Questions
On September 1, 2016, Carolina Electronics Company has 1,000 Blu-ray players ready for sale. On October...
On September 1, 2016, Carolina Electronics Company has 1,000 Blu-ray players ready for sale. On October 1, 2016, 900 are sold, on account, at $125 each with a 1-year assurance-type warranty. Carolina estimates that the warranty cost on each Blu-ray player sold will probably average $10 per unit. During the final 3 months of 2016, Carolina incurred warranty costs of $4,000, and in 2017 warranty costs were $5,000.
Required:
| 1. | Prepare the journal entries for the preceding transactions. |
| 2. | Show how the preceding items would be reported on the December 31, 2016, balance sheet. |
| 3. | Prepare the journal entries for the preceding transactions using the modified cash basis method. |
| 4. | Next Level Which method produces the better measure of income? Why? |
| CHART OF ACCOUNTS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carolina Electronics Company | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Ledger | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Prepare the necessary journal entries to record:
| 1. the sale of Blu-ray players on account on October 1, 2016 | |
| 2. the related warranty accrual on October 1, 2016 | |
| 3. the warranty costs paid during the last quarter of 2016 | |
| 4. the warranty costs paid during the 2017 | |
| Additional Instructions |
PAGE 9
GENERAL JOURNAL
| DATE | ACCOUNT TITLE | POST. REF. | DEBIT | CREDIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
|||||
|
2 |
|||||
|
3 |
|||||
|
4 |
|||||
|
5 |
|||||
|
6 |
|||||
|
7 |
|||||
|
8 |
Prepare the necessary journal entries to record the above transactions using the modified cash basis method.
PAGE 9
GENERAL JOURNAL
| DATE | ACCOUNT TITLE | POST. REF. | DEBIT | CREDIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
|||||
|
2 |
|||||
|
3 |
|||||
|
4 |
|||||
|
5 |
|||||
|
6 |
Show how the items would be reported on the December 31, 2016, balance sheet under U.S. GAAP. Additional Instructions
|
Carolina Electronics Company |
|
Partial Balance Sheet |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
1 |
Current Liabilities: |
|
|
2 |
Which method produces the better measure of income? Why?
Select the item below that is true in response to the better measure of income and the reason why.
The modified cash basis method provides the better measure of income because it properly matches warranty costs to the revenues that the warranties helped generate. This method also creates a contingent liability representing a company’s expected use of resources.
The accrual method provides the better measure of income because it properly matches warranty costs to the revenues that the warranties helped generate. This method also creates a contingent liability representing a company’s expected use of resources.
The direct expense method provides the better measure of income because it expenses warranty costs when incurred.
Under the accrual method, a company’s liabilities will be misstated. In addition, the accrual method misstates warranty expense, and income, because the actual warranty repair occurs in a period other than the period in which the sale occurs.
In: Accounting
Rule Ltd acquired all the issued capital of Book Ltd on 1 July 2014 for $1,500,000....
Rule Ltd acquired all the issued capital of Book Ltd on 1 July 2014 for $1,500,000. At that date the shareholders' equity of Book Ltd was:
Share Capital $1,100,000
Retained Earnings $ 300,000
Additional information for the year ended 30 June 2016:
Inter-company sales:
Rule Ltd to Book Ltd $11,000
Book Ltd to Rule Ltd $19,000
Unrealised profits in closing inventory as at 30 June 2016 is $2,400 for goods sold by Book Ltd to Rule Ltd and $1,200 for goods sold by Rule Ltd to Book Ltd.
Unrealised profit in opening inventory for goods sold by Rule Ltd to Book Ltd as at 1 July 2015 is $2,100 and for goods sold by Book to Rule is $1,400.
Rule Ltd employees provide legal advice to Book Ltd. For these services, Book Ltd pays an annual fee of $8,000 per annum.
The final dividend of $16,500, declared as at 30 June 2015, was paid by Book Ltd in October 2015.
An interim dividend of $14,000 was paid on 31 January and a final dividend was declared $20,000 at 30 June, 2016.
On 30 June 2016, Rule Ltd purchased a motor vehicle from Book Ltd for $15,000. Book Ltd made profit on this sale of $3,500.
Book Ltd raised funds from Rule Ltd by borrowing $100,000 at an interest rate of 10% per annum. The annual interest charge was paid by Book Ltd on 30 June 2016.
The directors review the balance of goodwill each year. They agree that for the year ended 30 June 2016, goodwill is to be unpaired by $20,000.
Please complete a Consolidated Worksheet
|
Consolidation Worksheet 30 June 2016 |
Rule Ltd |
Book Ltd |
Eliminations Dr Cr |
Consolidated Accounts |
|
|
Sales |
1,485,000 |
825,000 |
|||
|
Less Cost of Sales |
|||||
|
Inventory 01/07/2015 |
120,000 |
52,000 |
|||
|
Purchases |
625,000 |
313,000 |
|||
|
745,000 |
365,000 |
||||
|
Inventory 30/06/2016 |
115,000 |
49,000 |
|||
|
Cost of Goods Sold |
630,000 |
316,000 |
|||
|
Gross Profit |
855,000 |
509,000 |
|||
|
Legal fees received |
8,000 |
0 |
|||
|
Gain on sale of plant |
0 |
3,500 |
|||
|
Dividends received |
30,500 |
0 |
|||
|
Interest received from Book Ltd |
10,000 |
0 |
|||
|
903,500 |
512,500 |
||||
|
Less: Expenses - selling expenses |
80,000 |
35,500 |
|||
|
- Admin expenses |
291,500 |
314,000 |
|||
|
- Financial expenses |
52,000 |
8,000 |
|||
|
423,500 |
357,500 |
||||
|
Operating profit before tax |
480,000 |
155,000 |
|||
|
Less tax expense |
144,000 |
46,500 |
|||
|
Profit after tax |
336,000 |
108,500 |
|||
|
Retained earnings 01/07/2015 |
588,000 |
421,500 |
|||
|
Available for appropriation |
924,000 |
530,000 |
|||
|
Appropriations |
|||||
|
Interim dividend paid |
80,000 |
14,000 |
|||
|
Final dividend declared |
140,000 |
20,000 |
|||
|
Total appropriations |
220,000 |
34.000 |
|||
|
Retained earnings 30/06/2016 |
704,000 |
496,000 |
|||
|
Share capital |
2,000,000 |
1,100,000 |
|||
|
Loan from Rule Ltd |
0 |
100,000 |
|||
|
Accounts payable |
72,000 |
36,000 |
|||
|
Dividends payable |
140,000 |
20,000 |
|||
|
Taxation Payable |
94,000 |
25,000 |
|||
|
3,010,000 |
1,777,000 |
||||
|
Property, Plant & Equip (net) |
732,000 |
900,000 |
|||
|
Shares in Book Ltd |
1,500,000 |
0 |
|||
|
Loan to Book Ltd |
100,000 |
0 |
|||
|
Other non-current assets |
335,000 |
650,000 |
|||
|
Inventory |
115,000 |
49,000 |
|||
|
Other current assets |
228,000 |
178,000 |
|||
|
Goodwill on consolidation |
|||||
|
3,010,000 |
1,777,000 |
||||
In: Accounting
Several items are omitted from the income statement and cost of goods manufactured statement data for...
Several items are omitted from the income statement and cost of goods manufactured statement data for two different companies for the month of December 2016:
|
1 |
Prius Company |
Volt Company |
|
|
2 |
Materials inventory, December 1 |
$280,280.00 |
$179,000.00 |
|
3 |
Materials inventory, December 31 |
(a) |
177,500.00 |
|
4 |
Materials purchased |
712,000.00 |
340,000.00 |
|
5 |
Cost of direct materials used in production |
752,000.00 |
(a) |
|
6 |
Direct labor |
1,059,600.00 |
(b) |
|
7 |
Factory overhead |
325,200.00 |
179,600.00 |
|
8 |
Total manufacturing costs incurred during December |
(b) |
1,035,000.00 |
|
9 |
Total manufacturing costs |
2,676,800.00 |
1,479,500.00 |
|
10 |
Work in process inventory, December 1 |
540,000.00 |
444,500.00 |
|
11 |
Work in process inventory, December 31 |
451,400.00 |
(c) |
|
12 |
Cost of goods manufactured |
(c) |
1,027,500.00 |
|
13 |
Finished goods inventory, December 1 |
478,400.00 |
201,000.00 |
|
14 |
Finished goods inventory, December 31 |
495,200.00 |
(d) |
|
15 |
Sales |
4,143,000.00 |
1,676,500.00 |
|
16 |
Cost of goods sold |
(d) |
1,053,500.00 |
|
17 |
Gross profit |
(e) |
(e) |
|
18 |
Operating expenses |
540,000.00 |
(f) |
|
19 |
Net income |
(f) |
383,000.00 |
| Required: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A. | Determine the amounts of the missing items, identifying them by letter. Enter all amounts as positive numbers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | Prepare Volt Company’s statement of cost of goods manufactured for December.* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C. | Prepare Volt Company’s income
statement for December.*
|
In: Accounting
Several items are omitted from the income statement and cost of goods manufactured statement data for...
|
Several items are omitted from the income statement and cost of goods manufactured statement data for two different companies for the month of December 2016:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
In: Accounting
Sort these nucleotide building blocks by their name or classification.
Sort these nucleotide building blocks by their name or classification.
In: Biology
What is the IUPAC name for the compound shown below?
What is the IUPAC name for the compound shown below? Spelling and punctuation count!
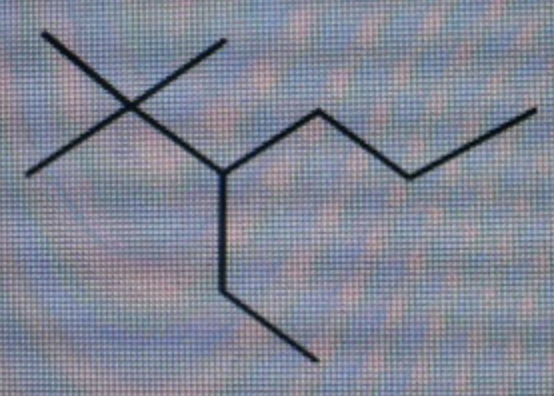
In: Chemistry
Name the parts of the female internal and external genitalia.
In: Nursing
Name three of the most common supervisors in the marketplace
Name three of the most common supervisors in the market place
In: Finance
A constructor, with a String parameter representing the name of the item.
USE JAVA
Item class
A constructor, with a String parameter representing the name of the item.
A name() method and a toString() method, both of which are identical and which return the name of the item.
BadAmountException Class
It must be a RuntimeException. A RuntimeException is a subclass of Exception which has the special property that we wouldn't need to declare it if we need to use it.
Inventory class
A constructor which takes a String parameter indicating the item type, an int parameter indicating the initial number of items in stock, and an int parameter indicating the limit to the number of items which can be purchased in any transaction. If we attempt to initialize the inventory with a negative number of items, the constructor should throw a BadAmountException with the message "Cannot keep a negative amount of items in stock".
A constructor which takes a String parameter indicating the item type, and an int parameter indicating the initial number of items in stock. This constructor assumes no purchase limit, so initialize the limit appropriately. If we attempt to initialize the inventory with a negative number of items, the constructor should throw a BadAmountException with the message "Cannot keep a negative amount of items in stock".
A getter and setter for the purchase limit, getLimit and setLimit.
A getter for the number of items currently in stock, getNum.
A getter for the type of item (i.e. the name of the item) in stock, getType.
A restock method which takes an int parameter and which doesn't return anything. This method restocks by adding the input amount to the current stock. If the input amount is negative, this method should throw a BadAmountException with the message "Cannot stock a negative amount of items".
A purchase method which takes an int parameter and which returns an array of Item. The input value represents a number of items to purchase. However, before a purchase can be made, several checks need to be done to make sure it is a legal transaction:If the transaction is valid, then we should purchase the specified number of items (updating the inventory accordingly), and return create and return an array of Item of the appropriate size and type (for example, if we request a purchase of two packages of "toilet paper", we would get back an array containing two Item objects whose name is "toilet paper").
Note that since InventoryException is a checked exception, we may need to declare it to use it.If the input is negative, then the method should throw a BadAmountException with the message "Cannot purchase a negative amount of items".
If the purchase amount is greater than the number of items in stock, then we should throw an InventoryException with the text "Not enough items in stock".
If the purchase limit is zero, that means that there is a purchase freeze, so we should throw an InventoryException with the text "Purchasing freeze on item".
If there is a limit but we've been requested to purchase more than the limit, we should throw a InventoryException with the text "Exceeded limit of LIMIT", where LIMIT is a number representing the purchase limit.
Otherwise the transaction is valid.
The StoreSim class contains a single static method:
public static void sim(Inventory stock, int[] purchases). If the purchase was successful, the method should output "purchased AMOUNT units ofITEMTYPE, REMAINNG remaining", for example, "purchased 50 units of toilet paper, 1 remaining". If an InventoryException is detected, then the method should print the exception's message and then continue as if nothing happened. If a BadAmountException is detected, then the method should print "(negative purchase AMOUNT ignored)" to the standard error stream instead of the standard output, and then continue as if nothing happened.
In: Computer Science
Which of the following is the name for the risk of changes in the price or...
Which of the following is the name for the risk of changes in the price or value of fixed-rate debt instruments resulting from changes in market interest rates?
-
Default risk
-
Liquidity risk
-
Inflation risk
-
Interest rate risk
In: Finance