Question
In: Physics
The absorption spectrum of an atom consists of the wavelengths 200 nm, 300nm, and 500 nm....
The absorption spectrum of an atom consists of the wavelengths 200 nm, 300nm, and 500 nm.
a) Draw the atom's energy-level diagram.
b) What wavelengths are seen in the atom's emission spectrum?
(Please show all the steps and calculations with simple explanation. Thank you)
Solutions
Expert Solution
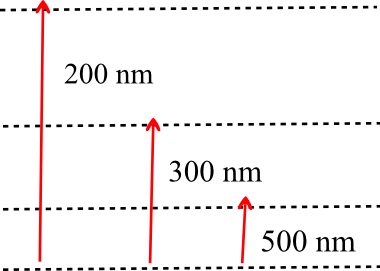
Absorption Spectrum implies the wavelength of photon required by electron to jump from one energy level to another energy level.
Since energy required to jump from level 1 to level 4 is maximum so it corresponds to 200nm
Similarly 300 nm corresponds to transition from level 1 to level 3
and 500 nm corresponds to transition from level 1 to level 2
Same photon will be released if the transition is same.
So
lambda41 = 200nm
lambda31= 300nm
lambda21 = 500nm
If the electron jumps from level 4 to level 2, the energy between these two levels is the difference of the energy of the photon required to reach these levels. Since energy is inversly proportional to lambda(E = hc/(lambda) )
we get
hc/(lambda42) = hc/lambda41 - hc/lambda21
1/lambda42 = 1/lambda41 - 1/lambda21
We get
lambda42 = (1/(1/200 - 1/500)) = 333.33 nm
Similarly
lambda 43 = (1/(1/200 - 1/300))= 600 nm
lambda 32 = (1/(1/300 - 1/500)) = 750nm
Related Solutions
An absorption spectrum can be described asSelect one:a. a continuous band of all wavelengths...
he K series of the discrete x-ray spectrum of tungsten contains wavelengths of 0.018 5 nm,...
The CO microwave spectrum has lines at 0.86 nm, 1.29 nm, and 2.59 nm. a) What...
Absorpstion spectrum of hydrogen shows line in 404.7 nm ; 435.8 nm and 486.3 nm. Determine:...
A spectrum of visible light colors from 400 nm to 700 nm is incident on a...
The human eye can readily detect wavelengths from about 400 nm to 700 nm
A laser emits two wavelengths (λ1 = 420 nm; λ2 = 630 nm). When these two...
Mercury vapor emits lights as several wavelengths, but the primary ones are 365.4 nm, 404.7 nm,...
Calculate the wavelengths of the following objects (in nm): a muon (a subatomic particle with a...
three of the strongest lines in the He+ ion spectrum are observed at the following wavelengths:...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 genius_generous answered 3 months ago
genius_generous answered 3 months ago