Questions
Which of the following terms would be used to describe a food that is good at...
Which of the following terms would be used to describe a food that is good at providing all of the essential amino acids?
Question 19 options:
|
A qualified protein |
|
|
A high-quality protein |
|
|
A low-quality protein |
|
|
A plant food |
|
|
A complementary protein |
Why are nonessential amino acids said to be nonessential?
Question 17 options:
|
All of the answers are correct |
|
|
Because they are only obtained through your diet |
|
|
Because they are only needed during times of rapid development |
|
|
Because they can be made by the body |
|
|
Because your body functions fine without them |
Which of the following lipids improve blood cholesterol levels?
Question 7 options:
|
Monounsaturated fats |
|
|
Saturated fats |
|
|
Trans fats |
|
|
Monosaccharaides |
|
|
Lipase |
True or false: All lipids are fats.
In: Biology
Look at this undecapeptide: Arg Asp Cys Glu Leu Lys Met Phe NH4+. What would each...
Look at this undecapeptide: Arg Asp Cys Glu Leu Lys Met Phe NH4+. What would each step do to the udecapeptide? Draw the final structure.
a. treatement with iodoacetate that had no affect on the undecapeptide.
b. treatment with 2 x 2-mercaptoethanol yielding a tripe-tide and octapeptide.
c. treatment with carboxypeptidase A liberated leucine.
d. treatment with cyanogen bromide yielding a methionine, a tripeptide and a heptapeptide.
The question states that these amino acids are only some components of the undecapeptide structure and that some amino acids within this structure may be repeated. The point is to determine the correct structure following several treatments. After these treatments, what conclusions can you make about the structure of the undecapeptide? What might the structure be?
In: Biology
Amino Acids and Proteins Lab, post lab questions 1.Which samples gave positive results in the biuret...
Amino Acids and Proteins Lab, post lab questions
1.Which samples gave positive results in the biuret test? Were there any differences in the color and intensity of the positive test results? How general is the biuret test for detecting proteins of different types?
2. Which amino acids are identified by means of the xanthoproteic test? Which protein samples gave positive xanthoproteic test results? Comment on the composition of the protein samples based on the results of this test.
3. Which amino acids are identified by means of the Sakaguchi test? Which protein samples gave positive Sakaguchi test results? Comment on the composition of the protein samples based on the results of this test.
4. Which amino acids are identified by means of the nitroprusside test? Which protein samples gave positive nitroprusside test results? Comment on the composition of the protein samples based on the results of this test.
5. Compare and contrast the effect of strong acid (HCl) on albumin, casein, and gelatin. Which protein was most sensitive to the action of strong acid? Least sensitive?
6. Which metal salts (CuSO4 and AgNO3) caused albumin denaturation? How does this observation relate to the toxicity of silver salts versus copper salts?
7. You have just been to the doctor’s office to receive an inoculation. Before administering the injection, the doctor wipes the area with an alcohol swab. Do the results for albumin denaturation support the use of isopropyl alcohol as a disinfectant? Explain.
8. The biuret test is used to identify proteins. Compare the results obtained in the biuret test with albumin and the filtrate after the salting-out procedure in Part B. How effective is the “salting-out” procedure with ammonium sulfate?
9. Is denaturation of albumin by ammonium sulfate reversible or irreversible? Explain on the basis of your observations for the biuret test with albumin and the redissolved precipitate, respectively.
In: Chemistry
Fill in the blanks with the following terms: Lactate NAD+ fermentation NADH aerobic anaerobic acetyl CoA...
Fill in the blanks with the following terms:
Lactate NAD+ fermentation
NADH aerobic anaerobic acetyl CoA
When oxygen is available during glycolysis, the three-carbon
pyruvate may be oxidized to form:
(1) ___________________ + CO2, The coenzyme (2) _________________
is reduced to (3) ___________.
Under (4) _______________ conditions, pyruvate is reduced to (5)
_________________. In yeast, pyruvate forms ethanol in a process
known as (6) __________________.
Associate each of the following descriptions with pathways in
glycogen metabolism:
a. glycogenesis b. glycogenolysis
1. _____ breakdown of glycogen to glucose 2._____ activated by
glucagon
3. _____ starting material is glucose-6-phosphate 4._____ synthesis
of glycogen from glucose
5. _____ activated by insulin 6._____ UDP activates glucose
Gluconeogenesis: Glucose Synthesis
Associate each of the following descriptions:
a) gluconeogenesis b) pyruvate c) pyruvate kinase
d) pyruvate carboxylase e) Cori cycle
1. _____ an enzyme in glycolysis that cannot be used in
gluconeogenesis
2. _____ a typical non-carbohydrate source of carbon atoms for
glucose synthesis.
3. _____ a process whereby lactate produced in muscle is used for
glucose synthesis in the liver and used again by the muscle.
4. _____ the metabolic pathway that converts non-carbohydrate
sources to glucose.
5. _____ an enzyme used in gluconeogenesis that is not used in
glycolysis.
6. _____ a metabolic pathway that is activated when glycogen
reserves are depleted.
Match each of the following with the correct metabolic
pathway:
A. glycolysis B. glycogenolysis C. gluconeogenesis
D. glycogenesis E. fermentation
1. _____ conversion of pyruvate to alcohol
2. _____ breakdown of glucose to pyruvate
3. _____ formation of glycogen
4. _____ synthesis of glucose
5. _____ breakdown of glycogen to glucose
In: Biology
Reverse Transcriptase (RTase) is an enzyme found in HIV. What is the function of this enzyme...
Reverse Transcriptase (RTase) is an enzyme found in HIV. What is the function of this enzyme in HIV’s life-cycle? What are some uses of RTase for human applications?
In: Biology
18. What attracts or directs the synthesis enzyme to the template in DNA Replication? a. Start...
18. What attracts or directs the synthesis enzyme to the template in DNA Replication? a. Start Codon b. Promoter c. 5'-cap d. Primer e. Poly-A Tail
32. Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? a. human genes do not have introns b. introns encode for gene products c. introns are part of the mRNA that are translated d. introns have no function
28.Protein function? a. is determined b interaction of amino groups with other molecules b. is the same even with single amino acid modifications resulting from mutations c. will not change in different environments d. will not be affected by pH e. is dependent on its three-dimensional structure
36.There are FOUR major events in cell division. Which of the following is NOT one of them? a. Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm and separation of the two new cells b. DNA segregation, which is the distribution of the DNA into the two new daugther cells c. Cell cycle arrest to allow the cells to recuperate d. Reproductive signals initiate cell division e. DNA Replication
In: Biology
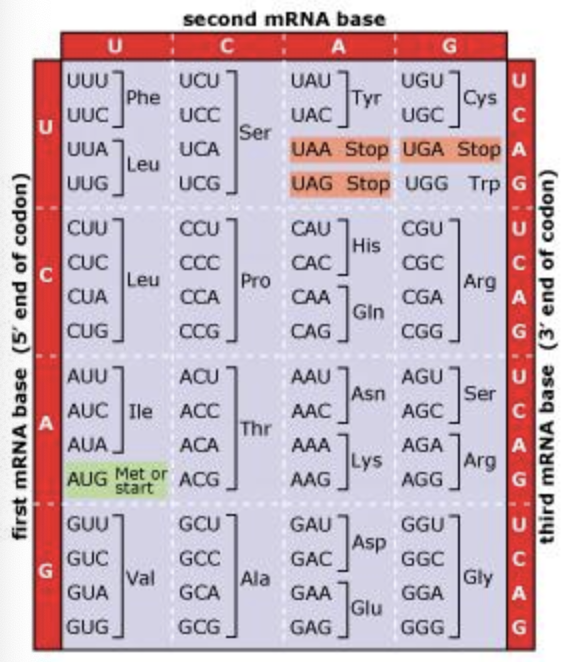
Based on the genetic code chart below, which of the following would be the result of this single base-pair substitution?
The diagram below shows an mRNA molecule that encodes a protein with 202 amino acids. The start and stop codons are highlighted, and a portion of the nucleotide sequence in the early part of the molecule is shown in detail. At position 35, a single base-pair substitution in the DNA has changed that would have been a uracil (U) in the mRNA to an adenine (A).
Based on the genetic code chart below, which of the following would be the result of this single base-pair substitution?
- A. a silent mutation (no change in the amino acid sequence of the protein)
- B. a frameshift mutation causing extensive change in the amino acid sequence of the protein
- C. a missense mutation causing a single amino acid change in the protein
- D. a frameshift mutation causing a single amino acid change in the protein
- E. a nonsense mutation resulting in early termination of translation
In: Biology
What types of modifications can occur after a polypeptide chain has been completed by a ribosome?...
What types of modifications can occur after a polypeptide chain has been completed by a ribosome? (Choose as many that apply) A) Glycosylation B) Removal of methionine C) Hydrolysis D) Addition of amino acids E) Phosphorylation
In: Biology
What types of modifications can occur after a polypeptide chain has been completed by a ribosome?...
What types of modifications can occur after a polypeptide chain has been completed by a ribosome? (Choose as many that apply)
A) Glycosylation
B) Removal of methionine
C) Hydrolysis
D) Addition of amino acids
E) Phosphorylation
In: Chemistry
You are to test the effectiveness and specificity of ninhydrin by spraying spots of water, the...
You are to test the effectiveness and specificity of ninhydrin by spraying spots of water, the protein bovine serum albumin (BSA), and amino acids with ninhydrin. What do you predict the results will be, and why? What assumptions must you make?
In: Chemistry