Question
In: Computer Science
Write a C program to take two integer arrays in ascending order and combine them in...
Write a C program to take two integer arrays in ascending order and combine them in a new array in descending order. Remove any duplicates in the final array, if any. Your code must store the arrays as a linked list of objects, each put in a “struct.” All operations should also be carried out using linked lists.
Input: 2 sorted arrays, each on a new line.
Output: An array sorted in descending order, without duplicates.
There is a single white space after each number, even after the last number. There is no new line at the end. Use the following struct as a reference:
struct ELEMENT {
int value;
struct ELEMENT *next;
};
=== Sample test case 1 ===
Input:
2 15 18 34 67 87 88
3 8 18 33 67 89 91
Output:
91 89 88 87 67 34 33 18 15 8 3 2
=== Sample test case 2 ===
Input:
28 36 57 59 68 69 420
17 37 57 59 68
Output:
420 69 68 59 57 37 36 28 17
Solutions
Expert Solution
Code---->
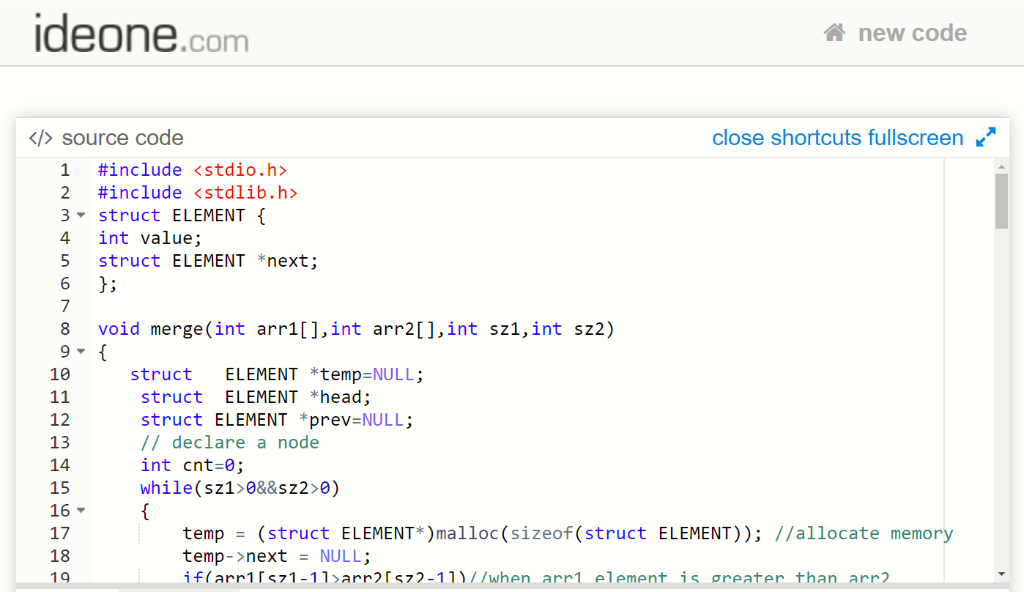
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ELEMENT {
int value;
struct ELEMENT *next;
};
void merge(int arr1[],int arr2[],int sz1,int sz2)
{
struct ELEMENT *temp=NULL;
struct ELEMENT *head;
struct ELEMENT *prev=NULL;
// declare a node
int cnt=0;
while(sz1>0&&sz2>0)
{
temp = (struct
ELEMENT*)malloc(sizeof(struct ELEMENT)); //allocate memory
temp->next = NULL;
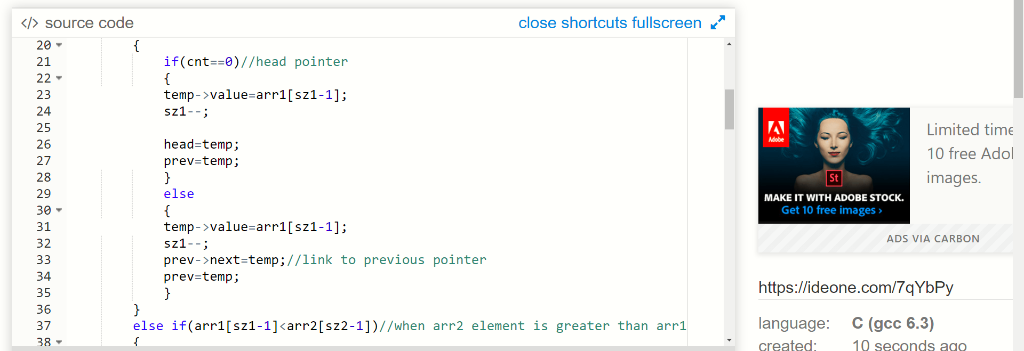
if(arr1[sz1-1]>arr2[sz2-1])//when arr1 element is greater than
arr2
{
if(cnt==0)//head
pointer
{
temp->value=arr1[sz1-1];
sz1--;
head=temp;
prev=temp;
}
else
{
temp->value=arr1[sz1-1];
sz1--;
prev->next=temp;//link to previous pointer
prev=temp;
}
}
else
if(arr1[sz1-1]<arr2[sz2-1])//when arr2 element is greater than
arr1
{
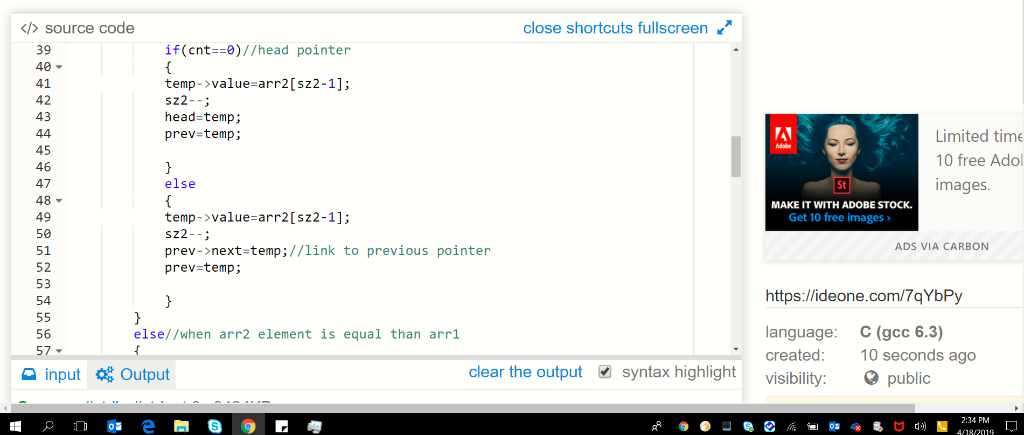
if(cnt==0)//head
pointer
{
temp->value=arr2[sz2-1];
sz2--;
head=temp;
prev=temp;
}
else
{
temp->value=arr2[sz2-1];
sz2--;
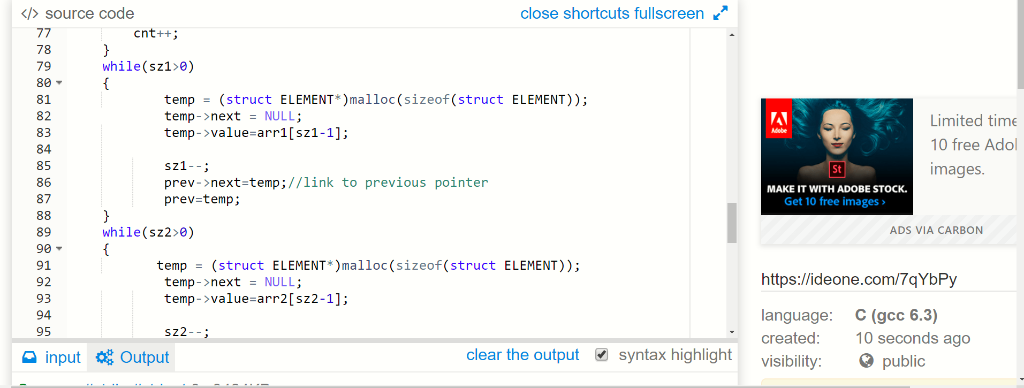
prev->next=temp;//link to previous pointer
prev=temp;
}
}
else//when arr2 element is equal
than arr1
{
if(cnt==0)//head
pointer
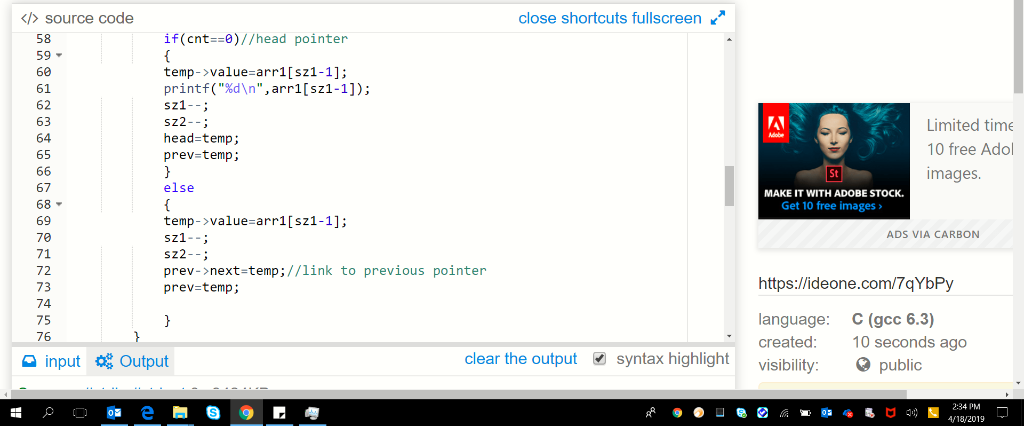
{
temp->value=arr1[sz1-1];
printf("%d\n",arr1[sz1-1]);
sz1--;
sz2--;
head=temp;
prev=temp;
}
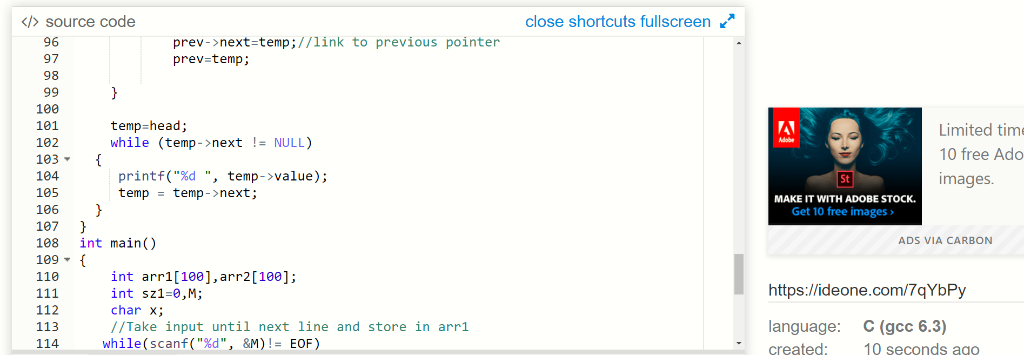
else
{
temp->value=arr1[sz1-1];
sz1--;
sz2--;
prev->next=temp;//link to previous pointer
prev=temp;
}
}
cnt++;
}
while(sz1>0)
{
temp = (struct
ELEMENT*)malloc(sizeof(struct ELEMENT));
temp->next = NULL;
temp->value=arr1[sz1-1];
sz1--;
prev->next=temp;//link to previous pointer
prev=temp;
}
while(sz2>0)
{
temp = (struct
ELEMENT*)malloc(sizeof(struct ELEMENT));
temp->next = NULL;
temp->value=arr2[sz2-1];
sz2--;
prev->next=temp;//link to previous pointer
prev=temp;
}
temp=head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", temp->value);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int arr1[100],arr2[100];
int sz1=0,M;
char x;
//Take input until next line and store in arr1
while(scanf("%d", &M)!= EOF)
{
arr1[sz1]=M;
scanf("%c",&x);
sz1++;
if(x=='\n')// Check for new line then break
break;
}
int sz2=0;
//Take input until next line and store in arr2
while(scanf("%d", &M)!= EOF)
{
arr2[sz2]=M;
scanf("%c",&x);
sz2++;
if(x=='\n')// Check for new line then break
break;
}
merge(arr1,arr2,sz1,sz2);
return 0;
}
Input:
28 36 57 59 68 69 420
17 37 57 59 68
output:
420 69 68 59 57 37 36 28
Ideone LINK :https://ideone.com/7qYbPy
 Any doubt ask in comments
section.Please Upvote.Thanks and regards
Any doubt ask in comments
section.Please Upvote.Thanks and regards
Related Solutions
Given two integer arrays sorted in the ascending order, code the function SortArrays to merge them...
Given two integer arrays sorted in the ascending order, code the function SortArrays to merge them...
Given two integer arrays sorted in the ascending order, code the function SortArrays to merge them...
in C++ Given two integer arrays sorted in the ascending order, code the function SortArrays to...
This phyton program takes in three integer parameters and displays them in ascending order. You can...
This is JAVA PROGRAMMING Sort the contents of the two files in ascending order and combine...
***C++ Coding*** Write a program for sorting a list of integers in ascending order using the...
C++ Write a program for sorting a list of integers in ascending order using the bubble...
Write a program that takes two integer arrays a and b of size n from the...
Write C program Multidimensional Arrays Design a program which uses two two-dimensional arrays as follows: an...
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
- Discuss pros and cons of using twins to estimate the rate of return to school
- John earned $59,000 of nominal income in 2017. The CPI is 242 for 2017. John earned...
- Write around 200 words only related to what do you understand about server virtualization.
 venereology answered 2 months ago
venereology answered 2 months ago