Question
In: Economics
7.EXERCISE 15.2 POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE SHOCKS Draw a labour market diagram where the economy is at...
7.EXERCISE 15.2 POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE SHOCKS
Draw a labour market diagram where the economy is at labor market equilibrium with stable prices. Now consider:
• A positive shock to aggregate demand that reduces the unemployment rate by 2 percentage points.
• A negative shock that increases it by 2 percentage points.
1.What happens to the bargaining gap in each case?
2.What would you expect to happen to the price level in each case? Explain your answers.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Sol 7 :
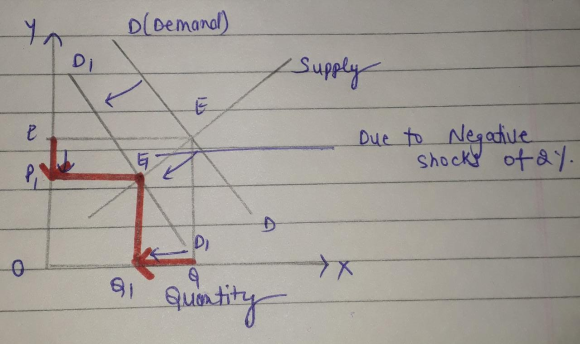
the diagram for market equilibrium is as follows :

1) The effect on labour market will be as follows
- Impact of Increase in AD by 2% : Increase in Aggregate demand . that will increase the price for the wages for the workers and more labourers will be employed as increase in Aggregate demand will demand for more productivity which can be increase by employing more labours. this will shift the demand curcve of labours forward due to which situation of excess demand is created in the market . Due to excess demand (Bargaining gap) , price of the wages shift upward and quantity of labour is also increases and market will reach at equilibrium (E1) .
- Impact of increase in unemployment rate by 2% : Increase in unemployment rate this will decrease the price for the wages for the workers and less labourers will be employed as decrease in unemployment rate will will shift the demand curve of labours backward due to which situation of excess supply is created in the market . Due to excess supply (Bargaining gap) , price of the wages shift backward and quantity of labour is also decreases and market will reach at equilibrium (E1) .
2)effect on prices of wages will be as follows :
- Increase in wages of labours : As, due to increase in AD demand
for labour increases and demand curve shifts from DD to DD' . Due
to excess demand , price fro the wages will increases and quantity
of more labour employed is also increased .

- decrease in wages of labours : As, due to increase in
unemployment rate , demand for labour decreases and demand curve
shifts from DD to DD' . Due to excess supply , price fro the wages
will decreases and quantity of more labour employed is also
decreased .
Related Solutions
Give examples of shocks that might result the market value of an FI to become negative...
Give examples of shocks that might result the market value of an
FI to become
negative (whereas it was positive before the shock)?
Present a positive and a negative impact of globalization on the USA economy.
Present a positive and a negative impact of globalization on the
USA economy.
Present a positive and negative impact of globalization on the US economy
Present a positive and negative impact of globalization on the US
economy
Assume that the economy is hit with successive positive demand shocks, lowering unemployment and inflation. What...
Assume that the economy is hit with successive positive demand
shocks, lowering unemployment and inflation. What policy would the
central bank pursue if the decrease in inflation lowered inflation
below their target (assuming the CB is operating under an inflation
rule for monetary policy).
a. Draw a scatter plot. Is this a positive or negative correlation? Explain what a positive correlation and negative correlation are. b.Compute the pearson correlation.
For the following scores,
x
y
0
4
2
9
1
6
1
9
a. Draw a scatter plot. Is this a positive or negative correlation? Explain what a positive correlation and negative correlation are. b.Compute the pearson correlation.
What does a positive and negative : (i) direct labour rate variance mean ? Explain in...
What does a positive and negative :
(i) direct labour rate variance mean ? Explain in details and go
beyond favourable and unfavourable variance?
(II) direct labour efficiency variance mean? Explain in details
and go beyond favourable and unfavourable variance?
In an economy, the supply of labour is given by S = 10 + 200Wn, where...
In an economy, the supply of labour is given by S = 10 + 200Wn,
where S is the quantity supplied of labour (hours of work), and Wn
is the after-tax wage rate (net wage). Assume that the before-tax
wage rate is fixed at $10.
a) Find the quantity supplied of labour and the total tax
revenue at the following tax rates: 15%, 30%, 50%, 70%, and 80%.
b) Calculate the net wage elasticity of labour supply at each of...
In an economy, the supply of labour is given by S = 10 + 200Wn, where...
In an economy, the supply of labour is given by S = 10 + 200Wn,
where S is the quantity supplied of labour (hours of work), and Wn
is the after-tax wage rate (net wage). Assume that the before-tax
wage rate is fixed at $10.
a) Find the quantity supplied of labour and the total tax
revenue at the following tax rates: 15%, 30%, 50%, 70%, and 80%.
b) Calculate the net wage elasticity of labour supply at each of...
In an economy, the supply of labour is given by S = 10 + 200Wn, where...
In an economy, the supply of labour is given by S = 10 + 200Wn,
where S is the quantity supplied of labour (hours of work), and Wn
is the after-tax wage rate (net wage). Assume that the before-tax
wage rate is fixed at $10.
a) Find the quantity supplied of labour and the total tax
revenue at the following tax rates: 15%, 30%, 50%, 70%, and
80%.
b) Calculate the net wage elasticity of labour supply at each of...
Is the informal economy of Peru positive or negative for the economic growth of the country?...
Is the informal economy of Peru positive or negative for the
economic growth of the country? (facts and figures).
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT


 Rahul Sunny answered 1 year ago
Rahul Sunny answered 1 year ago