Question
In: Computer Science
Write a Java Program using the following instruction: Create the following 3 methods that calculate and...
Write a Java Program using the following instruction:
Create the following 3 methods that calculate and display the sum or product of the integers from 1 to the number input.
getNum Receives no input. Prompts the user to enter a number, use a loop to validate. Returns the result.
calcSum Receives an integer as input. Calculates the sum of the integers from 1 to this number. Returns the result.
calcProd Receives an integer as input. Calculates the product of the integers from 1 to this number. Returns the result.
Main should: Prompt for a character that determines if you want to calculate the sum (‘S’ or ‘s’) or product (‘P’ or ‘p’). You should use a switch to process the choices. Upper and lower case values should work the same way. Use default to give an error message if anything else is entered. (You can input as String or char)
if a valid option is entered, use getNum to prompt for the number
Note that calcSum and calcProduct RETURN the result to main, and the output is printed in main. For example, if you input 5 as the number, and ‘S’, the program should calculate 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 and display the sum as 15. If you input 5 and ‘P’ the program should calculate 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 and display the product as 120. . The process should repeat as long as the user wants to continue. This loop should be in main. DO NOT use System.exit command to end the program. . See sample output below.
Enter S for sum, P for prod:z
Invalid choice Again(y/n)? y
Enter S for sum, P for prod:s
Enter an integer greater than 1: 1
Must be greater than 1, re-enter: -3
Must be greater than 1, re-enter: 3
The sum of the numbers from 1 to 3 is 6 Again(y/n)? y
Enter S for sum, P for prod:p
Enter an integer greater than 1: 4
The product of the numbers from 1 to 4 is 24 Again(y/n)? n
Solutions
Expert Solution
Answer
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
class MyCode
{
public static void main (String[] args) throws
java.lang.Exception
{
int num;
String ch,choice;
Scanner in=new
Scanner(System.in);
do
{
System.out.println("Enter S for sum, P for prod : ");
ch=in.next();
switch(ch.charAt(0))
{
case 'S':
case 's':
num=getNum();
System.out.println("The sum of the numbers from
1 to "+num+" is : "+calcSum(num));
break;
case 'P':
case 'p':
num=getNum();
System.out.println("The product of the numbers
from 1 to "+num+" is : "+calcProd(num));
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid
choice! Try Again..");
}
System.out.println("Try Again (Y/N) : ");
choice=in.next();
}while(choice.charAt(0)!='N'&&choice.charAt(0)!='n');
}
public static int getNum()
{
Scanner in=new
Scanner(System.in);
int n;
do
{
System.out.println("Enter an integer greater than 1 : ");
n=in.nextInt();
if(n<=1)
System.out.println("Must be greater than 1,
re-enter..");
else
break;
}while(n<=1);
return n;
}
public static int calcSum(int num)
{
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
sum+=i;
return sum;
}
public static int calcProd(int num)
{
int product=1;
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
product=product*i;
return product;
}
}
OUTPUT
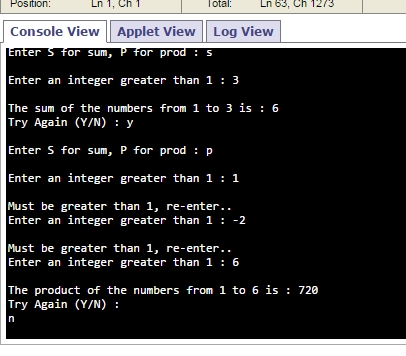
Related Solutions
(Java) Create a program using 3 methods. The methods must be public and static. Ask the...
3) Create a Java program that uses NO methods, but use scanner: Write a program where...
Write a java program using the following instructions: Write a program that determines election results. Create...
8) Create the following program using Java. Circle calculation using methods Create scanner declare double variable...
Write a program in java that uses methods to input data for calculation, calculate, and display...
Write a java program with 3 recursive methods that reverse the order of a string. The...
COP 2800, Java Programming Assignment 6-1 Using Java create a program using the “Methods” we covered...
4.) Create a Java program using the “extends” and “runnable” methods. You will be creating your...
Please write a java program that has the following methods in it: (preferably in order) a...
Create a Java Program to calculate luggage costs. USING ECLIPSE IDE The Business Rules are: A....
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 venereology answered 3 months ago
venereology answered 3 months ago