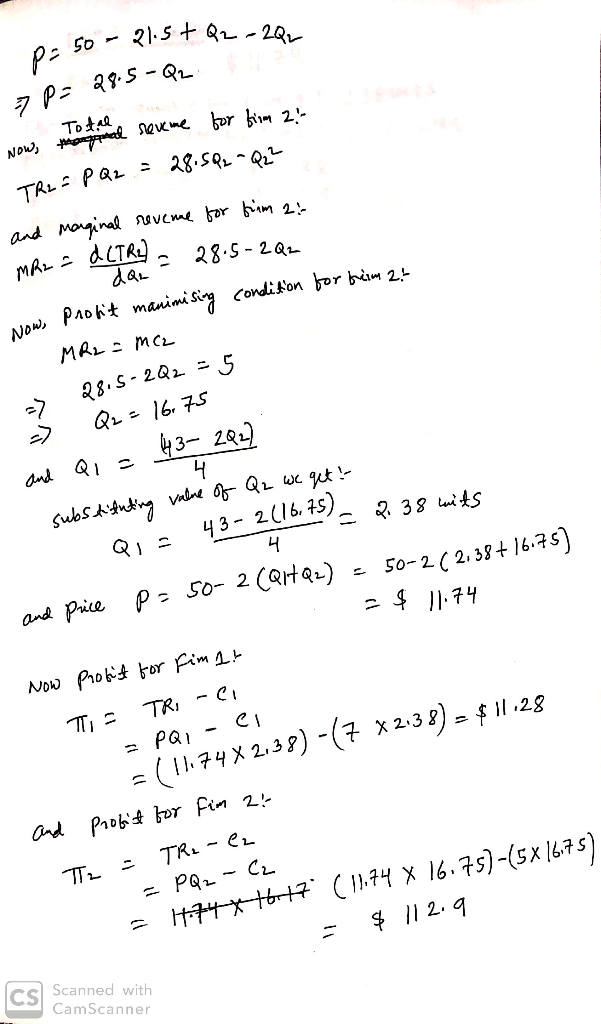

 Rahul Sunny answered 2 months ago
Rahul Sunny answered 2 months ago