Question
In: Operations Management
1. You are estimating costs for installing undersea cable in the Persian Gulf (aka the Arabian...
1. You are estimating costs for installing undersea cable in the Persian Gulf (aka the Arabian Gulf). You have the following information concerning installation costs:
• The material cost per kilometer for cable is $100,000.
• You are installing 100 kilometers of cable.
• The cost per kilometer for installation depends on the sea conditions (sea state). Sea State Cost/kilometer I $15,000 II $75,000
a. What would be the estimated cost of the project if you knew with certainty that, during the time you were installing the cable, you would encounter sea state I 75% of the time and sea state II 25% of the time?
b. Run a Crystal Ball calculation of the total estimated cost of the project, assuming the probability of sea state 1 is normally distributed with a mean of 25% and a standard deviation of 5%. Only sea states I and II are possible. Post your result, including your cost forecast.
c. What is your mean expected cost?
d. What estimated cost provides you 95% assurance that your actual cost will be less than that amount?
Solutions
Expert Solution
(a)
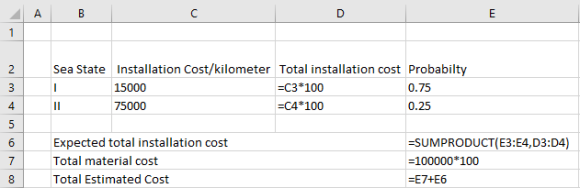
| Sea State | Installation Cost/kilometer | Total installation cost | Probabilty |
| I | $15,000 | $1,500,000 | 0.75 |
| II | $75,000 | $7,500,000 | 0.25 |
| Expected total installation cost | $3,000,000 | ||
| Total material cost | $10,000,000 | ||
| Total Estimated Cost | $13,000,000 |
(b)
Crystal ball Report of simulation (5,000 runs)

(c)
The expected cost is $16,005,044 (the value will change slightly for each fresh simulation attempts)
(d)
Following is the 95% confidence point (right-sided)
Mean + NORMSINV(0.95)*Std. Error
= $16,005,044 + NORMSINV(0.95)*$4,222 = $16,011,989.
So, we are 95% sure that the cost will be less than $16,011,989.
Related Solutions
1)When would you use the Power Sizing Method to estimate Costs? 2)In terms of cost estimating,...
1. What factors affect the costs of labor when estimating masonry? 2. How may the type...
(1) You are estimating the cost of optical sensors based on the radius of the sensors....
1.You are interested in estimating the the mean weight of the local adult population of female...
1. You have 25 km of optical cable with an attenuation coefficient of 0.27 dB/km. What...
Question 1 Why can you never have 100% confidence in correctly estimating the population characteristic of...
1. Suppose you have an investment that costs $80,000 at the beginning of the project, and...
You own a house that costs $1 million. You buy a $20,000 insurance policy to compensate...
Consider an asset that costs $130 today. You are going to hold it for 1 year...
1) You buy a lottery ticket to a lottery that costs $10 per ticket. There are...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 keosha answered 1 year ago
keosha answered 1 year ago