Question
In: Economics
Describe the consequences of a permanent decrease in the US Money Supply for the nominal exchange...
Describe the consequences of a permanent decrease in the US Money Supply for the nominal exchange rate and for the US interest rate, in the short run as well as over time and in the long run. Draw time path plots for real money balances in the US, the nominal exchange rate, and the interest rate. Explain how your results relate to the idea of “exchange rate overshooting,” in no more than one paragraph.
Solutions
Expert Solution
We assume flexible exchange rates and perfect capital mobility to depict consequences of decrease in the money supply.
- Suppose, Fed decreases the US Money supply permanently. Now in short run, prices are sticky so goods market will adjust slowly and prices won't change immediately. However, financial market will adjust quickly. The LM Curve will shift left to LM' and at point e' interest rate rises. This is also called liquidity effect.

- The decease in MS induces a current appreciation of the US$, so the nominal exchange rate decreases.
- Given the interest rate parity
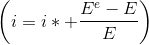 and rise in interest rate, there shall be decrease in Ee and
future depreciation of the exchange rate.
and rise in interest rate, there shall be decrease in Ee and
future depreciation of the exchange rate. - In order to generate an expected depreciation, the currency over-appreciates (i.e. overshoots) in short-run vs. it's long-run level.
- The currency appreciation, together with ΔP = 0 in the short-run, implies that q falls, and IS shifts to the left to IS'
- The shifts in IS and LM shift aggregate demand, which equals short-run aggregate supply. There is an decrease in output produced at point e1.
- Deficit in the aggregate demand reduces the prices in the US economy. Consequently, the decreased price level increases real money supply so the LM shifts back to its initial equilibrium. The interest rate falls to its initial position, and as this happens the domestic currency depreciates.
- The decreased prices, together with the currency depreciation, improves the U.S. economy's competitive advantage in the goods market (so the change in q is a sum of change in E and P), and IS shifts back to its initial level at point e.
- After so many adjustments, we finally reach the initial real equilibirum (Point e) with reduced prices and appreciated nominal exchange rate.
We can show above adjustment with time path which are similar to Exchange overshooting model.
- Suppose, Fed decreases the US Money supply by 10% from $100 billion to $90 billion and keeps it at this level permanently.
- As per above, the U.S. interest rate will rise immediately - say from 10% to 11% at time t0.
- Now, as per interest rate parity the interest rates in US are higher than the Rest of the world interest rate. Consequently, investors will increase demand for the US dollar to purchase US bonds. The immediate impact would be appreciation or decrease in the exchange rate. We assume dollar immediately appreciate by more than the 10 percent - say from $1 to $0.84 in the short run, so that in the long run it reaches long-run equilibirum of $0.90 by slow depreciation.
- The above happened due to the uncovered interest parity
condition which is explained by equation
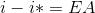 or
or 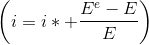 . The UIP says that interest differential between two countries
will always be equal the expected change in the exchange rate
between two currencies.
. The UIP says that interest differential between two countries
will always be equal the expected change in the exchange rate
between two currencies. - We can see that dollar appreciated more in the short run i.e. by 16%. However, it depreciate by 6% in the long run to remove excess appreciation at time t0. This is also necessary to hold PPP theory

This explanation is similar to the Dornbusch exchange rate overshooting model as we can clearly see that exchange rate overshoots due to the price expectations. Though prices were sticky and couldnot adjust quickly in the short run, their expectations changed quickly. Thus, explaining volatility in the exchange rates.
Related Solutions
Explain the exchange rate overshooting with a permanent decrease in the country's money supply by using...
From the equation of exchange, we know that a change in the money supply changes nominal...
Consider the short-run effect of a decrease in US money demand on interest rates and exchange...
Describe how a decrease in money supply on the monetary side of the economy is transmitted...
Describe how a decrease in the money supply on the economy causes the AD curve to...
use money supply and money demand model to show how a decrease in money supply shifts...
1. For some reason there is a permanent increase in money supply in the Country A...
What tools can the FED use to increase or decrease the money supply. Describe it full....
Explain how a decrease in the money supply affects the money market and the position of...
5. A. The initial impact of a rise in the nominal money supply will be to...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
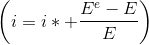 and rise in interest rate, there shall be decrease in Ee and
future depreciation of the exchange rate.
and rise in interest rate, there shall be decrease in Ee and
future depreciation of the exchange rate.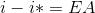 or
or  Rahul Sunny answered 1 year ago
Rahul Sunny answered 1 year ago