Question
In: Math
1. In a local agricultural reporting area, the average wheat yield is known to be 50...
1. In a local agricultural reporting area, the average wheat yield is known to be 50 bushels
per acre with a wheat yield standard deviation of 10 bushels. The wheat yield is known to
be approximately normally distributed.
a) What percentage of the wheat yield is below 40 bushels per acre?
b) If a random sample of 25 acres is selected, what is the probability that the sample
mean yield will be between 48 and 52 bushels?
2. The weight of cans of sardines from a production line are normally distributed with a
mean of 16.8 oz and a variance of 2.25 oz. For each run of the process, 100 cans are
selected randomly and weighted. What is the probability that the average weight of these
cans is between 16.5 and 17.1 oz?
3. The Sullivan Advertising Agency has determined that the average cost to develop a 30-
second commercial is P50,000. The cost is assumed to be normal. What is the probability
that a random sample of 25 commercials with a standard deviation of P6,000 will have a
mean cost of P51,582 or less?
4. Two sets of bolts are intended to have different lengths but the same diameter. The
diameters of bolts of Type I have a variance of 4 cm; the diameters of the bolts of Type II
have a variance of 12 cm. Random samples of 10 bolts of Type I and 20 bolts of Type II
are obtained. What is the probability that the sample means will differ by at least 1.5 cm?
5. A random sample of 10 students from QUAMETH EA has an average grade of 65 with a
variance of 25; an independent random sample of 18 students from QUAMETH EB has
an average grade of 70 with a variance of 20. Assume that the grades of the two sections
are independently normally distributed with the same variance and means differing by 5
with the average of grade of EB higher than that of EA. Find the probability that the
sample mean of QUAMETH EB is at least 10 points higher than the sample mean of
QUAMETH EA.
6. Manufacturers of golf balls are concerned with a scientific concept called the coefficient
of restitution, defined as the ratio of the relative velocity of the ball and club after impact
to the relative velocity before impact. A manufacturer has developed a new solid-core
golf ball which he wishes to sell side-by-side with his firm's standard brand. The mean
coefficient of restitution for the new solid-core ball and the firm's standard brand of golf
ball are 0.69 and 0.55, respectively. The standard deviations of the coefficient of
restitution are 0.18 for the solid-core golf ball and 0.22 for the firm's standard brand. The
coefficient of restitution of the two types of golf balls can be assumed to be normally
distributed. A large institutional buyer of golf balls selects a random sample of 25 solid-
core golf balls and another random sample of 21 standard golf balls to test and compare
the two brands. Referring to the samples:
a) What is the probability that the mean coefficient of restitution of the solid-core golf
ball is greater than that of the standard golf ball?
b) What is the probability that the variance of coefficient of restitution of the solid-core
golf ball is less than 0.01674?
c) What is the probability that the ratio of the variance of the solid-core golf ball to the
standard brand is between 1.3924 and 1.9145?
7. The washers used in a particular type of motor are required to be of uniform thickness and
are manufactured so that the thickness has a standard deviation of a 0.0001 cm. What is
the probability that the standard deviation of a random sample of 25 washers is between
0.000072 cm and 0.00014 cm? Assume normality of population.
8. The variance of population 1 is twice the variance of population 2. Independent random
samples of size 16 and 11 are taken from these two normal populations. What is the
probability that the sample variance from population 1 is less than 5.7 times the sample
variance from population 2?
9. It is known that 5% of the radio tubes produced by a certain manufacturer are defective. If
the manufacturer sends out lots containing 100 tubes, what is the probability that at least
98% of the tubes are good?
10. The proportion of male births in the country per week is 0.48. What is the probability that
UST Hospital, which normally carries out natal deliveries at the rate of 40 babies per
week, will deviate at most 10% from the national statistic?
11. The proportion of households who watch a TV special in Ilocos is 60%. In Leyte, the
proportion of households who watch the same special is 70%. If a sample of 50 is
obtained from each province, what is the probability that the sample proportion from
Ilocos is less than that of Leyte?
12. A manufacturer produces test tubes from two independent processes. Process 1 produces
10% defectives while Process 2 produces 15% defectives. Random samples of size 100
are obtained from each process on a daily basis. What is the probability that the sample
from Process 1 has fewer defectives than the of Process 2?
13. A new process will be installed if its mean processing time is at most 20 minutes. The
new procedure was tried. In a random sample of 50 trials, an average processing time of
22.2 minutes with a standard deviation of 4.3 minutes was obtained. At a level of
significance of 0.05, should the new process be installed?
14. The output of a chemical process is monitored by taking a sample of 20 vials to determine
the level of impurities. The desired mean level of impurities is 0.040 grams per vial. If the
mean level of impurities in the sample is too high, the process will be stopped and
purged; if the sample mean is too low, the process will be stopped and the values will be
readjusted. Otherwise, the process will continue.
a) Sample results provide sample mean to be equal to 0.047 grams with sample standard
deviation equal to 0.018. At a significance level of 0.01, should the process be
stopped? If so, what type of remedial action will be required?
b) Assume that the mean level of impurities is within tolerable limits. If the maximum
tolerable variability of the process is 0.0002, do the sample results verify the
suspicion that the maximum tolerable variability has been exceeded? Use a 5% level
of significance.
15. Two astronomers recorded observations on a certain star. The 35 readings obtained by the
first astronomer have a mean reading of 1.45. The 32 observations by the second
astronomer have a mean reading of 1.30. Past experience has indicated that each
astronomer obtains readings with a variance of 0.50. Is there any difference between the
mean readings of the two astronomers? Use a level of significance of 0.01.
17. An advertising executive claims 50% of the people who saw Voltes V will remember the
name of their product after they watched the show. If 65 viewers in a random sample of
150 remembered the name of the product after seeing the show, what conclusion can be
reached at the 1% level of significance?
18. In an attitude test, 55 out of 120 persons of Community 1 and 115 persons out of 400 of
Community 2 answered “Yes” to a certain question. Do these two communities differ
fundamentally in their attitudes on this question assuming a 5% level of significance?
20. An advertising company wants to determine if the cartoon series, Voltes V, appeals to
male viewers more than female viewers. Based on random telephone interviews, it was
found that 23 out of 48 females and 41 out of 90 females watch the series regularly. What
should the advertising company conclude at the 5% level of significance?
Solutions
Expert Solution
I can only answer one question at a time. Kindly specify the exact question for which you need the answer. For solving purpose I am providing the solution to the first question.
1) mean = 50 bushels per acre and sigma = 10; The wheat yield is assumed to be normally distributed.
a) Let X denote the wheat yield. We need to know:
P(X<40) = 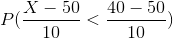
The first part is nothing but the standard normal variate i.e. Z. We need to know
P(Z<-1) = 0.1587 or we can say that 15.87% of the wheat yield is below 40 bushels per acre.
b) We are given that a random sample of 25 acres is selected. Thus the required probability can be written as:
P(48<X<52) = P(X<52) - P(X<48)
which is equal to
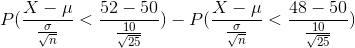
Using the standard normal tables we get:
P(Z<1) - P(Z<-1) = 0.8413 - 0.1587 = 0.6826
The probability that the sample mean yield will be between 48 and 52 bushels is 0.6826 or 68.26%.
Related Solutions
1. If the average product of 14 workers is 50 bushels of wheat and the average...
QUESTION 1 A sample of weights of 50 boxes of cereal yield a sample average of...
A local agriculture producer had a wheat yield last year of 72 bushels per acre. The...
1. The income elasticity for most staple foods, such as wheat, is known to be between...
Weights, standard deviation, and average returns for 50 stocks and a market index are known. The...
(1 point) An agricultural field trial compares the yield of two varieties of corn. The researchers...
1) A cereal farmer has a stock of wheat of 50 tonnes, and plans to sell...
The average yield on marketable securities is 9 percent/year; the fixed cost of transaction is $50...
1. aExplain why it is important to understand the accounting and reporting requirements for an area...
1. a. "On hold" times for callers to a local cable television company are known to...
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
 milcah answered 2 months ago
milcah answered 2 months ago