Question
In: Finance
Question 1 The market index experienced the following returns over the first 6 months of this...
Question 1
The market index experienced the following returns over the first 6 months of this year:
Month Return Month Return
January 0.68 April -1.71
February 5.43 May -2.44
March 1.12 June 3.58
What is the average return and standard deviation of returns over this six-month period?
Group of answer choices
1.33%, 2.75%
1.11%, 3.02%
1.11%, 2.33%
2.49%, 2.33%
Flag this question
Question 2
Which of the following investments is clearly preferred to the others?
Investment Return Standard Deviation
A 18% 20%
B 20% 20%
C 20% 18%
Group of answer choices
Investment B.
Investment C.
Investment A.
Cannot be determined without information regarding the risk aversion of the investor.
Flag this question
Question 3
What does beta measure?
Group of answer choices
The amount of credit risk the stock is exposed to
The amount of market risk the stock is exposed to
The amount of unique risk the stock is exposed to
The amount of business risk the stock is exposed to
Flag this question
Question 4
Orchestral Tissues Ltd has a beta of 1.35. The risk-free rate of return is 7 percent and return on the market portfolio is 11.5 percent. Using the CAPM, what is the required return on this Orchestral Tissues shares?
Group of answer choices
30.90%
13.08%
15.78%
8.94%
Flag this question
Question 5
In calculating the cost of capital for an average firm, which of the following statements is true?
Group of answer choices
The cost of a firm's retained earnings is less than the cost of its bonds.
The cost of a firm's ordinary shares is greater than the cost of its bonds.
The cost of a firm's preference shares is greater than the cost of its ordinary shares.
The cost of a firm's bonds is greater than the cost of its ordinary shares.
Flag this question
Question 6
Which of the following is a correct formula for calculating the cost of capital?
Group of answer choices
WACC = weighted cost of debt + weighted cost of preference shares + weighted cost of ordinary shares
WACC = (after-tax cost of debt + cost of preference shares + cost of ordinary shares )/3
WACC = weighted after-tax cost of debt + weighted cost of preference shares + weighted cost of ordinary shares
WACC = weighted after-tax cost of debt + weighted after-tax cost of preference shares + weighted after-tax cost of ordinary shares
Flag this question
Question 7
The last paid dividend is $2 for a share of ordinary shares that is currently selling for $20. What is the cost of ordinary equity if the long-term growth rate in dividends for the firm is expected to be 8%?
Group of answer choices
18.8%
12.8%
16.8%
14.8%
Flag this question
Question 8
Based on current market values, Shawhan Supply’s capital structure is 30% debt, 20% preference shares, and 50% ordinary shares. When using book values, capital structure is 25% debt, 10% preference shares, and 65% ordinary shares. The required return on each component is: debt—10%; preference shares—11%; and ordinary shares—18%. The marginal tax rate is 40%. What rate of return must Shawhan Supply earn on its investments if the value of the firm is to remain unchanged?
Group of answer choices
14.3%
10.0%
13.0%
18.0%
Flag this question
Question 9
________ measures the risk of a capital budgeting project by estimating the NPVs relating to a best case, base case and worst case cash flow estimates.
Group of answer choices
Monte Carlo analysis
Scenario analysis
Sensitivity analysis
Multiple regression analysis
Flag this question
Question 10
Jolly Roger Beverages Pty Ltd is considering purchasing one of two new rum fermenting machines to use at its Nowra distillery. The MegaDistiller 3000 costs $390,000 and is expected to have operating costs $33,000 per year for five years at which time it is considered worthless. The LiteBrewer 409 costs $350,000 and is expected to have operating costs of $29,500 per year for four years at which time it is considered worthless. Both machines perform the same function. The appropriate discount rate for the company is 10%. Based on an NPV analysis what should Jolly Roger Beverages do?
Group of answer choices
We do not have any information on revenues and therefore cannot make a decision.
Both have negative NPVs and therefore both should be rejected.
The company should buy the LiteBrewer 409.
The company should buy the MegaDistiller 3000.
Much appreciated!
Solutions
Expert Solution
1]
average return is 1.11%
standard deviation is 3.02%
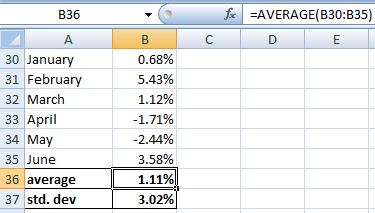
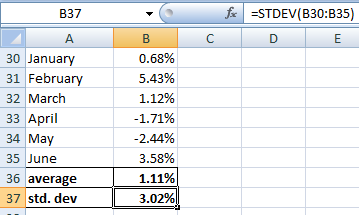
2]
Investment B is preferred over Investment A because Investment B has a higher return than Investment A for the same amount of risk.
Investment C is preferred over Investment B because Investment C has a the same return as Investment B, but with a lower amount of risk.
Hence, Investment C is clearly preferred to the others
3]
Beta measures market risk. It is the sensitivity of the security's price to changes in the overall market.
4]
required return = risk free rate + (beta * (market return - risk free rate))
required return = 7% + (1.35 * (11.5% - 7%)) = 13.08%
Related Solutions
A stock records the following returns over the last 6 months. What are the arithmetic returns...
A stock records the following returns over the last 6 months. What are the arithmetic returns...
A stock records the following returns over the last 6 months. What are the arithmetic...
The following monthly returns were observed on a security over 6 consecutive months: 5%, 2%, 6%,...
5. Suppose a spot price of a market index is $1000. After 6 months the market...
Question 1 a. Over the past twelve months, Lululemon had monthly returns of -5%, 0%, 0%,...
Consider the following 6 months of returns for 2 stocks and a portfolio of those 2...
Consider the following 6 months of returns for 2 stocks and a portfolio of those 2stocks:...
Assume that stock market returns have the market index as a common factor, and that all...
Assume that stock market returns have the market index as a common factor, and that all...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
 jeff jeffy answered 1 year ago
jeff jeffy answered 1 year ago