Question
In: Computer Science
What is an n-tier architecture? Why do we need to use n-tier architecture? What is a...
- What is an n-tier architecture? Why do we need to use n-tier architecture?
- What is a service-oriented architecture? Provide an example of a service-oriented architecture.
- Discuss the different architectural models for Database as a Service
Solutions
Expert Solution
1)
N-tier architecture is also called multi-tier architecture because the software is engineered to have the processing, data management, and presentation functions physically and logically separated. That means that these different functions are hosted on several machines or clusters, ensuring that services are provided without resources being shared and, as such, these services are delivered at top capacity. The “N” in the name n-tier architecture refers to any number from 1.
Not only does your software gain from being able to get services at the best possible rate, but it’s also easier to manage. This is because when you work on one section, the changes you make will not affect the other functions. And if there is a problem, you can easily pinpoint where it originates.
N-tier architecture would involve dividing an application into three different tiers. These would be the
- logic tier,
- the presentation tier, and
- the data tier.
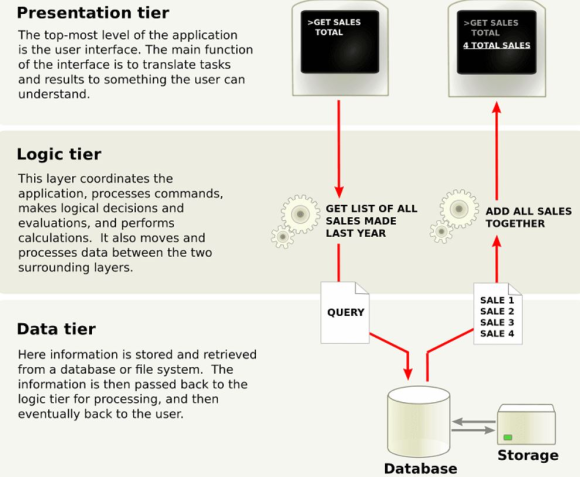
The separate physical location of these tiers is what differentiates n-tier architecture from the model-view-controller framework that only separates presentation, logic, and data tiers in concept. N-tier architecture also differs from MVC framework in that the former has a middle layer or a logic tier, which facilitates all communications between the different tiers. When you use the MVC framework, the interaction that happens is triangular; instead of going through the logic tier, it is the control layer that accesses the model and view layers, while the model layer accesses the view layer. Additionally, the control layer makes a model using the requirements and then pushes that model into the view layer.
This is not to say that you can only use either the MVC framework or the n-tier architecture. There are a lot of software that brings together these two frameworks. For instance, you can use the n-tier architecture as the overall architecture, or use the MVC framework in the presentation tier.
Considerations for Using N-Tier Architecture for Your Applications
Because you are going to work with several tiers, you need to make sure that network bandwidth and hardware are fast. If not, the application’s performance might be slow. Also, this would mean that you would have to pay more for the network, the hardware, and the maintenance needed to ensure that you have better network bandwidth.
Also, use as fewer tiers as possible. Remember that each tier you add to your software or project means an added layer of complexity, more hardware to purchase, as well as higher maintenance and deployment costs. To make your n-tier applications make sense, it should have the minimum number of tiers needed to still enjoy the scalability, security and other benefits brought about by using this architecture. If you need only three tiers, don’t deploy four or more tiers.
2)
Service-Oriented Architecture
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is an architectural approach in which applications make use of services available in the network. In this architecture, services are provided to form applications, through a communication call over the internet.
- SOA allows users to combine a large number of facilities from existing services to form applications.
- SOA encompasses a set of design principles that structure system development and provide means for integrating components into a coherent and decentralized system.
- SOA based computing packages functionalities into a set of interoperable services, which can be integrated into different software systems belonging to separate business domains.
There are two major roles within Service-oriented Architecture:
- Service provider: The service provider is the maintainer of the service and the organization that makes available one or more services for others to use. To advertise services, the provider can publish them in a registry, together with a service contract that specifies the nature of the service, how to use it, the requirements for the service, and the fees charged.
- Service consumer: The service consumer can locate the service metadata in the registry and develop the required client components to bind and use the service.

Services might aggregate information and data retrieved from other services or create workflows of services to satisfy the request of a given service consumer. This practice is known as service orchestration Another important interaction pattern is service choreography, which is the coordinated interaction of services without a single point of control.
Components of SOA:

Guiding Principles of SOA:
- Standardized service contract: Specified through one or more service description documents.
- Loose coupling: Services are designed as self-contained components, maintain relationships that minimize dependencies on other services.
- Abstraction: A service is completely defined by service contracts and description documents. They hide their logic, which is encapsulated within their implementation.
- Reusability: Designed as components, services can be reused more effectively, thus reducing development time and the associated costs.
- Autonomy: Services have control over the logic they encapsulate and, from a service consumer point of view, there is no need to know about their implementation.
- Discoverability: Services are defined by description documents that constitute supplemental metadata through which they can be effectively discovered. Service discovery provides an effective means for utilizing third-party resources.
- Composability: Using services as building blocks, sophisticated and complex operations can be implemented. Service orchestration and choreography provide a solid support for composing services and achieving business goals.
Advantages of SOA:
- Service reusability: In SOA, applications are made from existing services.Thus, services can be reused to make many applications.
- Easy maintenance: As services are independent of each other they can be updated and modified easily without affecting other services.
- Platform independant: SOA allows making a complex application by combining services picked from different sources, independent of the platform.
- Availability: SOA facilities are easily available to anyone on request.
- Reliability: SOA applications are more reliable because it is easy to debug small services rather than huge codes
- Scalability: Services can run on different servers within an environment, this increases scalability
Disadvantages of SOA:
- High overhead: A validation of input parameters of services is done whenever services interact this decreases performance as it increases load and response time.
- High investment: A huge initial investment is required for SOA.
- Complex service management: When services interact they exchange messages to tasks. the number of messages may go in millions. It becomes a cumbersome task to handle a large number of messages.
Practical applications of SOA: SOA is used in many ways around us whether it is mentioned or not.
- SOA infrastructure is used by many armies and air force to deploy situational awareness systems.
- SOA is used to improve the healthcare delivery.
- Nowadays many apps are games and they use inbuilt functions to run. For example, an app might need GPS so it uses inbuilt GPS functions of the device. This is SOA in mobile solutions.
- SOA helps maintain museums a virtualized storage pool for their information and content.
3)
What Is Database Architecture?
Database architecture uses programming languages to design a particular type of software for businesses or organizations.Database architecture focuses on the design, development, implementation and maintenance of computer programs that store and organize information for businesses, agencies and institutions. A database architect develops and implements software to meet the needs of users.
The design of a DBMS depends on its architecture. It can be centralized or decentralized or hierarchical. The architecture of a DBMS can be seen as either single tier or multi-tier. The tiers are classified as follows :
- 1-tier architecture
- 2-tier architecture
- 3-tier architecture
- n-tier architecture
1-tier architecture:
One-tier architecture involves putting all of the required components for a software application or technology on a single server or platform.


1-tier architecture
Basically, a one-tier architecture keeps all of the elements of an application, including the interface, Middleware and back-end data, in one place. Developers see these types of systems as the simplest and most direct way.
2-tier architecture:
The two-tier is based on Client Server architecture. The two-tier architecture is like client server application. The direct communication takes place between client and server. There is no intermediate between client and server.


2-tier architecture
3-tier architecture:
A 3-tier architecture separates its tiers from each other based on the complexity of the users and how they use the data present in the database. It is the most widely used architecture to design a DBMS.


3-tier architecture
This architecture has different usages with different applications. It can be used in web applications and distributed applications. The strength in particular is when using this architecture over distributed systems.
- Database (Data) Tier − At this tier, the database resides along with its query processing languages. We also have the relations that define the data and their constraints at this level.
- Application (Middle) Tier − At this tier reside the application server and the programs that access the database. For a user, this application tier presents an abstracted view of the database. End-users are unaware of any existence of the database beyond the application. At the other end, the database tier is not aware of any other user beyond the application tier. Hence, the application layer sits in the middle and acts as a mediator between the end-user and the database.
- User (Presentation) Tier − End-users operate on this tier and they know nothing about any existence of the database beyond this layer. At this layer, multiple views of the database can be provided by the application. All views are generated by applications that reside in the application tier.
n-tier architecture:
N-tier architecture would involve dividing an application into three different tiers. These would be the
- logic tier,
- the presentation tier, and
- the data tier.


n-tier architecture
It is the physical separation of the different parts of the application as opposed to the usually conceptual or logical separation of the elements in the model-view-controller (MVC) framework. Another difference from the MVC framework is that n-tier layers are connected linearly, meaning all communication must go through the middle layer, which is the logic tier. In MVC, there is no actual middle layer because the interaction is triangular; the control layer has access to both the view and model layers and the model also accesses the view; the controller also creates a model based on the requirements and pushes this to the view. However, they are not mutually exclusive, as the MVC framework can be used in conjunction with the n-tier architecture, with the n-tier being the overall architecture used and MVC used as the framework for the presentation tier.
Related Solutions
What is software architecture? Why do we need it? Distinguish between architecture and design.
In web programming, what is the three tier architecture?
Describe the three-schema architecture. Why do we need mappings among schema levels?
What is the G-factor in the strain gage, and why do we need to use materials...
Why do we use S/N ratios as the criterion for optimization?
Why do we need to use degrees of freedom with the t distribution, but not the...
What are the ledgers, why do we use them? And then HOW do we use them,...
Intuitively, what is the discount rate, why do we need it, and how do we choose...
Why do we need to use a decrement operator to get it to write the numbers...
For statistics we use the central limit theorem rule for n>30. But what do we use...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.

 venereology answered 1 year ago
venereology answered 1 year ago