Questions
Capsular Staining. Some bacterial cells are enclosed with an extracellular gel-like layer that occurs outside the...
- Capsular Staining. Some bacterial cells are enclosed with an extracellular gel-like layer that occurs outside the cell wall. Capsules are pathogenic factors that also function in attachment. If the capsule stain is not properly prepared the gel-like material may shrink and will not be seen during microscopy. Which of the following is INCORRECT?
- a capsular stain was used to prepare Klebsiella pneumonia slides for microcopy
- the smear is air-dried
- the smear was heat fixed
- all the above are incorrect
- none of the above are incorrect
- Differential Staining requires the use of more than one chemical stain. QUESTION: The Gram Stain is a NOT a Differential Stain. T or F
- Motility in bacteria can be determined
using which of the following methods
- Wet mount
- Flagella stain and wet mount
- Wet mount and SIM media
- Wet mount, flagella, stain, or SIM media
- Biochemical Procedures that use selective & differential media identify:
- the shape and arrangement of bacteria
- the microscopic properties of bacteria
- enzymatic properties of bacteria
- the size characteristics of bacteria
- In a SIM test, one SIM tube was inoculated with two unknown bacteria. The results were then used to identify both bacteria. T or F
- Selective Medium support the growth of one type of organism and inhibits the growth of another. T or F
- Sulfide, Indole, Motility (SIM): Bacteria that have the enzyme tryptophanase, can convert the amino acid tryptophan to indole. Indole reacts with Kovac’s reagent to form a Black Color. T or F
- GROWTH ON EMB & MAC: Which Observations are INCORRECT?
- both EMB and MAC contain dyes that inhibits gram-positive bacteria.
- both EMB and MAC differentiate gram negative organisms based on their ability to ferment lactose
- both EMB and MAC indicate that the pH becomes basic (alkaline) because of fermentation
- all the above are incorrect
- none of the above
- GROWTH On MSA (7.5% NaCl). Which
Observations are CORRECT?
- MSA is selective for Staphylococci
- Staphylococci species are Gram +
- MSA is differential based on acid production
- Acid production on MSA changes the phenol red (acid indictor) to yellow
- All the above
- Blood Agar is differential with
respect to Hemolysis. Which of the following is CORRECT?
- hemolytic enzymes are produced in produced hemolysis
- Beta (ß) hemolysis and results in the complete breakdown of the RBCs
- Alpha (a) hemolysis Partial destruction of the RBCs leads to a greenish brown color
- Gamma(γ)hemolysis causes no damage to the RBCs
- all the above are correct
- Blood Agar Plates have the enzyme catalase. We use blood agar to determine whether an unknown bacterium is catalase positive. T or F
- Differential and/or Selective Media
include EMB, MSA, MAC, Blood Agar Plates, Simmons Citrate
& SIM Tubes. Regarding what was observed on these media, which
is CORRECT?
- a change in color on any of those media means we are looking at the result of enzyme activity
- acid production, or no -acid production indicate the presence or absence of specific enzymes
- all the above are correct
- none of the above are correct
- A pH sensitive dye (in media) responds to acid
production with a change in color, and
- MacConkey (MAC) media turns reddish
- Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar media inoculated with Escherichia coli produces a green metallic sheen
- Mannitol-salt agar (MSA) turns yellow
- all the above
- none of the above
- Page 284 of Benson’s summaries some “characteristics of
common Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial Species.”. The
Table identifies a list of Gram (-) bacteria that are all catalase
+. Which of the following makes sense?
- the catalase test can be used to categorize bacteria., i.e. they can be categorized as catalase (+ or -)
- the catalase test alone could be used to identify a specific Gram (-) bacteria on that list
- all the above makes sense
- none of the above makes sense
In: Biology
Label the four mutated DNA segments shown below according to the type of point mutation each represents.
Label the four mutated DNA segments shown below according to the type of point mutation each represents. Use the codon table above to determine how each mutation would affect the amino acid coding for each segment.
Drag the labels to their appropriate locations to identify the type of point mutation shown.
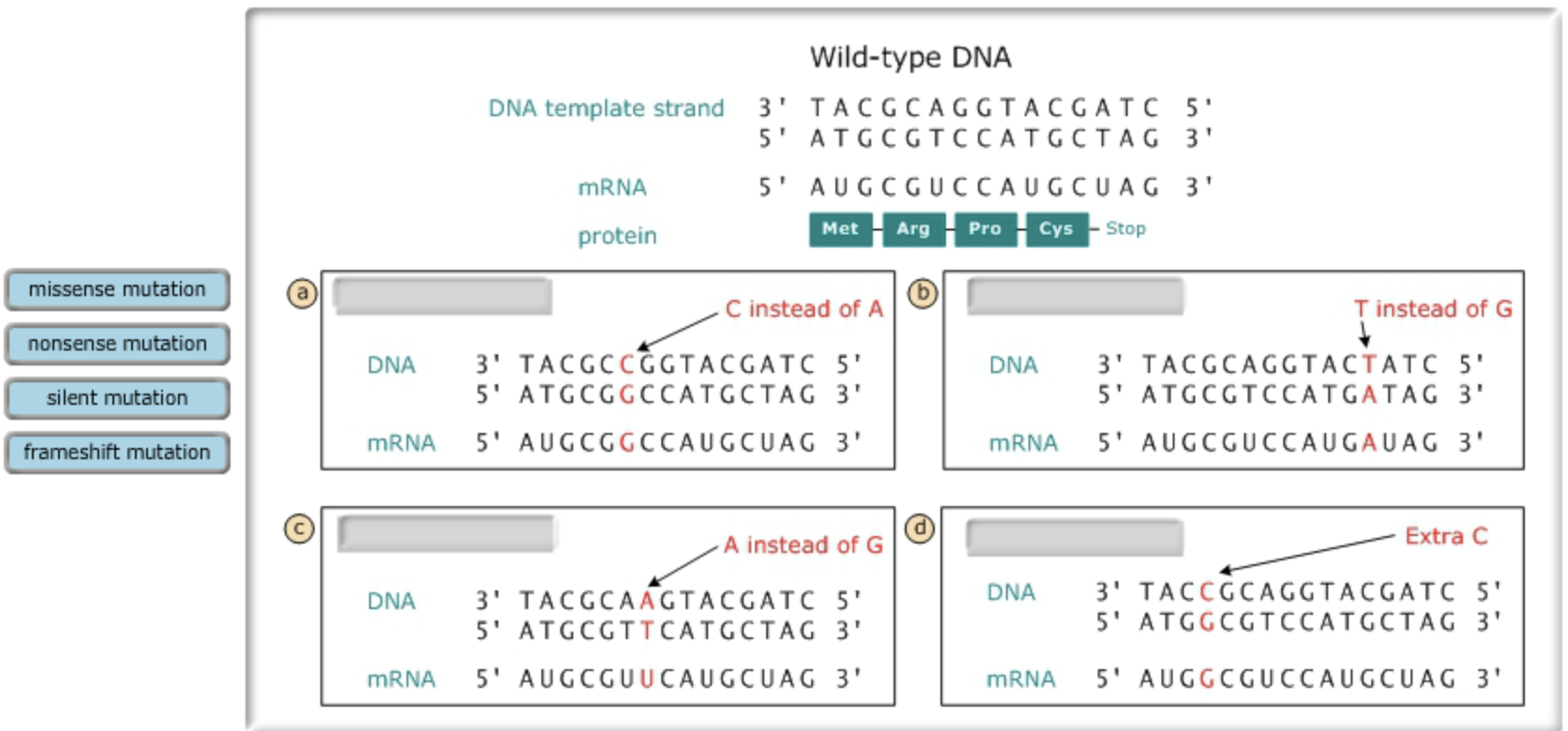
In: Biology
1) What is BLAST? What does it do? What is in a BLAST "result"? What is...
1) What is BLAST? What does it do? What is in a BLAST "result"? What is an "alignment" in the case of BLAST?
2) There is always a symbol indicating a relationship between each pairwise amino acid in the query and subject; what do the different symbols mean?
"+" vs "-" vs " " vs "<a specific letter matching letter>"
In: Biology
Given the DNA strand, 3’ TTG-TAA-CGC-CAT-ATG-GAC-AGC 5’, what is the resulting amino acid sequence of this...
Given the DNA strand, 3’ TTG-TAA-CGC-CAT-ATG-GAC-AGC 5’, what is the resulting
amino acid sequence of this polypeptide?
. What tRNA anti codon would bind to each mRNA codon in the last part? Draw how this works by
drawing the mRNA interacting with the tRNA in the ribosome.
In: Biology
5. Draw a diagram with the following components : a.) mRNA with 15 nucleotides (indicate the...
5. Draw a diagram with the following components :
a.) mRNA with 15 nucleotides (indicate the sequence); label 5’
and 3’ ends.
b.) small and large ribosomal subunits (show the tRNA binding sites
and label them A,P,E)
c.) tRNA carrying an amino acid that corresponds to the codon being
read by the ribosome
In: Biology
“Protein A” is phosphorylated at one amino acid by a kinase, “protein B”, and dephosphorylated by...
“Protein A” is phosphorylated at one amino acid by a kinase, “protein B”, and dephosphorylated by a phosphatase, “protein C”.
You have purified all three of these proteins and want to determine the structural changes that occur when protein A is phosphorylated or dephosphorylated. Explain in detail how you would go about designing and conducting this investigation.
In: Biology
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disease resulting from a single amino acid substitution in the...
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disease resulting from a single amino acid substitution in the hemoglobin β chain. This mutation causes hemoglobin to polymerize into strands in the deoxygenated state, leading to the erythrocytes forming a sickled shape. Why does the mutation lead to polymerization and why does this only occur in the deoxygenated state?
In: Biology
Human Resource professionals has certain set of skills, give at least five (5) essential human resource...
Human Resource professionals has certain set of skills, give at least five (5) essential human resource management skills needed to run a successful human resource department and explain how these skills are used. Provide an examples.
In: Economics
How is fat digested and absorbed after eating a peanut and jelly sandwich on whole wheat...
How is fat digested and absorbed after eating a peanut and jelly sandwich on whole wheat including the constituents representing fat and how and where they are digested and absorbed and how and where fat is utilized or stored in the body. Include the chemical, hormonal, and enzyme changes that impact the proper environment of this meal.
In: Nursing
5. Give an example each of a glycerophospholipid and a glycolipid. What are the products of...
5. Give an example each of a glycerophospholipid and a glycolipid. What are the products of their complete hydrolysis? Show on a hand-drawn diagram the action of each hydrolytic enzyme to release the products you mentioned?
|
Name |
Product of complete hydrolysis |
|
|
Glycerophospholipid |
||
|
Glycolipid |
Diagram of positions acted upon by the hydrolytic enzymes:
In: Biology