Question
In: Economics
5) The demand for a good varies A) directly with the prices of substitutes and also...
5) The demand for a good varies A) directly with the prices of substitutes and also directly with the prices of complements. B) directly with the prices of substitutes and inversely with the prices of complements. C) inversely with the prices of substitutes and directly with the prices of complements. D) inversely with the prices of substitutes and also inversely with the prices of complements. 11) Over the past decade technological improvements in producing computers have increased A) both the supply and the quantity supplied. B) the supply but not the quantity supplied. C) the quantity supplied but not the supply. D) neither the supply nor the quantity supplied. 17) When the price is below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded A) is less than the equilibrium quantity. So is the quantity supplied. B) is less than the equilibrium quantity. The quantity supplied exceeds the equilibrium quantity. C) exceeds the equilibrium quantity. So does the quantity supplied. D) exceeds the equilibrium quantity. The quantity supplied is less than the equilibrium quantity. 18) Which of the following correctly describes how price adjustment eliminates a shortage? A) As the price rises, the quantity demanded decreases while the quantity supplied increases. B) As the price rises, the quantity demanded increases while the quantity supplied decreases. C) As the price falls, the quantity demanded decreases while the quantity supplied increases. D) As the price falls, the quantity demanded increases while the quantity supplied decreases.
Solutions
Expert Solution
5) The demand for a good varies
B) directly with the prices of substitutes and inversely with the prices of complements.

11) Over the past decade technological improvements in producing computers have increased
A) both the supply and the quantity supplied
17) When the price is below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded
D) exceeds the equilibrium quantity. The quantity supplied is less than the equilibrium quantity.
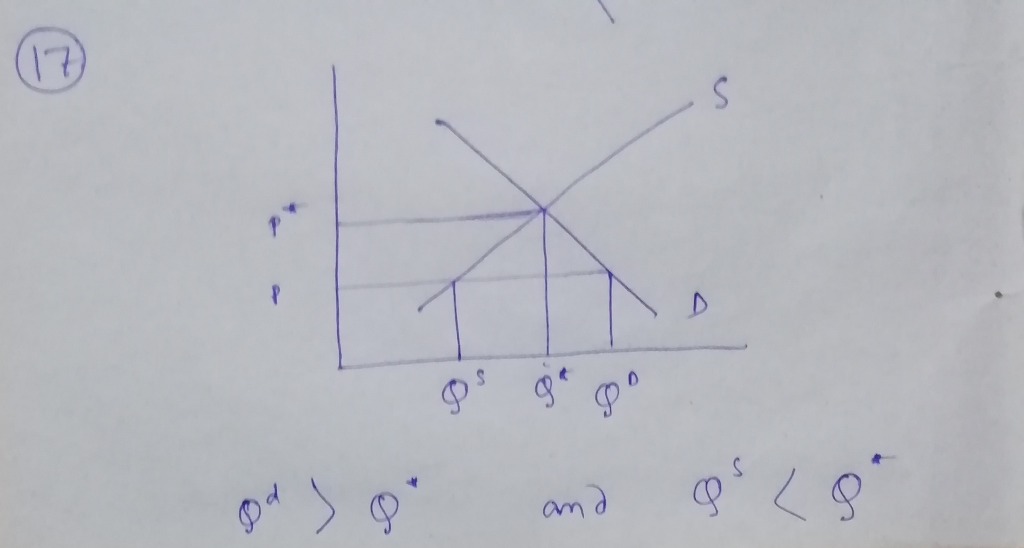
18) Which of the following correctly describes how price adjustment eliminates a shortage?
A) As the price rises, the quantity demanded decreases while the quantity supplied increases.
Consider the diagram where when price increases Qd falls and converges to Q* and Qs increases and converges to Q*.
Related Solutions
Consumer surplus a. varies directly with price b. varies indirectly with price c. is independent of...
Are the Ireader good substitutes for paper books?
A good with many close substitutes is likely to have relatively demand, since consumers can easily...
Good 1 and Good 2 are perfect substitutes. Suppose that good 1 is an ordinary good....
Good 1 and Good 2 are perfect substitutes. Suppose that good 1 is an ordinary good....
The consumer’s demand function for a good in general depends on the prices of all goods...
Consider the demand for apples. If the prices of a substitute good(bananas) increases and the price...
Suppose that the demand curve of a good is vertical over a given range of prices....
1. Suppose that good X and good Y are substitutes: 1.1) What will happen to the...
The electrical resistance of a wire varies directly as its length and inversely as the square...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Rahul Sunny answered 2 months ago
Rahul Sunny answered 2 months ago