Question
In: Chemistry
The formate ion, HCO2-, is formed when formic acid dissolves in water.
The formate ion, HCO2-, is formed when formic acid dissolves in water. A number of possible resonance structures for this ion are shown.
Which of these structures are valid and which are invalid?
Drag each item to the appropriate bin.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
Resonance structures are Lewis structures that are obtained due to the motion of lone pair or pi-electron cloud in the structure.
These structures are electronically equivalent and indicated by double-headed arrow \((\leftrightarrow)\)
Fundamentals
Resonance structures : Resonance structure are structures which are indicating the same molecule but differ in their electrinical geometry. Let \(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B},\) and \(\mathrm{C}\) are resonance structures, indicated as follows. \(\mathrm{A} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{B} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{C}\)
Charge on every canonical structure (resonance structure) should be equal.
Given ion is formate ion \(\left(\mathrm{HCO}_{2}^{-}\right)\) Given that this formate ion produced by dissolving the formic acid in water. Complete reaction is as follows:
\(\mathrm{HCOOH}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{HCOO}^{-}+\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\)
Lewis structure of the formate ion is shown below.
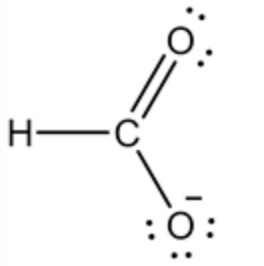
Formate ion is produced by dissolving the formic acid in the water, this reaction has been shown. And the Lewis dot structure has been given for the formate ion.
Formate ion structure is shown below:

The resonance structure for this formate ion is as follows:
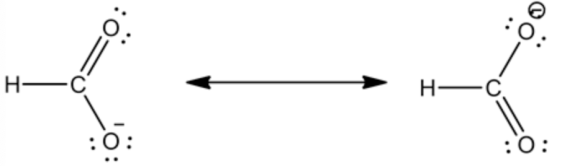
Therefore, only two possible resonance structures are there for formate ion.
Resonance structures have been drawn for the formate ion, which is produced during the dissolving process of formic acid in water.
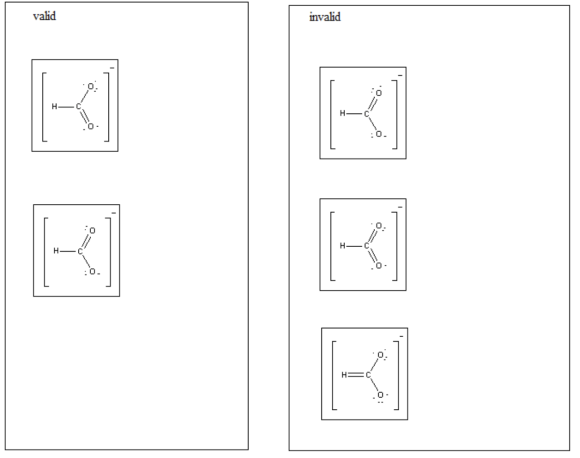
Related Solutions
A.) What ions are formed when KCN dissolves in water? Identify the ion in KCN which...
A chemist is working with a formic acid � formate ion buffer system. HCHO2(aq) + H2O(l)...
(19) Ammonium formate, NH4(HCOO), dissolves in water to give ammonium ions and formate ions. These ions...
(a) What is the pH of 0.89 M potassium formate, HCOOK? (The Ka of formic acid...
1. Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to determine the ratio of base/acid in a formic acid-formate buffer...
Formic acid,HCHO2 , is used to make methyl formate (a fumigant for dried fruit) and ethyl...
With the same initial solution of 0.75 moles formate and 0.85 moles formic acid to make...
the Al(H2O)63+ ion is formed when an Al3+ ion acting as a Lewis acid picks up...
A.You have 1 M solutions of formic acid and sodium formate. Calculate the volume of sodium...
2.0 mL of 0.5M HCl was added to 50 mL of 0.5M Formate-formic acid buffer at...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago