Question
In: Physics
1.) Motors and generators a) In a homopolar motor (like Faraday’s motor), what happens to the...
1.) Motors and generators
a) In a homopolar motor (like Faraday’s motor), what happens to the motion if the current is reversed?
b) Who was William Sturgeon and what was his connection to motor improvement?
c) What is the voltage induced in a generator with 974 turns, an area of 195 mm2 turning at a rate of 42 rpm with a constant field of 0.0209 T?
Solutions
Expert Solution
(a)In a homopolar motor (like Faraday’s motor), what happens to the motion if the current is reversed then the direction of the rotation of the blades will be also reversed.
(b) William Sturgeon was an English electrical engineer. In 1825 he built the first practical electromagnet, in 1832 invented the commutator for electric motors and in 1836 made the first moving-coil galvanometer and carried out research into atmospheric charge. His Annals of Electricity (1836) was the first journal of its kind in Britain. His electromagnet was capable of supporting more than its own weight. This device led to the invention of the telegraph, the electric motor, and numerous other devices basic to modern technology.
(c) Since, induced emf = NBA 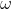
Here, N= 974, B = 0.0209 T, A = 195 mm2 = 195 x
10-6 m2 and 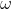 =42 rpm = 4.398
rad/s
=42 rpm = 4.398
rad/s
Therefore, induced emf = (974)(0.0209 T)(195 x 10-6 m2)(4.398 rad/s) = 0.01746 Volts
Related Solutions
What happens to the market for generators in areas hit by a hurricane when the price...
1. Motor Company manufactures two types of specialty electric motors, a commercial motor and a residential...
A robotic arm is controlled by several stepper motors. Stepper motor (or step motor) is a...
Pineapple Motor Company manufactures two types of specialty electric motors, a commercial motor and a residential...
Pineapple Motor Company manufactures two types of specialty electric motors, a commercial motor and a residential...
Pineapple Motor Company manufactures two types of specialty electric motors, a commercial motor and a residential...
Pineapple Motor Company manufactures two types of specialty electric motors, a commercial motor and a residential...
Pineapple Motor Company manufactures two types of specialty electric motors, a commercial motor and a residential...
1. Generators: A. What is the use of each essential part of a generator? B. What...
Explain what a faraday’s cage and it’s importance in Physics?
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
 genius_generous answered 1 year ago
genius_generous answered 1 year ago