Question
In: Chemistry
A zero order reaction starts with an initial concentration of reactant of 1.00 M and has...
A zero order reaction starts with an initial concentration of reactant of 1.00 M and has a rate constant of 1.65x10-5M/s. What is the concentration of the reactant after 100 seconds?
Solutions
Expert Solution
A Zero order reaction has a rate that is independent of the concentration of the reactant(s). Increasing the concentration of the reacting species will not speed up the rate of the reaction i.e. the amount of substance reacted is proportional to the time. Zero order reactions are typically found when a material that is required for the reaction to proceed, such as a surface or a catalyst, is saturated by the reactants. The rate law for a zero order reaction is

where r is the reaction rate and k is the reaction rate coefficient with units of concentration or time. If, and only if, this zeroth order reaction 1) occurs in a closed system, 2) there is no net build-up of intermediates, and 3) there are no other reactions occurring, it can be shown by solving a mass balance equation for the system that:

If this differential equation is integrated it gives an equation often called the integrated zero order rate law.

where 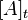 represents the concentration of the chemical of interest at a
particular time, and
represents the concentration of the chemical of interest at a
particular time, and  represents the initial concentration.
represents the initial concentration.
A reaction is zero order if concentration data are plotted
versus time and the result is a straight line. A plot of 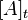 vs. time t gives a straight line with a slope of
vs. time t gives a straight line with a slope of  .
.
The half-life of a reaction describes the time needed for half of the reactant to be depleted (same as the half-life involved in nuclear decay, which is a first order reaction). For a zero order reaction the half-life is given by
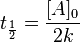
In our case,
k=1.65x10-5M/s
Ao=1M
t=100seconds
using equation->
At= -1.65x10-5M/s * 100s +1M = 0.99835M
Related Solutions
1.)For a second-order reaction, the initial reactant concentration is 0.62 M. After 36.3 min, the concentration...
Part A The reactant concentration in a zero-order reaction was 9.00×10−2 M after 105 s and...
Part A The reactant concentration in a zero-order reaction was 5.00×10−2 M after 190 s and...
A) The reactant concentration in a zero-order reaction was 9.00×10−2 M after 155 s and 2.00×10−2...
Part A The reactant concentration in a zero-order reaction was 0.100 M after 105 s and 3.00×10−2 M after 350 s
A certain zero order reaction has a half live of 2.5 seconds when the initial concentration...
Part A The reactant concentration in a zero-order reaction was 5.00×10−2M after 190 s and 2.50×10−2M...
Part A The reactant concentration in a zero-order reaction was 5.00×10−2M after 130 s and 4.00×10−2M...
It takes 41.0 min for the concentration of a reactant in a first-order reaction to drop...
Suppose the half-life is 55.0 s for a first order reaction and the reactant concentration is...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago