Questions
Research the financial press (online media) to find two companies that merged within the last 5...
Research the financial press (online media) to find two companies that merged within the last 5 years. Determine or estimate the following:
(maybe the companies, Saudi Aramco and SABIC)
- Summarize the chronology of events from the first offer that was made by the acquiring firm until the final acquisition was agreed. Include information about other firms that were involved, even in an indirect manner (for example, where there any “white knights” out there?) and the potential synergies that drove the merger, if any.
- Was the deal 1) all equity, 2) all cash, or 3) a combination thereof?
- Consider your answer to part (c). Is this a taxable event to 1) the target firm’s existing shareholders, and 2) the acquiring firm’s existing shareholders?
- Was there a premium offered for the shares of the target firm?
If so, try to approximate it
.
In: Finance
4) Consider a decision that you made recently (i.e. within the last two weeks or so)....
4) Consider a decision that you made recently (i.e. within the last two weeks or so). Answer the following questions:
-
a) What were the benefits and costs that you considered when making your decision?
-
b) Would any of those costs that you identified in (a) above be considered sunk costs?
-
c) Were there any additional marginal benefits or marginal costs associated with the decision that you think you should have considered?
In: Economics
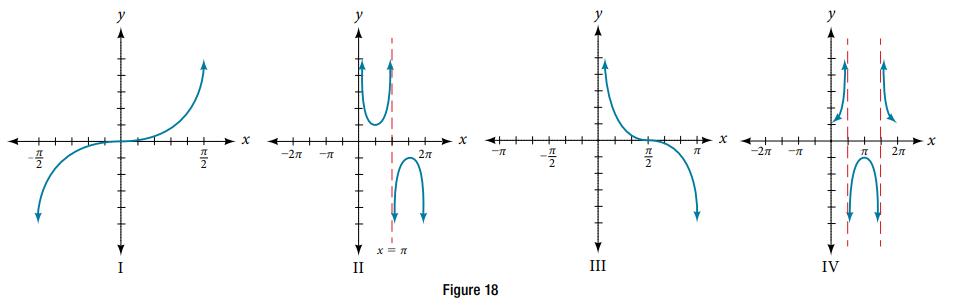
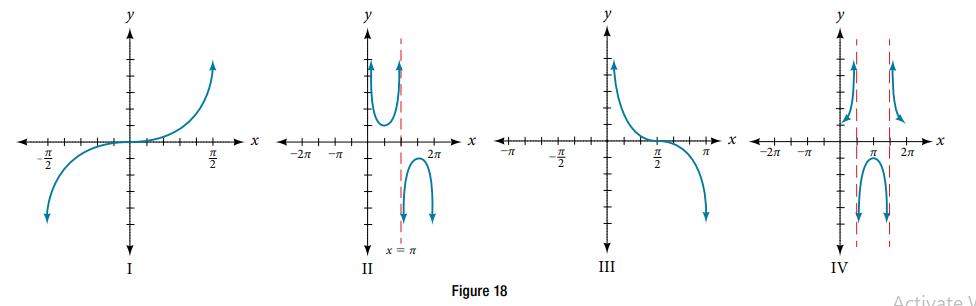
For the following exercises, match each trigonometric function with one of the graphs in Figure 18. f(x) = sec x
For the following exercises, match each trigonometric function with one of the graphs in Figure 18.
f(x) = sec x
In: Advanced Math
For the following exercises, match each trigonometric function with one of the graphs in Figure 18. f(x) = tan x
For the following exercises, match each trigonometric function with one of the graphs in Figure 18.
f(x) = tan x
In: Advanced Math
A PC store sells many types of computers. The PC can have either 16 or 8...
A PC store sells many types of computers. The PC can have either 16 or 8 gigabytes of memory.
The quality of the PCs can be either New, Refurbished, or Dented.
The price list is given as follows:
Memory size/Status New Refurbished Dented
16 gigabytes 849.99 729.99 609.99
8 gigabytes 699.99 579.99 439.99
Determine the price of a given PC dependent on the user inputs. The sale tax is 9.25% for each PC.
User input can only be 8 or 16 for memory size and 'N', 'R', or 'D' for quality (upper-case). The input quantityt should be 0 or positive.
If any user input is not correct, display an error message and skip all calculation.
All currency amount should be displayed with 2 digits in decimal fraction.
Here are several separate program sample runs. There is No need to use loop for repetition.
Enter the memory size of the PC (8 or 16 gigabytes): 16
Enter the quality of the PC (N for New, R for Refurbished, or D for Dented): N
Enter PC quantity want to buy: 2
The item price is $1699.98
The sale tax is $157.25
The total bill is $1,857.23
----------------------
Enter the memory size of the PC (8 or 16 gigabytes): 8
Enter the quality of the PC (N for New, R for Refurbished, or D for Dented): R
Enter PC quantity want to buy: 3
The item price is $1739.97
The sale tax is $160.95
The total bill is $1900.92
----------------------
Enter the memory size of the PC (8 or 16 gigabytes): 15
Invalid memory size!
----------------------
Enter the memory size of the PC (8 or 16 gigabytes): 8
Enter the quality of the PC (N for New, R for Refurbished, or D for Dented): A
Invalid PC quality!
----------------------
Enter the memory size of the PC (8 or 16 gigabytes): 8
Enter the quality of the PC (N for New, R for Refurbished, or D for Dented): (user hit Tab key)
Invalid PC quality!
----------------------
Enter the memory size of the PC (8 or 16 gigabytes): 16
Enter the quality of the PC (N for New, R for Refurbished, or D for Dented): R
Enter PC quantity want to buy: -2
Invalid PC quantity!
[C++ PROGRAMING]
In: Computer Science
A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. Air resistance is...
A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. Air resistance is considered negligible. (1) At what time does it reach the peak? (2) What is the maximum height it reaches? (3) What is speed of the stone just before it hits the ground?
The velocity of a 1-kg particle moving along the x axis changes from vi = -2m/s to vf = -5m/s in 3s. (1) What are the change in momentum and impulse for vi = –2m/s and vf = –5m/s? (2) What is the average force acting in the 3s duration
At time t = 0s a 2-kg particle has a velocity of (4 m/s) � – (3 m/s) �. At t = 3 s its velocity is (2 m/s) � + (3 m/s) �. (1) What is the average force acting during the time interval between t=0s and t=3s? (2) What is the change of the kinetic energy of the particle in the same time interval? (3) What is the average power in the same time interval?
In: Physics
Jackson Smith, a 18 year-old male, was admitted to the Emergency Department at 9pm with severe...
Jackson Smith, a 18 year-old male, was admitted to the Emergency Department at 9pm with severe breathlessness. His family informed you that the patient has a history of Asthma that had been diagnosed when he was two years old. On admission to the Emergency Department the clinical manifestations were:
- Severe dyspnoea, inability to speak sentences in one breath
- Respiratory rate of 32 breaths/minute
- SpO2 94%, on room air
- Pulse rate of 130 beats/minute
- Auscultation of lungs identifies diminished breath sounds and widespread wheeze
- Chest x-ray shows clear and hyper-inflated lung fields
A provisional diagnosis of Acute Severe Asthma is made.
This is the case, and how would you explain or describe the clinical manifestation and the pathogenesis causing the clinical manifestations with which Mr Smith presented.
In: Nursing
A person commits a crime in a city with a population of 5 million. A suspect...
A person commits a crime in a city with a population of 5 million. A suspect is identified and arrested. Moreover, the suspect’s DNA matches a sample found at the crime scene. The odds of an erroneous DNA match are one in 1 million. At trial, the prosecutor uses this one-in-a-million statistic to argue that the suspect is guilty. However, the suspect’s defense attorney is well-trained in statistics, and is able to show that there is in fact an 83% chance that an innocent person’s DNA would match the sample found at the crime scene. How did he arrive at this conclusion?
In: Statistics and Probability
8 Question Please match the explanation to the term concerning learning. Learning by association 1. Classical...
8 Question
Please match the explanation to the term concerning learning.
Learning by association
1. Classical conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Learning by observation
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Learning by consequence
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Anything that increases the response rate
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Anything that decreases the response rate
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Positive punishment and negative reinforcement
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Noting similarities
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Negative reinforcement and negative punishment
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Positive punishment
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
To note differences
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
The waning of the response due to the removal of the reward
1. Classical
conditioning
2. Toxic side effects
3. Social-Learning
4. Punishment
5. Difficult to control
6. Aversive conditioning
7. Reinforcement
?
In: Psychology
Assume that R1 = 44 Ω , R2 = 75 Ω , R3 = 19 Ω...
Assume that R1 = 44 Ω , R2 = 75 Ω , R3 = 19 Ω , R4 = 79 Ω , R5 = 20 Ω , and R6 = 23 Ω .
fig 1

fig 2

fig 3

fig 4

Part A
Find the equivalent resistance of the combination shown in the figure (Figure 1) .
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Req =______ Ω
Part B
Find the equivalent resistance of the combination shown in the figure (Figure 2) .
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Req =______ Ω
Part C
Find the equivalent resistance of the combination shown in the figure (Figure 3) .
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Req =______ Ω
Part D
Find the equivalent resistance of the combination shown in the figure (Figure 4) .
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Req =______ Ω
In: Physics